I have the following code.
bereik = c(0, 0.05, 0.5, 0.95, 1)
#xvalues of plots
xval1 = c(0, 400, 4000, 10000, 10960)
xval2 = c(0, 1101, 2760, 4550, 10960)
xval3 = c(0, 1000, 3000, 5000, 10960)
xval4 = c(0, 2000, 5000, 8000, 10960)
xval5 = c(0, 400, 1250, 5000, 10960)
#plot 5 graphs
plot(xval1, bereik, type="l", col ="blue")
par(new=TRUE)
plot(xval2, bereik, type="l", col="red")
par(new=TRUE)
plot(xval3, bereik, type="l", col="yellow")
par(new=TRUE)
plot(xval4, bereik, type="l", col="green")
par(new=TRUE)
plot(xval5, bereik, type="l", col="purple")
How can I include in this plot a sixth graph, which is the average of the 5 given graphs. That is, call graph1 F1, graph2 F2, ..., graph 5 F5, how to include in the plot the graph F6 = 0.2F1 0.2F2 ... 0.2*F5?
CodePudding user response:
You could cbind the vectors to a matrix, then cbind the rowMeans. Make an empty plot and use lines in a for loop afterwards.
mat <- do.call(cbind, mget(ls(pattern='^xval\\d$')))
(mat <- cbind(mat, ave=rowMeans(mat)))
# xval1 xval2 xval3 xval4 xval5 ave
# [1,] 0 0 0 0 0 0.0
# [2,] 400 1101 1000 2000 400 980.2
# [3,] 4000 2760 3000 5000 1250 3202.0
# [4,] 10000 4550 5000 8000 5000 6510.0
# [5,] 10960 10960 10960 10960 10960 10960.0
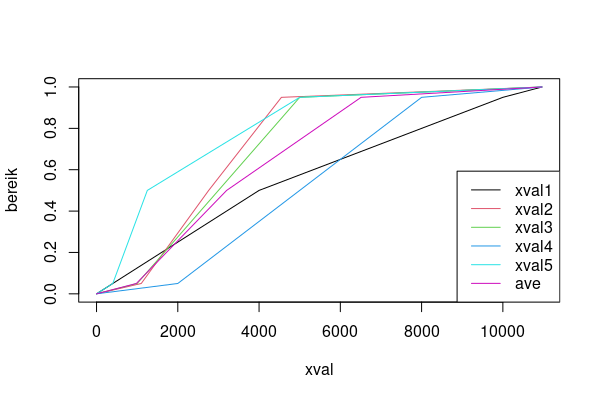
plot(xval1, bereik, type="n", xlab='xval')
for (i in seq_len(ncol(mat))) lines(mat[, i], bereik, col=i)
legend('bottomright', lty=1, col=seq_len(ncol(mat)), legend=colnames(mat))
Edit
Perhaps, you may want to try to interpolate bereik to the unique xval's (i.e. the other way round) to see if it's better.
mat2 <- do.call(cbind, mget(ls(pattern='^xval\\d$')))
xval <- sort(unique(as.vector(mat2)))
f <- \(x) approx(x, bereik, xval)$y
(mat2_ip <- `rownames<-`(apply(mat2, 2, f), xval))
# xval1 xval2 xval3 xval4 xval5
# 0 0.000000 0.00000000 0.0000000 0.0000000 0.0000000
# 400 0.050000 0.01816530 0.0200000 0.0100000 0.0500000
# 1000 0.125000 0.04541326 0.0500000 0.0250000 0.3676471
# 1101 0.137625 0.05000000 0.0727250 0.0275250 0.4211176
# 1250 0.156250 0.09041591 0.1062500 0.0312500 0.5000000
# 2000 0.250000 0.29385172 0.2750000 0.0500000 0.5900000
# 2760 0.345000 0.50000000 0.4460000 0.1640000 0.6812000
# 3000 0.375000 0.56033520 0.5000000 0.2000000 0.7100000
# 4000 0.500000 0.81173184 0.7250000 0.3500000 0.8300000
# 4550 0.541250 0.95000000 0.8487500 0.4325000 0.8960000
# 5000 0.575000 0.95351014 0.9500000 0.5000000 0.9500000
# 8000 0.800000 0.97691108 0.9751678 0.9500000 0.9751678
# 10000 0.950000 0.99251170 0.9919463 0.9837838 0.9919463
# 10960 1.000000 1.00000000 1.0000000 1.0000000 1.0000000
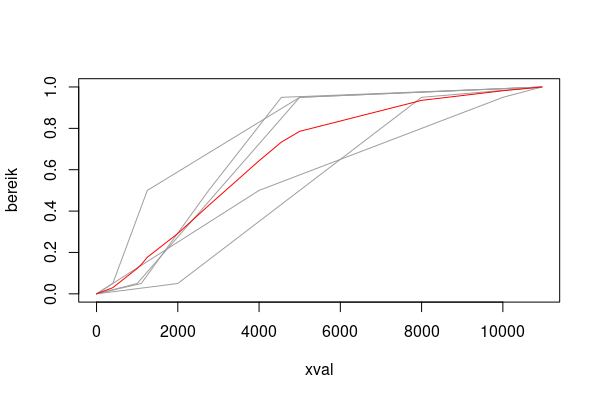
plot(xval1, bereik, type="n", xlab='xval')
for (i in seq_len(ncol(mat2))) lines(mat2[, i], bereik, col=8)
lines(xval, rowMeans(mat2_ip), type='l', col='red')
CodePudding user response:
One way of doing this is creating a wide dataframe and using rowwise() with mutate() from dplyr to create a new column containing the means.
library(dplyr)
df <- data.frame(bereik, xval1, xval2, xval3, xval4, xval5)
df <- df %>%
rowwise() %>%
mutate(xmean = mean(c(xval1, xval2, xval3, xval4, xval5)))
plot(df$xmean, df$bereik, type="l")