How to plot a map of a semi-sphere (eg northern hemisphere) using cartopy.
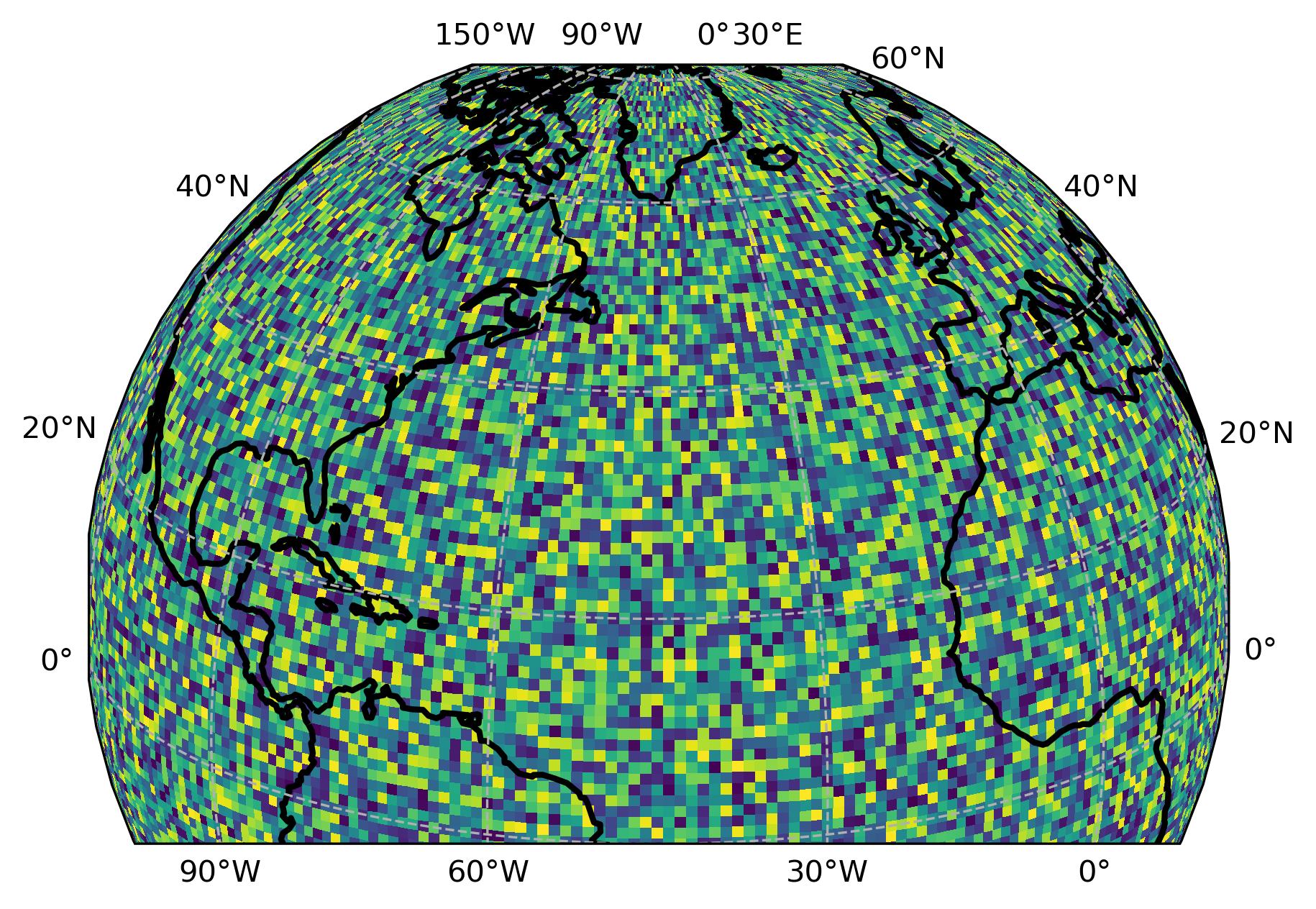
I'm trying to plot a map of the northern hemisphere using cartopy. But I don't understand how should I define the extent of the map so that only this region of interest is plotted. I would like the map to be cut off at 0° latitude. I would like to have code where I could easily define any subset of the glob using the ccrs.NearsidePerspective projection, or the ccrs.Orthographic projection.
