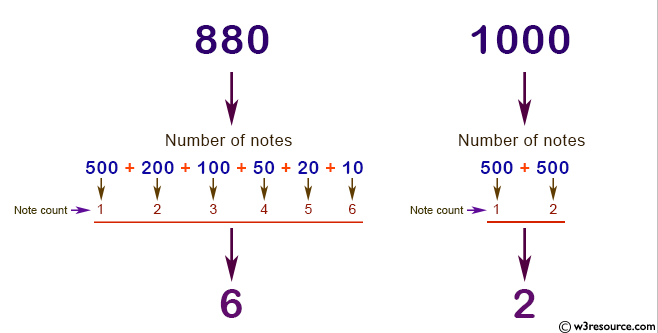
Look at this image for easier understanding
This is what the python program should do. The notes to use are [500, 200, 100, 50, 20, 10]
Can someone explain what is wrong with my code? I've been sitting here and scratching my head for the longest time.
def note_calculator(num):
notes = [500, 200, 100, 50, 20, 10]
counter = 0
mult = 0
for x in range(6):
enote = notes[x]
if num <= enote:
if num % enote == 0:
mult = num / enote
num = num - (mult * enote)
counter = mult
if num == 0:
break
else:
num = num - enote
counter = 1
if num == 0:
break
else:
continue
return counter
Basically, my method is to put sample notes in a list and iterate through all of them. If the number you input is greater or equal to the first iteration (500) it will then check the divisibility, if there are no remainders, I calculate the multiple. Then I subtract the multiple * the sample note iteration (500) because the program should run until the input (num) is equal to zero. Then I add to the counter, which will tell me the number of notes. If it is not divisible with remainders I simply subtract the first iteration (500) and add it to the counter. This repeats until the last iteration (10)
I know there is an easier and shorter way to do this, but whatever.
CodePudding user response:
Your algorithm works fine, but I noticed two bugs, first one:
if num <= enote: should be if num >= enote:
You want to get enote when it's not bigger than rest amount, not otherwise.
Second, notice that when if num % enote == 0: you correctly take proper amount of enotes, but in else clause you take only one. You should take as much as you can, so do something similar as in if:
counter = num // enote
num = num % enote
And one small thing, your function now returns float (as / operator do so). You can use //, look:
print(type(10/2)) # <class 'float'>
print(type(10//2)) # <class 'int'>
CodePudding user response:
It appears you are looking for the builtin divmod.
notes = [500, 200, 100, 50, 20, 10]
x = 880
s = 0
for n in notes:
q,r = divmod(x,n)
x = r
s = q
print(s)
CodePudding user response:
Here is how I would implement it (Python 3):
def note_calculator(num):
counter = 0
for note in [500, 200, 100, 50, 20, 10]:
counter = num // note
num %= note
return counter
In Python 2, you can just replace the // with a /.