I have the following payload:
{
"KeyA": "ValueA",
"KeyB": "ValueB",
"KeyC": "ValueC"
...
"KeyZ": "ValueZ"
}
That I am able to parse properly in a spring boot controller with:
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<Object> createABC(
@RequestBody final Map<MyDTO, MyDTO> map
) {
For the sake of brevity, consider MyDTO as:
@Data
@ToString(includeFieldNames=false)
public class MyDTO implements Comparable<MyDTO> {
private final String name;
The problem is:
I can have duplicated keys on the input:
{
"KeyA": "ValueA",
"KeyA": "ValueA.1",
...
}
Which then gets deduplicated by the native Java Map implementation - only the second key gets saved and I am okay with that. I found out 
If you want to use com.google.common.collect.Multimap
there is no other way to send a request.
If you want to send a request in the form you mentioned in the question (withot [] brackets), as far as I can see, you have two options:
- Use
org.apache.commons.collections4.MultiValuedMapwith custom deserilizer;
Here is how your custom deserilizer should look like:
import com.example.demo.dto.MyDTO;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonParser;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonToken;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationContext;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonDeserializer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.MultiValuedMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.multimap.ArrayListValuedHashMap;
import java.io.IOException;
class MultiValuedMapJsonDeerializer extends JsonDeserializer<MultiValuedMap> {
@Override
public MultiValuedMap deserialize(JsonParser jp, DeserializationContext deserializationContext) throws IOException {
MultiValuedMap<MyDTO, MyDTO> myDTOMyDTOMultiValuedMap = new ArrayListValuedHashMap<>();
if (jp.getCurrentToken() != JsonToken.START_OBJECT) {
throw new IOException("invalid start marker");
}
while (jp.nextToken() != JsonToken.END_OBJECT) {
String fieldname = jp.getCurrentName();
jp.nextToken();
String value = jp.getText();
MyDTO key = new MyDTO(fieldname);
MyDTO myDTO = new MyDTO(value);
myDTOMyDTOMultiValuedMap.put(key, myDTO);
}
jp.close();
return myDTOMyDTOMultiValuedMap;
}
@Override
public Class<MultiValuedMap> handledType() {
return MultiValuedMap.class;
}
}
Here is how endpoint shoud look like:
@PostMapping("/test")
public void createABC(@RequestBody final MultiValuedMap<MyDTO, MyDTO> map) {
System.out.println(map);
}
When you hit this endpoint, you should see output like this:
{MyDTO(keyB)=[MyDTO(B)], MyDTO(keyC)=[MyDTO(C), MyDTO(D)], MyDTO(keyA)=[MyDTO(A)]}
- Use
org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap
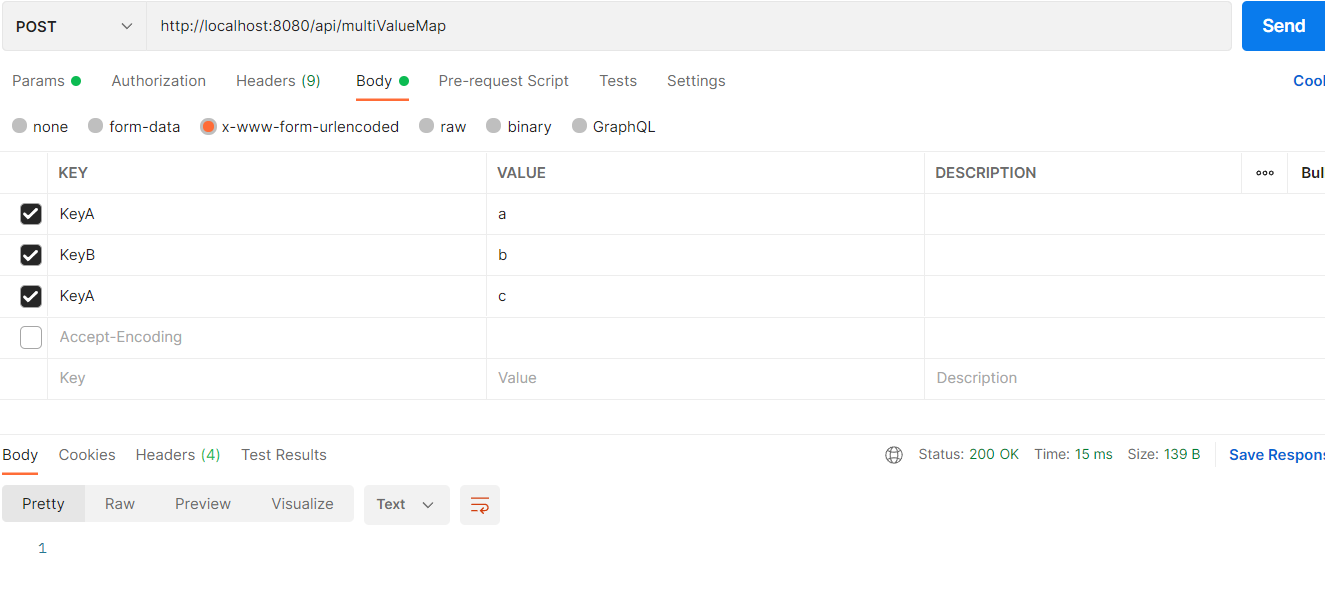
If you want to use this class, you shoud send your request body as x-www-form-urlencoded. Here is an example from Postman:
And finally, if you decide to use this option here is an example how controller method should look like:
@PostMapping("/multiValueMap")
public void multiValueMap(@RequestBody MultiValueMap<MyDTO, MyDTO> multiValueMap) {
System.out.println(multiValueMap);
}
Using this approach, you should see output like this:
{KeyB=[b], KeyA=[a, c]}
CodePudding user response:
It seems that you've successfully added GuavaModule to Jackson's configuration, so you're only missing an additional Spring HttpMessageConverter for Jackson as documented here. In your case it's MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter, ex.:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class MyHttpMessageConvertersConfiguration {
@Bean
public HttpMessageConverters customConverters() {
return new HttpMessageConverters(new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter());
}
}
(Or use constructor with explicit ObjectMapper for the custom converter if necessary, please consult the documentation.)