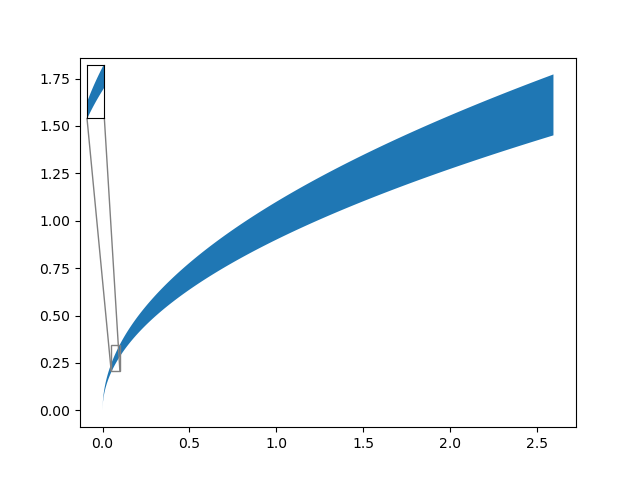
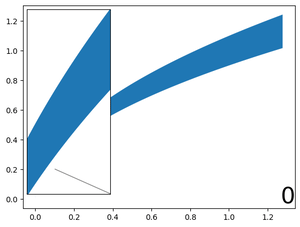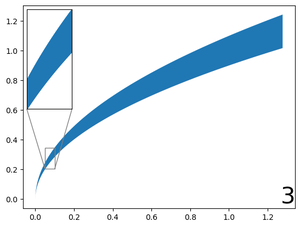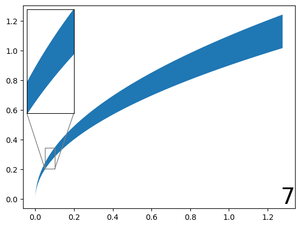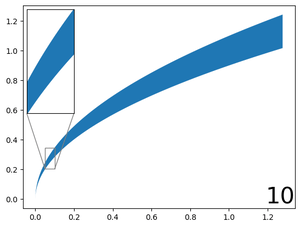
I am creating plots that include zoom inserts. The data is diverse it is impossoble for me to know what the data will be like before the program starts. I want to make the zoom insert zoom in as much as possible, without overlapping with any other element of my plot. Here is an example, where I use a zoom of 2. Ideally, I would like to automatically determine what this number should be:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import zoomed_inset_axes
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import mark_inset
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
xin = np.linspace(0, np.random.uniform(.5, 4), 1000)
x_samples = np.random.uniform(0.9, 1.1, (1, 1000)) * np.sqrt(xin[:, np.newaxis])
ax.fill_between(xin, x_samples.min(1), x_samples.max(1))
axins = zoomed_inset_axes(ax, zoom=2, loc='upper left')
axins.fill_between(xin, x_samples.min(1), x_samples.max(1))
axins.set_xlim(.05, .1)
idx = np.logical_and(xin > 0.05, xin < 0.1)
axins.set_ylim(x_samples.min(1)[idx].min(), x_samples.max(1)[idx].max())
axins.set_xticks([])
axins.set_yticks([])
mark_inset(ax, axins, loc1=4, loc2=3, fc="none", ec="0.5")
plt.savefig('hey')
plt.clf()
As you can see, zoom=2 was too low of a value. I can manually set the zoom parameter to a correct value. This is a tedious process. Is there a way to automatically find the zoom parameter that will maximize the insert size while avoiding overlaps with other parts of the plot?
CodePudding user response:
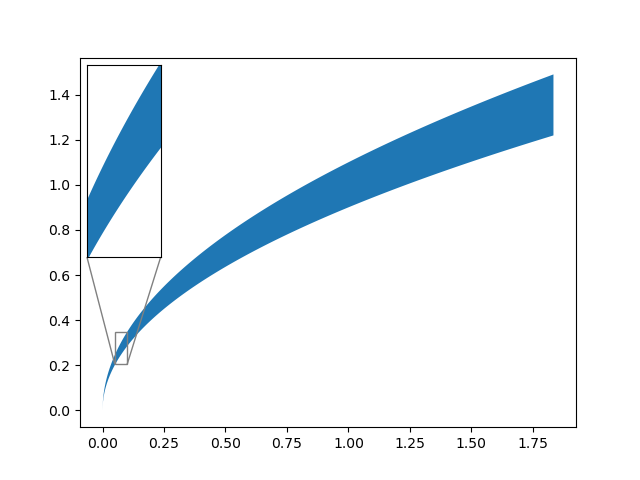
We can face this problem in an iterative way:
- Start with the maximum possible zoom (such that the inset occupies the whole height of the plot). As a result, part of the inset will overlap the plot.
- Check how much vertical gap exists before the point where the overlapping starts.
- Based on the current height of the inset, scale it down to avoid overlapping.
- After the rescaling, the width of the inset is also reduced, so we can scale it up again with the free vertical gap that has been left behind.
- Go back to 2. until convergence / maximum number of iterations is reached.
In practice the convergence is fast and reached in less than 10 iterations with the given data.
