I am new to Azure and have to create JSON Array from separate XML messages received by the logic app. The logic app requests data and receives the response in XML format. I proposed an approach that is saving the message in Azure storage then through the Azure function create the JSON array. Is this approach affect the performance? Is there any idea?
Thanks in advance
CodePudding user response:
There are 2 ways where you can completely rely on Logic apps without involving Azure functions
Consider this to be the sample xml
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<PurchaseOrder PurchaseOrderNumber="99503" OrderDate="1999-10-20">
<Address Type="Shipping">
<Name>Adam Murphy</Name>
<Street>123 Maple Street</Street>
<City>Mill Valley</City>
<State>CA</State>
<Zip>10999</Zip>
<Country>Ireland</Country>
</Address>
<Address Type="Billing">
<Name>Tai Yee</Name>
<Street>8 Oak Avenue</Street>
<City>Old Town</City>
<State>PA</State>
<Zip>95819</Zip>
<Country>Ireland</Country>
</Address>
<DeliveryNotes />
</PurchaseOrder>
WAY-1
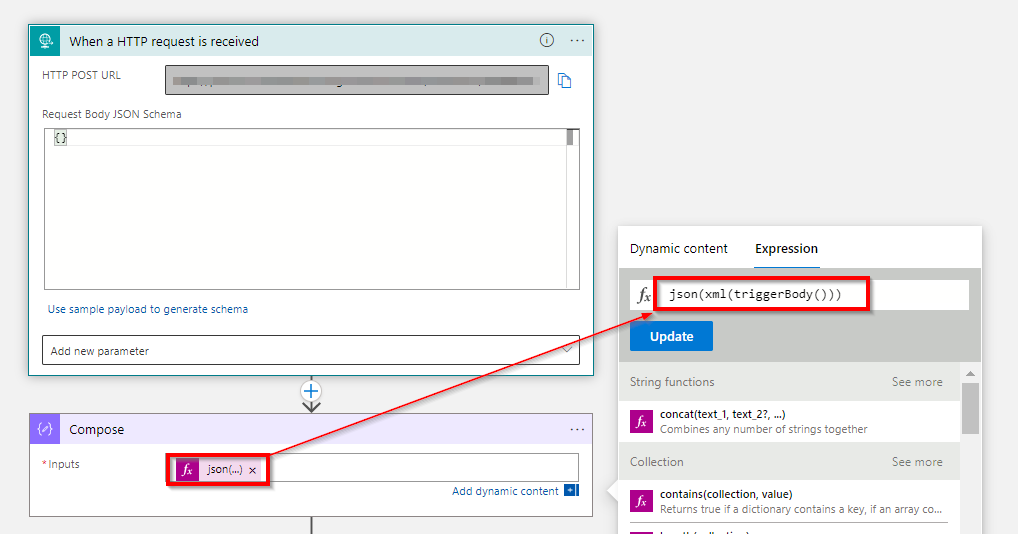
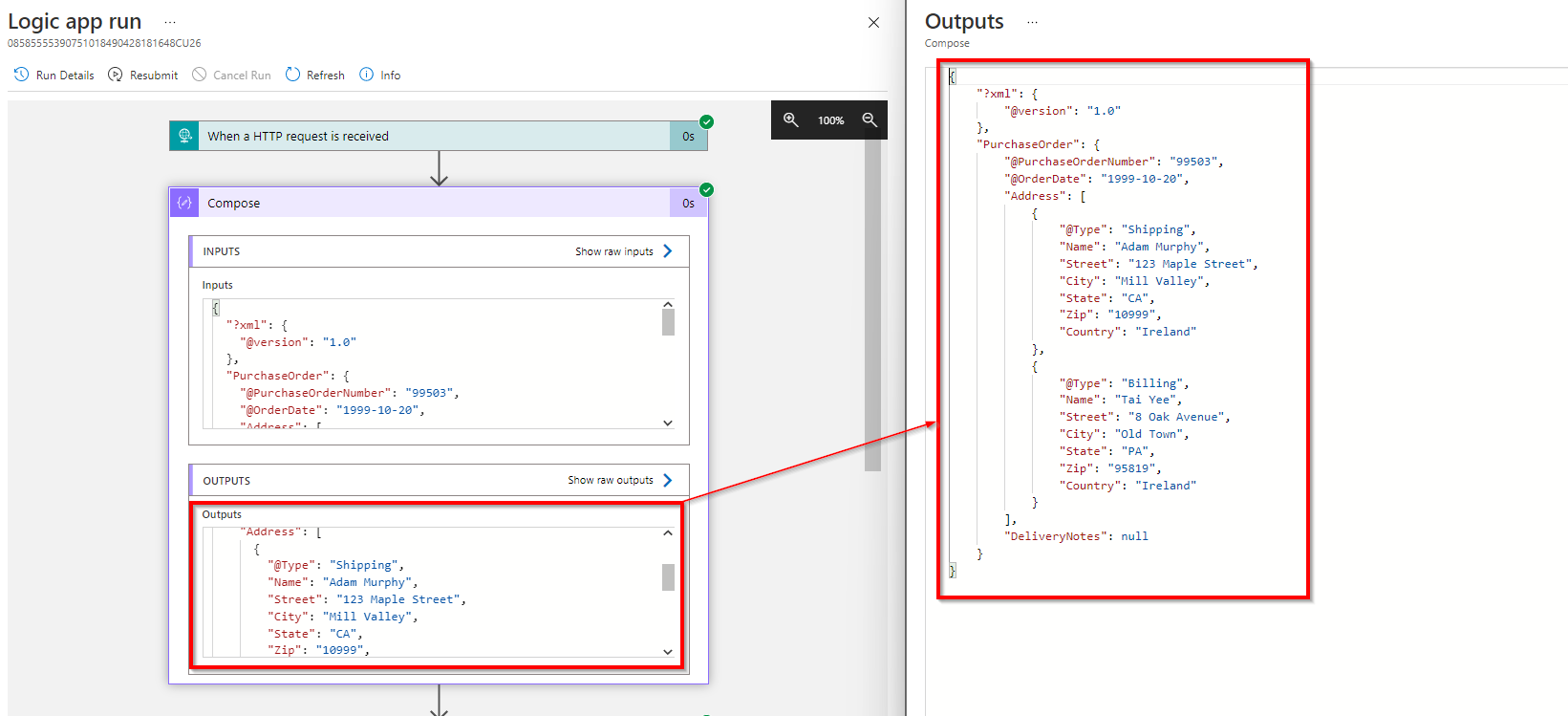
You can directly convert xml to json using json(xml(triggerBody()))
Here is the logic app for your reference -
output
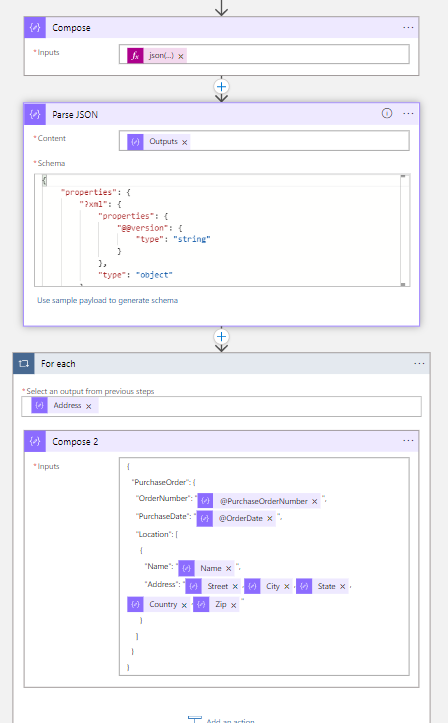
If you want to have a custom json, then you can create one using Parse_Json and Compose Connectors.
