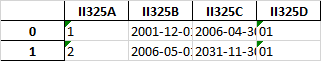
I have an XML file like this:
<table chgFlag="i" id="II325">
<row chgFlag="i" idVal="1">
<fld id="II325A">
<datVl chgFlag="i">1</datVl>
</fld>
<fld id="II325B">
<datVl chgFlag="i">2001-12-01</datVl>
</fld>
<fld id="II325C">
<datVl chgFlag="i">2006-04-30</datVl>
</fld>
<fld id="II325D">
<datVl chgFlag="i">01</datVl>
</fld>
</row>
<row chgFlag="i" idVal="2">
<fld id="II325A">
<datVl chgFlag="i">2</datVl>
</fld>
<fld id="II325B">
<datVl chgFlag="i">2006-05-01</datVl>
</fld>
<fld id="II325C">
<datVl chgFlag="i">2031-11-30</datVl>
</fld>
<fld id="II325D">
<datVl chgFlag="i">01</datVl>
</fld>
</row>
</table>
If I just put it into read_xml I get something like this:
chgFlag idVal fld
0 i 1 NaN
1 i 2 NaN
It take sthe attributes in each row as columns. I don't want that, I want value of id in fld as the column and the text inside datVl as the value.
Something like this.
I manage to get the result I wanted using this code:
data_dict = xmltodict.parse(ET.tostring(table))
table_list = []
if type(data_dict["table"]["row"]) == list:
for row in data_dict["table"]["row"]:
row_dict = {}
for field in row["fld"]:
row_dict[field["@id"]] = field["datVl"]["#text"]
table_list.append(row_dict)
df = pd.DataFrame(table_list)
I was wondering if there is more a general solution, perhaps setting some parameter inside read_xml?
I might need to scale my current solution, that is why I am asking.
CodePudding user response:
As mentioned in the comments to this similar question:
read_xml does not parse beyond its immediate descendants.
But you can use the approach mentioned in the above answer: transforming the XML with XSLT to a palatable format. In your case you can use the stylesheet parameter of read_xml with this XSLT
<xsl:stylesheet version="1.0" xmlns:xsl="http://www.w3.org/1999/XSL/Transform">
<xsl:output method="xml" omit-xml-declaration="yes"/>
<xsl:template match="/table">
<Root><xsl:apply-templates /></Root>
</xsl:template>
<xsl:template match="row">
<Item>
<xsl:element name="II325A"><xsl:value-of select="fld[@id='II325A']/datVl" /></xsl:element>
<xsl:element name="II325B"><xsl:value-of select="fld[@id='II325B']/datVl" /></xsl:element>
<xsl:element name="II325C"><xsl:value-of select="fld[@id='II325C']/datVl" /></xsl:element>
<xsl:element name="II325D"><xsl:value-of select="fld[@id='II325D']/datVl" /></xsl:element>
</Item>
</xsl:template>
</xsl:stylesheet>
or, a more general approach for the second template iterating over all of the children of row:
<xsl:template match="row">
<Item>
<xsl:for-each select="fld">
<xsl:element name="{@id}"><xsl:value-of select="datVl" /></xsl:element>
</xsl:for-each>
</Item>
</xsl:template>
which creates, in both versions, the following intermediate XML
<Root>
<Item><II325A>1</II325A><II325B>2001-12-01</II325B><II325C>2006-04-30</II325C><II325D>1</II325D></Item>
<Item><II325A>2</II325A><II325B>2006-05-01</II325B><II325C>2031-11-30</II325C><II325D>1</II325D></Item>
</Root>
and can be used with the following python code:
dataFolder = './'
df_bulk = pd.read_xml(
dataFolder 'input.xml',
stylesheet='transform.xslt',
xpath='/Root/Item',
)
print(df_bulk.head(10))
The output is:
II325A II325B II325C II325D
0 1 2001-12-01 2006-04-30 1
1 2 2006-05-01 2031-11-30 1
CodePudding user response:
one option is to use the xpath parameter, and pass the specified sections of the xml :
(pd
.read_xml(data, xpath = ".//fld")
.assign(counter = lambda df: df.groupby('id').cumcount())
.pivot('counter', 'id', 'datVl')
.rename_axis(index = None, columns = None)
)
II325A II325B II325C II325D
0 1 2001-12-01 2006-04-30 01
1 2 2006-05-01 2031-11-30 01