I have 4D data in a data frame. I need to convert it to 3D Numpy array. I can do it with for-loops, but is there more efficient way?
# Data:
df = pd.DataFrame()
df['variable'] = ['A', 'A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C', 'C', 'D', 'D', 'D', 'A',
'A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C', 'C', 'D', 'D', 'D']
df['date'] = [101,102,103]*8
df['itemID'] = ['item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item1', 'item2',
'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2', 'item2']
df['value1'] = [1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12,1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12]
df['value2'] = [1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12,1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12]
df['value3'] = [1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12,1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12]
df['value4'] = [1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12,1,5,9,2,6,10,3,7,11,4,8,12]
# Pivoting:
pivoted = df.pivot(index=['itemID', 'date'], columns='variable', values=[*df.columns[df.columns.str.startswith('value')]])
pivoted.index.levshape
Level shape is: (2, 3)
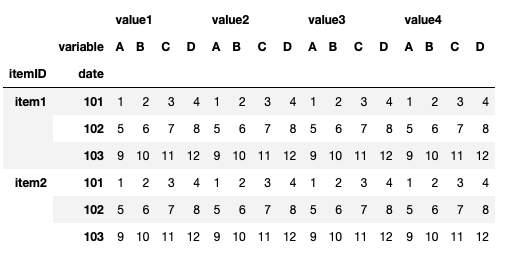
And it looks like this:
# To Numpy:
pivoted2array = pivoted.to_numpy()
pivoted2array.shape
Shape is now: (6, 16)
# Reshaping to 3D:
pivoted2array3d = pivoted2array.reshape(*pivoted.index.levshape,-1)
pivoted2array3d.shape
Shape is now: (2, 3, 16)
And it looks like this:
array([[[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 5, 6, 7, 8, 5, 6, 7, 8, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12, 9, 10, 11, 12, 9, 10, 11, 12, 9, 10, 11, 12]],
[[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 5, 6, 7, 8, 5, 6, 7, 8, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11, 12, 9, 10, 11, 12, 9, 10, 11, 12, 9, 10, 11, 12]]])
And this is the troublesome part where I convert (reorder) the values with for-loops:
dimension3 = []
for k in range(pivoted2array3d.shape[0]): # unique items
for j in range(pivoted2array3d.shape[1]): # unique dates
for i in range(pivoted2array3d.shape[2])[0:pivoted2array3d.shape[2]:4]:
element = pivoted2array3d[k][j][i]
dimension3.append(element)
for l in range(pivoted2array3d.shape[2])[0 1:pivoted2array3d.shape[2]:4]:
element = pivoted2array3d[k][j][l]
dimension3.append(element)
for m in range(pivoted2array3d.shape[2])[0 2:pivoted2array3d.shape[2]:4]:
element = pivoted2array3d[k][j][m]
dimension3.append(element)
for n in range(pivoted2array3d.shape[2])[0 3:pivoted2array3d.shape[2]:4]:
element = pivoted2array3d[k][j][n]
dimension3.append(element)
len(dimension3)
As a result I have a list of length 96.
Then I reshape it back to 3D Numpy array:
final = np.array(dimension3).reshape(*pivoted2array3d.shape)
final.shape
It has again shape: (2, 3, 16)
And the final result looks like this as desired:
array([[[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4],
[ 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12]],
[[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4],
[ 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12]]])
Is there computationally more elegant way to reorder my array? And is there a way to do less reshaping steps? I would really like to learn how to use Numpy operations!
My real data include thousands of items, hundreds of dates, tens of variables and value-variables.
CodePudding user response:
It looks like you only need to swap the column level of pivoted:
a = df.pivot(index=['itemID','date'], columns=['variable']).stack(level=0).unstack()
a.to_numpy().reshape(-1, df.date.nunique(), a.shape[1])
Output:
array([[[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4],
[ 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12]],
[[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4],
[ 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12]]])
CodePudding user response:
It seems like np.swapaxes does the trick you need: arr.reshape(2,3,4,4).swapaxes(2,3).reshape(2,3,16)
The main idea is to swap the axes in the most inner data:
[ 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 4] ->
[[ 1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]] ->
[ 1, 1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2, 2], [3, 3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4, 4]] ->
[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4]
CodePudding user response:
We can try sorting the index then reshape using the index levels
pivoted.sort_index(level=1, axis=1)\
.values.reshape(*pivoted.index.levshape[:2], -1)
array([[[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4],
[ 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12]],
[[ 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4],
[ 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8],
[ 9, 9, 9, 9, 10, 10, 10, 10, 11, 11, 11, 11, 12, 12, 12, 12]]])