I've seen multiple of examples of this online, but I've not found anything that helps me solve the problem I'm faced with. I'm trying to convert a JSON object into an HTML table, but I'm faced with a couple of issues.
Suppose I have the following object, call it tableJson, which is essentially representative of a table with only column headers:
[
{
"firstColumn": []
},
{
"secondColumn": []
},
{
"thirdColumn": []
}
]
In trying to convert this into an HTML table, I have done the following:
jsonDumps = json.dumps(jsonTable)
htmlTable = json2html.convert(json = jsonDumps)
Seems pretty simply. However, the result of htmlTable gives me two issues:
- The output is in a bullet point list format
- Each column header is treated as a separate table
For example, the result of htmlTable above is:
<ul>
<li>
<table border="1">
<tr><th>firstColumn</th><td></td></tr>
</table>
</li>
<li>
<table border="1">
<tr><th>secondColumn</th><td></td></tr>
</table>
</li>
<li>
<table border="1">
<tr><th>thirdColumn</th><td></td></tr>
</table>
</li>
</ul>
What is the simply way of creating a table (correctly) so that I don't have it in a bullet point list and so that each column is treated as a correct column rather than a table?
Is there a problem with the way the JSON object is represented? If so, what is the correct syntax so that json2html converts it correctly into a table?
CodePudding user response:
There's some issue with the original structure if your table, which is clearer when you attempt to create a DataFrame from it; if you restructure it as a single dict first, you may find it much easier to work with and can directly use Pandas to render your table
Starting Values
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> src_table = [
... {
... "firstColumn": []
... },
... {
... "secondColumn": []
... },
... {
... "thirdColumn": []
... }
... ]
Demo of issue
(each column is unique, rather than being in the same collection)
>>> pd.DataFrame(src_table)
firstColumn secondColumn thirdColumn
0 [] NaN NaN
1 NaN [] NaN
2 NaN NaN []
Flatten list of dicts and Display
With a few values inserted
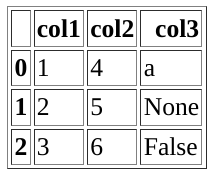
>>> pd.DataFrame({"col1": [1,2,3], "col2": [4,5,6], "col3": ['a', None, False]}).to_html()
'<table border="1" class="dataframe">\n <thead>\n <tr style="text-align: right;">\n <th></th>\n <th>col1</th>\n <th>col2</th>\n <th>col3</th>\n </tr>\n </thead>\n <tbody>\n <tr>\n <th>0</th>\n <td>1</td>\n <td>4</td>\n <td>a</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <th>1</th>\n <td>2</td>\n <td>5</td>\n <td>None</td>\n </tr>\n <tr>\n <th>2</th>\n <td>3</td>\n <td>6</td>\n <td>False</td>\n </tr>\n </tbody>\n</table>'
Rendered
You can use different arguments to the .to_html() method to omit major table features like the index and do the rest in CSS