Visually:
Code for insets at the upper-left location.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import zoomed_inset_axes, mark_inset
def get_inset_max_zoom(x, y, xlim_inset, ylim_inset, max_iters=10):
""" Zoom that maximizes inset size without overlapping the artists """
# width and height of the inset in non-scaled coordinates.
inset_w = xlim_inset[1] - xlim_inset[0]
inset_h = ylim_inset[1] - ylim_inset[0]
# max y-coordinate of the whole plot.
y_max_plot = y.max()
# start with maximum zoom.
y_gap = y_max_plot - y.min()
zoom = y_gap / inset_h
for i in range(max_iters):
y_affected_max = y[x < zoom * inset_w].max()
# recalculate zoom by adjusting the gap.
y_gap = y_max_plot - y_affected_max
zoom = y_gap / inset_h
return zoom
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Change the seed to show produce different values.
rng = np.random.RandomState(seed=0)
# main plot.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
xin = np.linspace(0, rng.uniform(.5, 4), 1000)
x_samples = rng.uniform(
0.9, 1.1, (1, 1000)) * np.sqrt(xin[:, np.newaxis])
ax.fill_between(xin, x_samples.min(1), x_samples.max(1))
# get xy pairs.
y = x_samples.ravel()
x = np.repeat(xin, x_samples.shape[1])
# define the limits and location of the zoom inset.
xlim_inset = (.05, .1)
idx = np.logical_and(xin > xlim_inset[0], xin < xlim_inset[1])
ylim_inset = (x_samples.min(1)[idx].min(), x_samples.max(1)[idx].max())
loc = 'upper left'
# get max zoom.
zoom = get_inset_max_zoom(x, y, xlim_inset, ylim_inset, max_iters=5)
# create the inset.
axins = zoomed_inset_axes(ax, zoom=zoom, loc=loc, borderpad=0.5)
axins.set(
xlim=xlim_inset,
ylim=ylim_inset,
xticks=[], yticks=[])
# connect the bboxes.
mark_inset(ax, axins, loc1=4, loc2=3, fc="none", ec="0.5")
# plot within the inset.
axins.fill_between(xin, x_samples.min(1), x_samples.max(1))
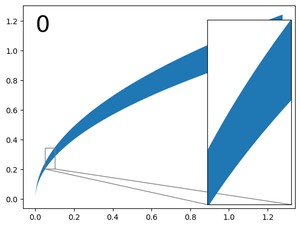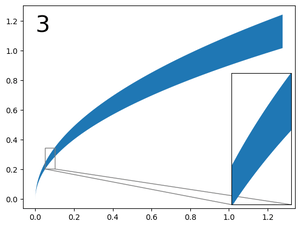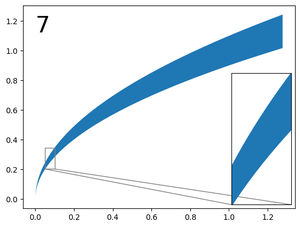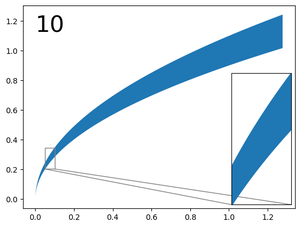
Generalizing to the 4 corner locations {upper-left, upper-right, lower-right, lower-left}. For instance, with loc = 'lower right':
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator import zoomed_inset_axes, mark_inset
def get_inset_max_zoom_given_loc(
x, y, xlim_inset, ylim_inset, loc='upper left', max_iters=10):
""" Zoom that maximizes inset size without overlapping the artists """
# width and height of the inset in non-scaled coordinates.
inset_w = xlim_inset[1] - xlim_inset[0]
inset_h = ylim_inset[1] - ylim_inset[0]
# handy variables.
is_left = 'left' in loc
is_upper = 'upper' in loc
y_min_plot, y_max_plot = y.min(), y.max()
y_xtm_plot = y_max_plot if is_upper else y_min_plot
x_max_plot = x.max()
# start with maximum zoom.
y_gap = y_max_plot - y_min_plot
zoom = y_gap / inset_h
for i in range(max_iters):
# get affected x-coordinate range.
if is_left:
x_affected = x < zoom * inset_w
else:
x_affected = x > x_max_plot - zoom * inset_w
# get affected y-coordinate extremum.
y_affected = y[x_affected]
y_affected_xtm = y_affected.max() if is_upper else y_affected.min()
# recalculate zoom by adjusting the gap.
y_gap = abs(y_xtm_plot - y_affected_xtm)
zoom = y_gap / inset_h
return zoom
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Change the seed to show produce different values.
rng = np.random.RandomState(seed=0)
# main plot.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
xin = np.linspace(0, rng.uniform(.5, 4), 1000)
x_samples = rng.uniform(
0.9, 1.1, (1, 1000)) * np.sqrt(xin[:, np.newaxis])
ax.fill_between(xin, x_samples.min(1), x_samples.max(1))
# get xy pairs.
y = x_samples.ravel()
x = np.repeat(xin, x_samples.shape[1])
# define the limits and location of the zoom inset.
xlim_inset = (.05, .1)
idx = np.logical_and(xin > xlim_inset[0], xin < xlim_inset[1])
ylim_inset = (x_samples.min(1)[idx].min(), x_samples.max(1)[idx].max())
loc = 'lower right'
# get max zoom.
zoom = get_inset_max_zoom_given_loc(
x, y, xlim_inset, ylim_inset, loc=loc, max_iters=10)
# create the inset.
axins = zoomed_inset_axes(ax, zoom=zoom, loc=loc, borderpad=0.5)
axins.set(
xlim=xlim_inset,
ylim=ylim_inset,
xticks=[], yticks=[])
# connect the bboxes.
mark_inset(ax, axins, loc1=4, loc2=3, fc="none", ec="0.5")
# plot within the inset.
axins.fill_between(xin, x_samples.min(1), x_samples.max(1))