I'm learning to write basic Win32 apps in C and am trying to pass typed text from one editable textbox to a new window after pressing a button.
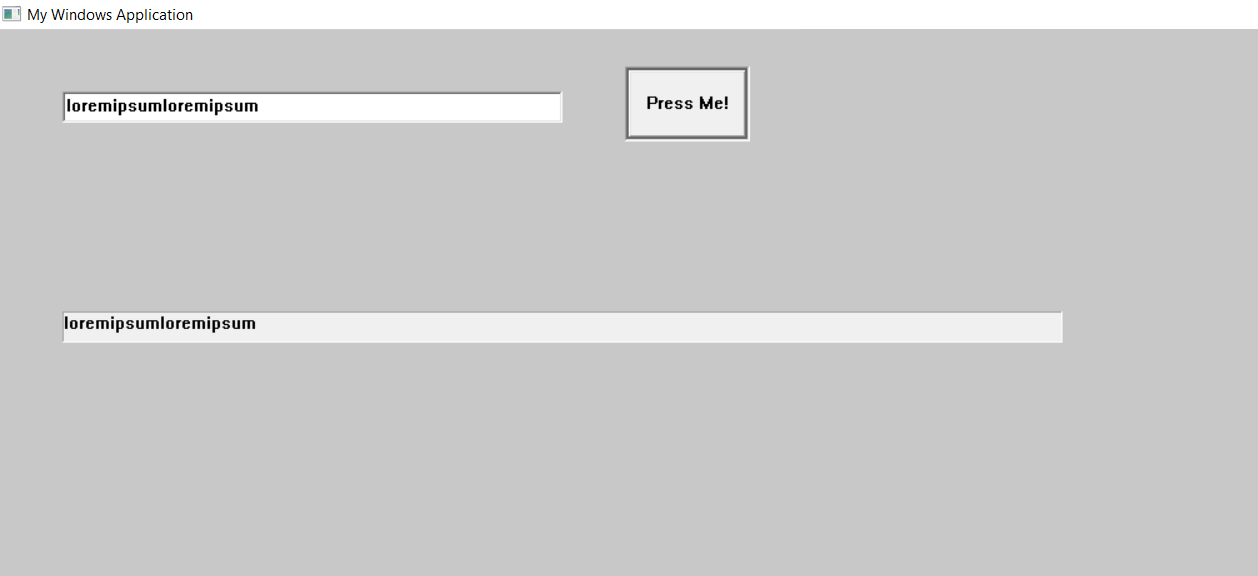
I noticed that the default text buffer capacity for such a transfer is 20 characters in Visual Studio 2019 (I am on 64-bit Windows 10). After I try to pass a string longer than 20 characters, I get an exception thrown.
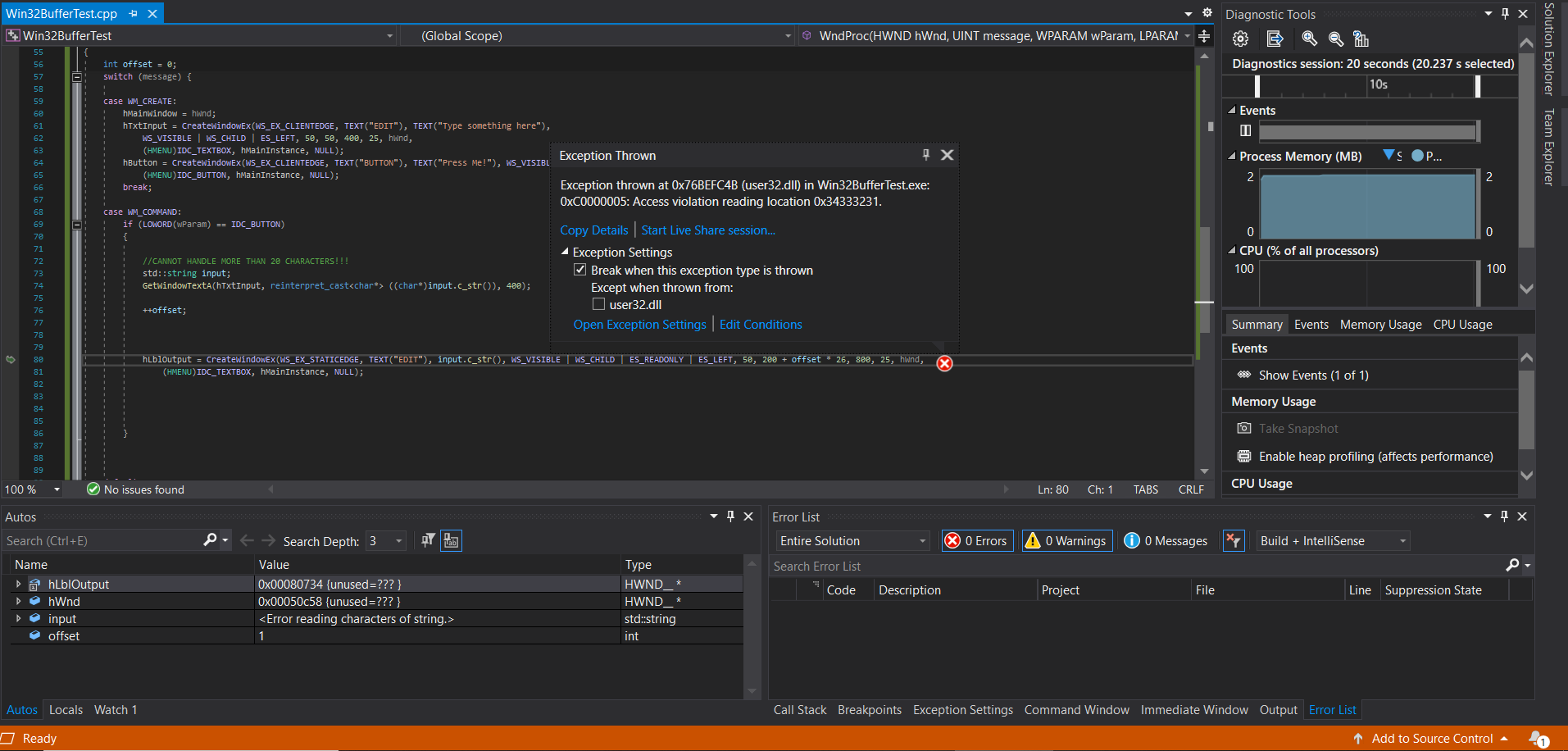
I would like to know how to increase that buffer capacity, since eventually I want to be able to pass a filepath into the text input window and open that file.
My code:
#include <windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
//lresult callback prototype
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
//window handles
HWND hMainWindow;
HINSTANCE hMainInstance;
HWND hLblOutput;
HWND hTxtInput;
HWND hButton;
#define IDC_TEXTBOX 1000
#define IDC_BUTTON 1001
//call to winmain - equivalent of main for win32 environments
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
MSG msg = { 0 };
WNDCLASS wc = { 0 };
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_BACKGROUND);
wc.lpszClassName = TEXT("NiceWindowsApp");
if (!RegisterClass(&wc))
return 1;
hMainWindow = CreateWindow(wc.lpszClassName, TEXT("My Windows Application"), WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_VISIBLE, 0, 0, 640, 480, 0, 0, hInstance, NULL);
hMainInstance = wc.hInstance;
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return 0;
}
//callback definition
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
int offset = 0;
switch (message) {
case WM_CREATE:
hMainWindow = hWnd;
hTxtInput = CreateWindowEx(WS_EX_CLIENTEDGE, TEXT("EDIT"), TEXT("Type something here"),
WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD | ES_LEFT, 50, 50, 400, 25, hWnd,
(HMENU)IDC_TEXTBOX, hMainInstance, NULL);
hButton = CreateWindowEx(WS_EX_CLIENTEDGE, TEXT("BUTTON"), TEXT("Press Me!"), WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD | WM_COPY | ES_LEFT, 500, 30, 100, 60, hWnd,
(HMENU)IDC_BUTTON, hMainInstance, NULL);
break;
case WM_COMMAND:
if (LOWORD(wParam) == IDC_BUTTON)
{
//CANNOT HANDLE MORE THAN 20 CHARACTERS!!!