Here I'm just taking the output of Compose Connector to Parse_Json in order to parse the resultant Json to get the custom JSON script. Below is the Json I'm trying to create.
{
"PurchaseOrder": {
"OrderNumber": "@{body('Parse_JSON')?['PurchaseOrder']?['@PurchaseOrderNumber']}",
"PurchaseDate": "@{body('Parse_JSON')?['PurchaseOrder']?['@OrderDate']}",
"Location": [
{
"Name": "@{items('For_each')?['Name']}",
"Address": "@{items('For_each')?['Street']},@{items('For_each')?['City']},@{items('For_each')?['State']},@{items('For_each')?['Country']},@{items('For_each')?['Zip']}"
}
]
}
}
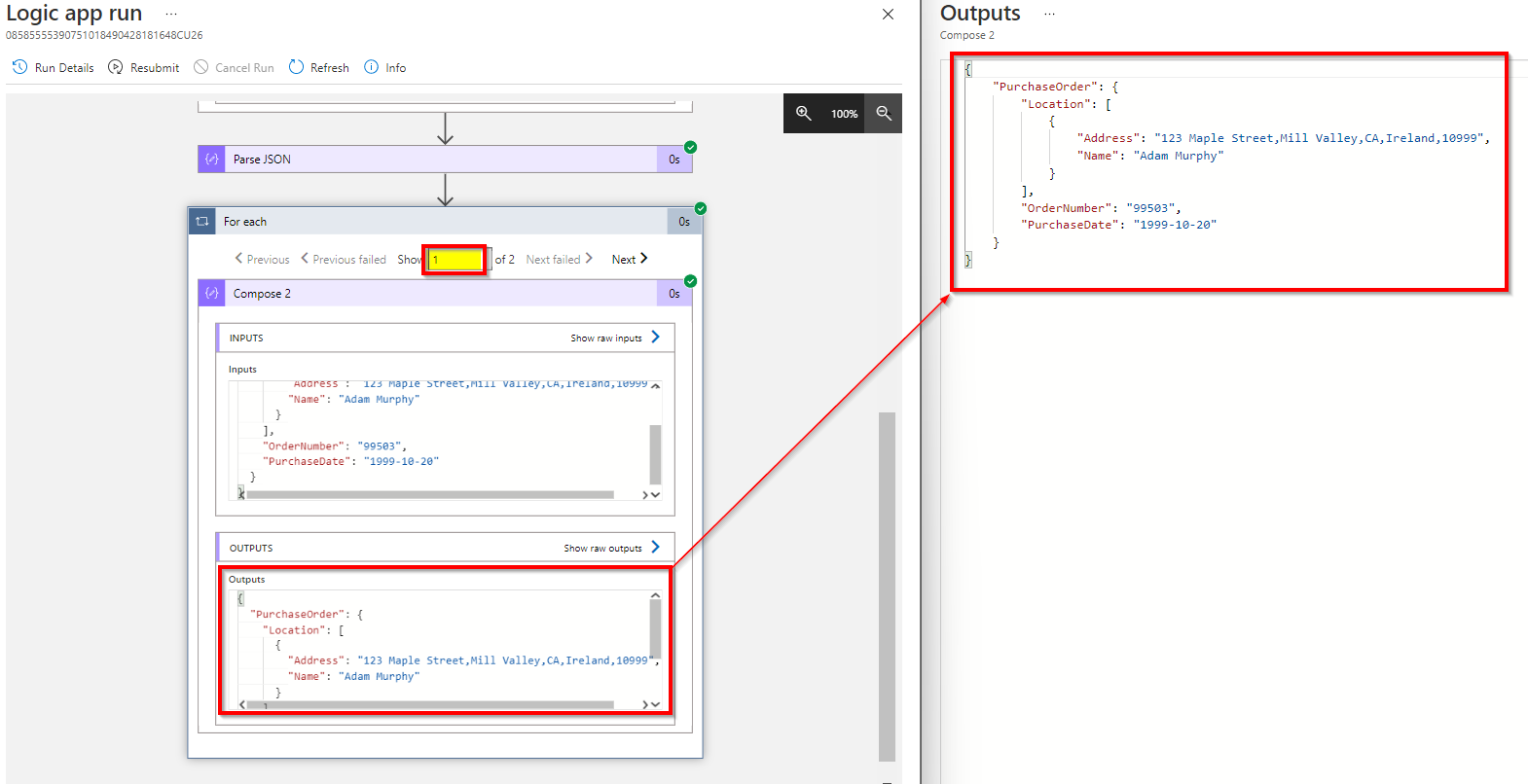
output
Here is the code view of my logic app. You can directly use this to get the exact workflow in your logic app.
{
"definition": {
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/providers/Microsoft.Logic/schemas/2016-06-01/workflowdefinition.json#",
"actions": {
"Compose": {
"inputs": "@json(xml(triggerBody()))",
"runAfter": {},
"type": "Compose"
},
"For_each": {
"actions": {
"Compose_2": {
"inputs": {
"PurchaseOrder": {
"Location": [
{
"Address": "@{items('For_each')?['Street']},@{items('For_each')?['City']},@{items('For_each')?['State']},@{items('For_each')?['Country']},@{items('For_each')?['Zip']}",
"Name": "@{items('For_each')?['Name']}"
}
],
"OrderNumber": "@{body('Parse_JSON')?['PurchaseOrder']?['@PurchaseOrderNumber']}",
"PurchaseDate": "@{body('Parse_JSON')?['PurchaseOrder']?['@OrderDate']}"