Below I leave a code for reproduction.
import numpy as np
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Creating fake data
x = np.linspace(-180, 180, 361)
y = np.linspace(-90, 90, 181)
lon, lat = np.meshgrid(x, y)
values = np.random.random(lon.shape)*20
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
proj = ccrs.NearsidePerspective(central_longitude=-45, central_latitude=21)
ax = fig.add_subplot(121, projection=proj)
ax.set_extent([-120, 40, 0, 60])
ax.pcolormesh(lon, lat, values, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.coastlines(linewidth=2)
gl = ax.gridlines(draw_labels=True, linestyle='--')
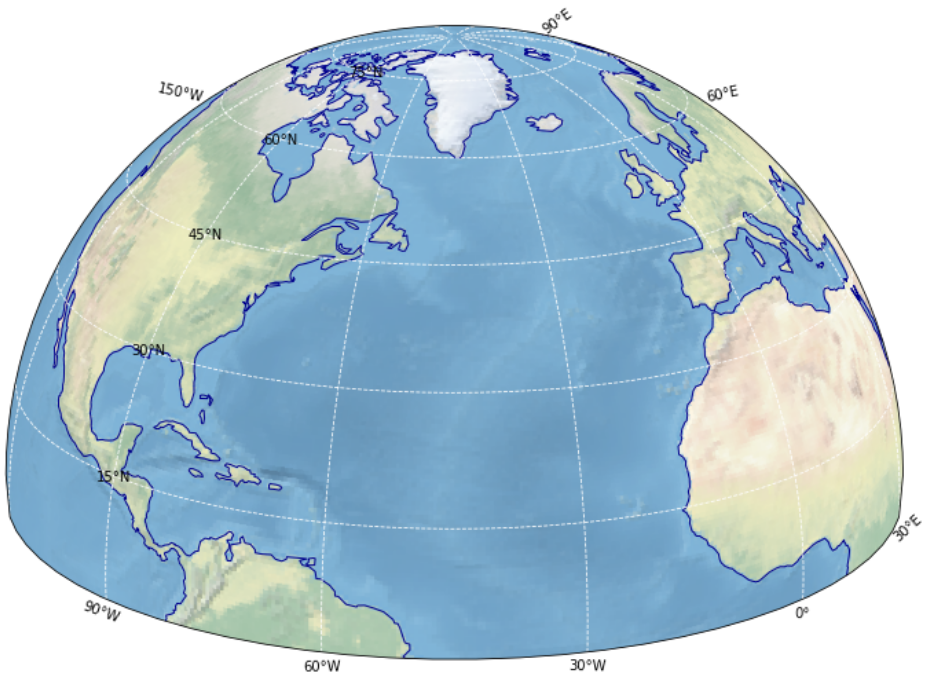
The code generates the following figure:
 Thank you very much in advance.
Robson
Thank you very much in advance.
Robson
CodePudding user response:
To plot only the upper hemisphere part of the map projection, a polygon of that part is needed to use as the projection boundary.
That polygon is created as a matplotlib-path object. It vertices' coordinates are data coordinates in my code, so that, no transformation is required when applied to the final plot.
This is a complete code:-
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import matplotlib.path as mpath
import numpy as np
from geographiclib.geodesic import Geodesic
fig = plt.figure(figsize=[12, 12])
proj = ccrs.NearsidePerspective(central_longitude=-45, central_latitude=21, satellite_height=35785831)
ax = plt.subplot(projection=proj)
# The value of r is obtained by previous run of this code ...
# with the line .. #print(ax.get_xlim()) uncommented
r = 5476336.098
ax.set_xlim(-r, r)
ax.set_ylim(-r, r)
ax.stock_img()
ax.coastlines(lw=1, color="darkblue")
# Find the locations of points along the equatorial arc
# start location
lon_fr, lat_fr = 30, 0
# end location
lon_to, lat_to = -120, 0
# This gets geodesic between the two points, WGS84 ellipsoid is used
geodl = Geodesic.WGS84.InverseLine(lat_fr, lon_fr, lat_to, lon_to)
lonlist, latlist = [], []
num_points = 32 #for series of points on geodesic/equator
for ea in np.linspace(0, geodl.s13, num_points):
g = geodl.Position(ea, Geodesic.STANDARD | Geodesic.LONG_UNROLL)
#print("{:.0f} {:.5f} {:.5f} {:.5f}".format(g['s12'], g['lat2'], g['lon2'], g['azi2']))
lon2, lat2 = g['lon2'], g['lat2']
lonlist.append( g['lon2'] )
latlist.append( g['lat2'] )
# Get data-coords from (lonlist, latlist)
# .. as points along equatorial arc
dataxy = proj.transform_points(ccrs.PlateCarree(), np.array(lonlist), np.array(latlist))
# (Uncomment to) Plot equator line
#ax.plot(dataxy[:, 0:1], dataxy[:, 1:2], "go-", linewidth=2, markersize=5, zorder=10)
# Top semi-circle arc for map extent
theta = np.linspace(-0.5*np.pi, 0.5*np.pi, 64)
center, radius = [0, 0], r
verts = np.vstack([np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)]).T
# Combine vertices of the semi-circle and equatorial arcs
# These points are in data coordinates, ready to plot on the axes.
verts = np.vstack([verts*r, dataxy[:, 0:2]])
polygon = mpath.Path(verts center)
ax.set_boundary(polygon)
gl = ax.gridlines(draw_labels=True, xlocs=range(-150,180,30), ylocs=range(0, 90, 15),
y_inline=True, linestyle='--', lw= 5, color= "w", )
# Get limits, the values are the radius of the circular map extent
# The values is then used as r = 5476336.09797 on top of the code
#print(ax.get_xlim())
#print(ax.get_ylim())
plt.show()