I have two tables one that reads voltage and one that reads current. The entries in these tables represent a change, therefore a specific value is constant until the next row.
I need to collect a voltage reading ONLY when the current has been between a certain range for at least 8 seconds.
The actual data sets are very very large and so far I have been using a left join on the condition where timestamps match and the timestamp_diff is less than 8. This is obviously massively inefficient and takes over an hour to complete.
anti_current_data contains all rows where the current is outside of the desired values.
LEFT JOIN anti_current_data ON
TIMESTAMP_DIFF(voltage_data.timestamp, anti_current_data.timestamp, SECOND) > -8
AND TIMESTAMP_DIFF(voltage_data.timestamp, anti_current_data.timestamp, SECOND) < 0
How could I approach this scenario more effectively?
Example:
in these tables, if the current is positive for 8 seconds, I can use the final row and collect the voltage as 46v.
| timestamp | current |
|---|---|
| 15/07/2022 09:05:22 | -2 |
| 15/07/2022 09:05:42 | -1 |
| 15/07/2022 09:06:04 | 6 |
| 15/07/2022 09:06:16 | 2 |
| timestamp | voltage |
|---|---|
| 15/07/2022 09:05:22 | 42 |
| 15/07/2022 09:05:42 | 44 |
| 15/07/2022 09:06:04 | 48 |
| 15/07/2022 09:06:16 | 46 |
CodePudding user response:
The main problem you are facing is needing to analyze previous records. To achieve this you can use a 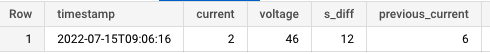
CodePudding user response:
How about likes this?
voltage_data.timestamp between (anti_current_data.timestamp - 8s) and anti_current_data.timestamp
SELECT
TIMESTAMP("2008-12-25 15:30:00 00") AS original,
TIMESTAMP_SUB(TIMESTAMP "2008-12-25 15:30:00 00", INTERVAL -8 SECOND ) AS earlier;
