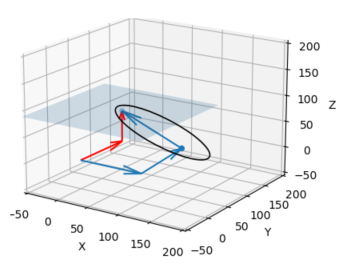
I am trying to find a way to fit a straight line through a known vector in the first step. The second step should be to find the intersection between this line and the shown plane. The vector I want to fit a line through is marked with the black ellipse and is named vector_3 in the code.
The goal is to adapt the length of vector_3 as the blue vector path rotates around the x- or y-axis to get a new vector which always ends at the plane.
Here is the code (reduced to what is relevant for now) and the resulting graph:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Import 6D-Pose
translation_6D_pose = np.array([100, 0, 0, 1])
rotation_6D_pose = np.array([0, 0, 0])
# Definition of vectors
origin = np.array([0, 0, 0])
vector_1 = np.array([0, 100, 10, 1])
vector_2 = np.array([-100, 0, 50, 1])
vector_3 = np.array([0, 100, 0, 1])
vector_4 = np.array([0, 0, 60, 1])
X, Y, Z = origin
U, V, W, _ = translation_6D_pose
A, B, C, _ = vector_1
D, E, F, _ = vector_2
G, H, I, _ = vector_3
J, K, L, _ = vector_4
# Plot figure:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.set_xlabel("X")
ax.set_ylabel("Y")
ax.set_zlabel("Z")
ax.set_xlim([-50, 200])
ax.set_ylim([-50, 200])
ax.set_zlim([-50, 200])
# Make plane:
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(range(-100, 100), range(0, 200))
z = xx*0 60
ax.plot_surface(xx, yy, z, alpha=0.2)
# Plot vectors:
ax.quiver(X, Y, Z, U, V, W)
ax.quiver(U, V, W, A, B, C)
ax.quiver(U A, V B, W C, D, E, F)
ax.quiver(X, Y, Z, G, H, I, color="r")
ax.quiver(G, H, I, J, K, L, color="r")
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
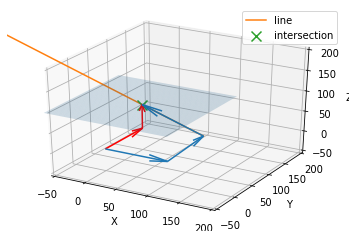
To plot a line through your vector you can just create points that are aligned with the vector and plot them. To find the intersection, you can use the intersection function from sympy. Note that in your case you can also calculate it directly. Your plane is simply z=60 so the calculation is pretty straightforward.
See code below for an example where I used sympy in order to make the answer more general:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sympy import Point3D, Line3D, Plane
# Import 6D-Pose
translation_6D_pose = np.array([100, 0, 0, 1])
rotation_6D_pose = np.array([0, 0, 0])
# Definition of vectors
origin = np.array([0, 0, 0])
vector_1 = np.array([0, 100, 10, 1])
vector_2 = np.array([-100, 0, 50, 1])
vector_3 = np.array([0, 100, 0, 1])
vector_4 = np.array([0, 0, 60, 1])
X, Y, Z = origin
U, V, W, _ = translation_6D_pose
A, B, C, _ = vector_1
D, E, F, _ = vector_2
G, H, I, _ = vector_3
J, K, L, _ = vector_4
# Plot figure:
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.set_xlabel("X")
ax.set_ylabel("Y")
ax.set_zlabel("Z")
ax.set_xlim([-50, 200])
ax.set_ylim([-50, 200])
ax.set_zlim([-50, 200])
# Make plane:
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(range(-100, 100), range(0, 200))
z = xx*0 60
ax.plot_surface(xx, yy, z, alpha=0.2)
# Plot vectors:
ax.quiver(X, Y, Z, U, V, W)
ax.quiver(U, V, W, A, B, C)
ax.quiver(U A, V B, W C, D, E, F)
x=[U A k*D for k in range(10)]
y=[V B k*E for k in range(10)]
z=[W C k*F for k in range(10)]
ax.quiver(X, Y, Z, G, H, I, color="r")
ax.quiver(G, H, I, J, K, L, color="r")
#Computing intersection
plane = Plane(Point3D(0, 0, 60),(50,0,60),(0,50,60))
line = Line3D(Point3D(U A, V B, W C), Point3D(U A 10*D, V B 10*E, W C 10*F))
inter=plane.intersection(line)
#PLotting intersection
ax.scatter(float(inter[0][0]),float(inter[0][1]),float(inter[0][2]),color='tab:green',marker='x',s=100,label='intersection')
#PLotting line
ax.plot(x,y,z,label='line')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
And the output gives: