I am trying to make a program loop with a timer that runs separately which for every iteration, the code continues where the timer countdown is left.
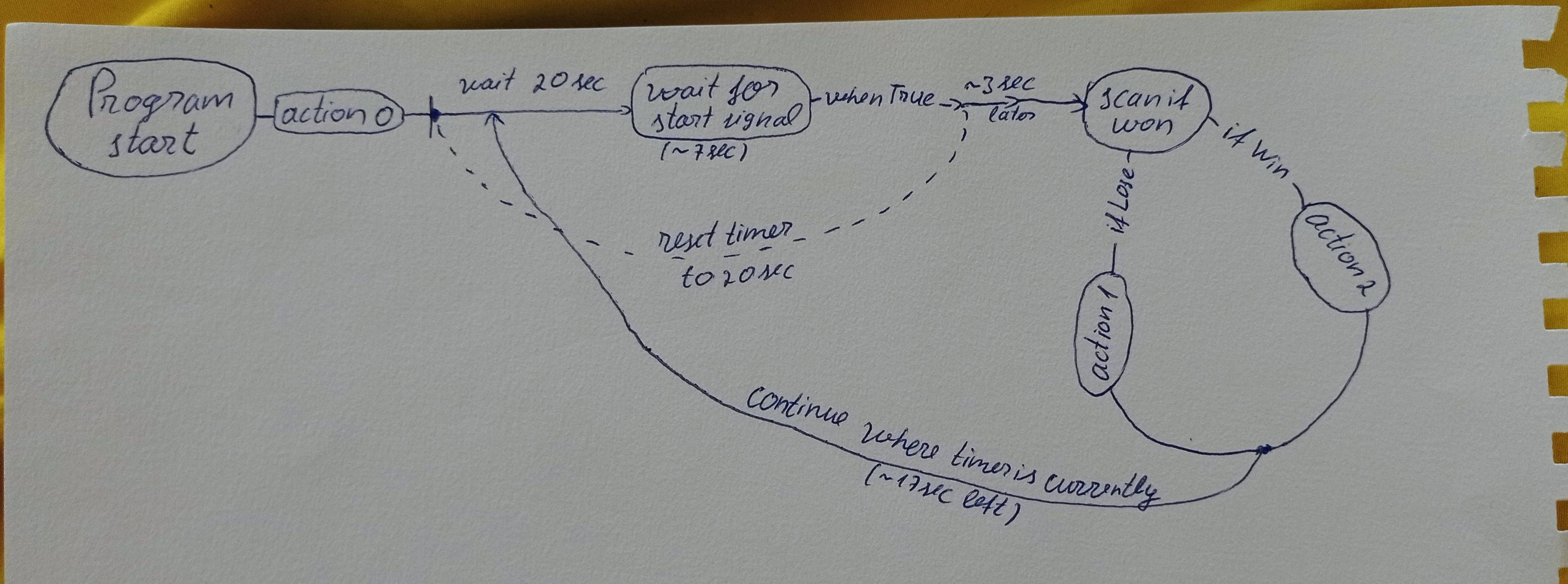
I drawed this pseudo code. It is the main idea on what i am trying to achieve (please play close attention). Basically while the timer is going, i want the next iteration to jump to where the timer currently is.
I tried writing a code, of course its wrong
import time
import threading
def scan_if_won():
#returns True or False
def wait_for_start_signal():
#returns True or False
def main():
print("Action 0")
while True:
time.sleep(20) #or any other timer function
while wait_for_start_signal() == False: #usually takes 6-9 seconds, we never know exact time
start = wait_for_start_signal()
if start == True:
break
#reset timer, countdown from 20
time.sleep(3)
result = scan_if_won() #this scan is not instant, can take from 1 to 2 seconds
if result == False
print("Action 1")
if result == True
print("Action 2")
#Now somehow, at next iteration, time.sleep() value should be the 20 - 3 - scan_if_won() time
main()
Was thinking of implementing threading but i have no idea how to start the thread from inside loop, kill it (if needed) and share variables (timer current value) between threads while being in a loop. Please look at my pseudo code again for fully understanding my issue. Thanks
CodePudding user response:
I think below code solve the problem if no bug. Event() class is very usefull for this kind of problems. I modified a little your code.
import time
import threading
def scan_if_won():
time.sleep(2)
return False
def wait_for_start_signal():
time.sleep(7)
return True
def check_start_signal(time):
event2.wait(timeout=time)
event2.clear()
while 1:
start=wait_for_start_signal()
if start:
event.set()
return
def main():
print("Action 0")
while True:
try:
t # is thread (t) created ?
event.wait()
event.clear()
except UnboundLocalError:
check_start_signal(20)
t=threading.Thread(target=check_start_signal,args=(20,))
t.start()
start=time.time()
time.sleep(3)
result = scan_if_won() #this scan is not instant, can take from 1 to 2 seconds
if result == False:
print("Action 1")
if result == True:
print("Action 2")
passed=time.time()-start
time.sleep(20-passed)
event2.set()
#Now somehow, at next iteration, time.sleep() value should be the 20 - 3 - scan_if_won() time
event=threading.Event()
event2=threading.Event()
main()
CodePudding user response:
normal in c# we have "events" so u should google it for the pyhton.