}
},
"runAfter": {},
"type": "Compose"
}
},
"foreach": "@body('Parse_JSON')?['PurchaseOrder']?['Address']",
"runAfter": {
"Parse_JSON": [
"Succeeded"
]
},
"type": "Foreach"
},
"Parse_JSON": {
"inputs": {
"content": "@outputs('Compose')",
"schema": {
"properties": {
"?xml": {
"properties": {
"@@version": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"type": "object"
},
"PurchaseOrder": {
"properties": {
"@@OrderDate": {
"type": "string"
},
"@@PurchaseOrderNumber": {
"type": "string"
},
"Address": {
"items": {
"properties": {
"@@Type": {
"type": "string"
},
"City": {
"type": "string"
},
"Country": {
"type": "string"
},
"Name": {
"type": "string"
},
"State": {
"type": "string"
},
"Street": {
"type": "string"
},
"Zip": {
"type": "string"
}
},
"required": [
"@@Type",
"Name",
"Street",
"City",
"State",
"Zip",
"Country"
],
"type": "object"
},
"type": "array"
}
},
"type": "object"
}
},
"type": "object"
}
},
"runAfter": {
"Compose": [
"Succeeded"
]
},
"type": "ParseJson"
}
},
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"outputs": {},
"parameters": {},
"triggers": {
"manual": {
"inputs": {
"schema": {}
},
"kind": "Http",
"type": "Request"
}
}
},
"parameters": {}
}
WAY-2
You can use liquid templates in order to convert xml to json using Transform XML to JSON Connector. For more information you can refer thread1 and thread2.
REFERENCES: Logic App: Basic XML to JSON Expression Conversion