I am attempting to create a staging WordPress site where the PHP and WordPress versions are very outdated. When I visit localhost, I get the following error:
Your PHP installation appears to be missing the MySQL extension which is required by WordPress.
Ubuntu version: 20.04.2 LTS
PHP version CLI: PHP 7.2.34-24 ubuntu20.04.1 deb.sury.org 1
MySQL version: 8.0.26-0ubuntu0.20.04.3 for Linux on x86_64 ((Ubuntu))
WordPress version: 5.3.9
I need the PHP version to be 7.2.34 and the WordPress version to be 5.3.9.
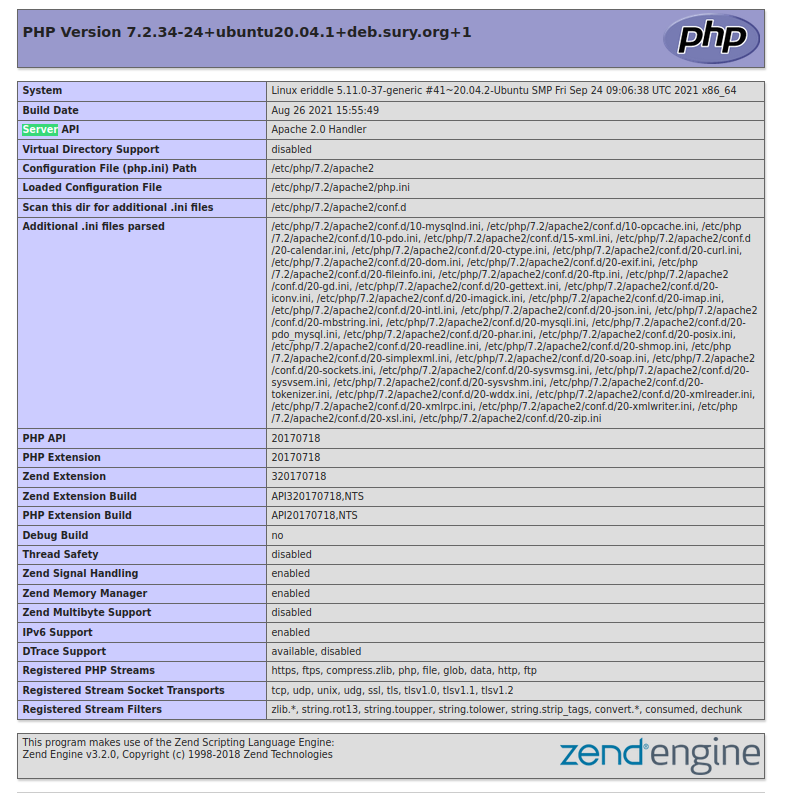
In my info.php file, the Loaded Configuration path and extension_dir path are as follows:
Loaded Configuration File /etc/php/7.2/apache2/php.ini
extension_dir /usr/lib/php/20170718
Do these need to be the same?
Here is the Client API Library version. I'm a bit confused as to why this error is being thrown, doesn't this mean the extension is installed? I'm aware that in newer MySQL versions it was removed, but I am at a loss as to how to proceed.
Client API library version mysqlnd 5.0.12-dev - 20150407 - $Id: 3591daad22de08524295e1bd073aceeff11e6579 $
I have searched through the similar questions that have been posted, but none of the answers were helpful to this situation. Please let me know if I need to provide more information. Thank you.
CodePudding user response:
To check which extensions are installed, you can run this from the command line:
php -m
Or you can run this PHP script:
<?php
var_dump(get_loaded_extensions());
Look for 'mysql' in the results. Or you can grep for it from CLI:
php -m | grep -i 'mysql'
If you don't see any mysql module installed, that would suggest you have installed PHP in a pretty unusual fashion. For Ubuntu, you might need to install the mysql module like so:
# let APT decide which version
sudo apt install php-mysql
# or install a more specific version depending on which php you have:
sudo apt install php7.2-mysql
It's not clear if you have your system configured with PHP running as apache module or via PHP-FPM. If it's the latter, you'll need to restart php-fpm. I'd restart apache just for good measure:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Also, that looks like a pretty old version of the client. Maybe check phpinfo() and see what information it has about mysql.
EDIT: some additional information.
I believe the wordpress function that is causing your error is wp_check_php_mysql_versions().
As you can see, that error could be caused by a number of conditions:
if ( ! extension_loaded( 'mysql' ) && ! extension_loaded( 'mysqli' ) && ! extension_loaded( 'mysqlnd' )
// This runs before default constants are defined, so we can't assume WP_CONTENT_DIR is set yet.
&& ( defined( 'WP_CONTENT_DIR' ) && ! file_exists( WP_CONTENT_DIR . '/db.php' )
|| ! file_exists( ABSPATH . 'wp-content/db.php' ) )
) {
require_once ABSPATH . WPINC . '/functions.php';
wp_load_translations_early();
$args = array(
'exit' => false,
'code' => 'mysql_not_found',
);
wp_die(
__( 'Your PHP installation appears to be missing the MySQL extension which is required by WordPress.' ),
__( 'Requirements Not Met' ),
$args
);
exit( 1 );
}
Try running this php script and it should tell you if the problem is lack of suitable extension or a missing file problem:
if (!extension_loaded('mysql')
&& !extension_loaded('mysqli')
&& !extension_loaded('mysqlnd')) {
die("You lack any suitable mysql extensions\n");
} else {
die("perhaps you are missing a file db.php?\n");
}
CodePudding user response:
You've got to make sure that the current version of MySQL and the corresponding version of the PHP extension are both installed and available.
PHP has necessarily become a modular system: various built-in functions are implemented by a particular module. (And are only "built in" if such a module is installed.)