std::string input;
GetWindowTextA(hTxtInput, reinterpret_cast<char*> ((char*)input.c_str()), 400);
offset;
hLblOutput = CreateWindowEx(WS_EX_STATICEDGE, TEXT("EDIT"), input.c_str(), WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD | ES_READONLY | ES_LEFT, 50, 200 offset * 26, 800, 25, hWnd,
(HMENU)IDC_TEXTBOX, hMainInstance, NULL);
}
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
I have tried to increase the third parameter in GetWindowTextA() to various numbers up to 4000, but it didn't seem to help.
CodePudding user response:
One correct way to do this is:
std::wstring text;
text.resize(GetWindowTextLengthW(hTxtInput));
text.resize(GetWindowTextW(hTxtInput, text.data(), text.size() 1));
CodePudding user response:
Solved as per the below:
#include <windows.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
//lresult callback prototype
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam);
//window handles
HWND hMainWindow;
HINSTANCE hMainInstance;
HWND hLblOutput;
HWND hTxtInput;
HWND hButton;
CHAR s_text_1[]{ "Some text.." };
CHAR s_text_2[]{ 0 };
#define IDC_TEXTBOX 1000
#define IDC_BUTTON 1001
//call to winmain - equivalent of main for win32 environments
int WINAPI WinMain(HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
MSG msg = { 0 };
WNDCLASS wc = { 0 };
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_BACKGROUND);
wc.lpszClassName = TEXT("NiceWindowsApp");
if (!RegisterClass(&wc))
return 1;
hMainWindow = CreateWindow(wc.lpszClassName, TEXT("My Windows Application"), WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW | WS_VISIBLE,
0, 0, 640, 480, 0, 0, hInstance, NULL);
hMainInstance = wc.hInstance;
while (GetMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0))
{
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
return 0;
}
//callback definition
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc(HWND hWnd, UINT message, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
int offset = 0;
switch (message) {
case WM_CREATE:
hMainWindow = hWnd;
hTxtInput = CreateWindowEx(WS_EX_CLIENTEDGE, TEXT("EDIT"), s_text_1,
WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD | ES_LEFT, 50, 50, 400, 25, hWnd,
(HMENU)IDC_TEXTBOX, hMainInstance, NULL);
hButton = CreateWindowEx(WS_EX_CLIENTEDGE, TEXT("BUTTON"), TEXT("Press Me!"), WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD | WM_COPY | ES_LEFT, 500, 30, 100, 60, hWnd,
(HMENU)IDC_BUTTON, hMainInstance, NULL);
break;
case WM_COMMAND:
if (LOWORD(wParam) == IDC_BUTTON)
{
//CANNOT HANDLE MORE THAN 20 CHARACTERS!!!
std::wstring input;
//GetWindowTextW(hTxtInput, reinterpret_cast<char*> ((char*)input.c_str()), 400);
int lgth = GetWindowTextLength(hTxtInput);
//GetWindowTextW(hTxtInput, reinterpret_cast<wchar_t*> ((wchar_t*)input.c_str()), lgth);
//GetWindowTextA(hTxtInput, char[], 400);
GetWindowText(hTxtInput, s_text_1, 255);
offset;
hLblOutput = CreateWindowEx(WS_EX_STATICEDGE, TEXT("EDIT"), s_text_1, WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD | ES_READONLY | ES_LEFT, 50, 200 offset * 26, 800, 25, hWnd,
(HMENU)IDC_TEXTBOX, hMainInstance, NULL);
SetWindowText(hLblOutput, s_text_1);
}
default:
return DefWindowProc(hWnd, message, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
Thanks for your hints everybody.
EDIT: I now realise that this solution is not technically perfect and can lead to undefined behaviour and/or memory leaks. I'll take the advice presented in the other answers and comments into account and adjust the code accordingly.

