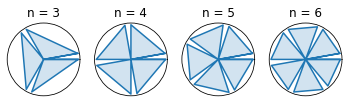
I am trying to generate symmetrical circular images using python, but I couldn't find an easy way to do it.
Here is an example sort of what I want:
So far, I listed the processes, but I couldn't find an easy way to implement them.:
Is there a simple way to do it?
I appreciate any help
CodePudding user response:
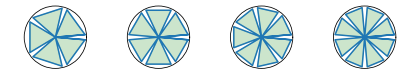
I would use a polar plot, then it's just a matter of calculating the coordinates. For this, I am using np.linspace and I combine a division of the trigonometric circle, the same points shifted by 10°, and zeros:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from itertools import chain
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={'projection': 'polar'})
ax.grid(False)
ax.xaxis.set_visible(False)
ax.yaxis.set_visible(False)
n = 6
# division of the circle
a = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n 1)
# angles
theta = list(chain.from_iterable(zip(a, np.zeros(n 1), a (np.pi/180*10))))
# distance to center
r = np.tile([1,0,1], n 1)
# plotting line
ax.plot(theta, r)
# plotting fill (needs an extra (0,0) point)
ax.fill(theta [0], list(r) [0], alpha=0.2)
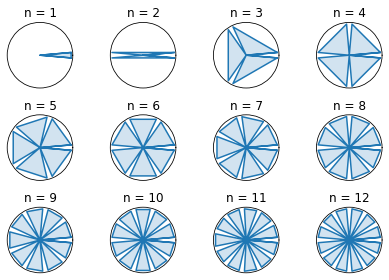
example:
example with a loop
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from itertools import chain
fig, axes = plt.subplots(ncols=4, nrows=3, subplot_kw={'projection': 'polar'})
axes = axes.flatten()
def plot_shape(ax, n=3, delta=np.pi/180*10):
ax.grid(False)
ax.xaxis.set_visible(False)
ax.yaxis.set_visible(False)
a = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n 1)-delta/2
theta = list(chain.from_iterable(zip(a, np.zeros(n 1), a delta)))
r = np.tile([1,0,1], n 1)
ax.plot(theta, r)
ax.fill(theta [0], list(r) [0], alpha=0.2)
for i in range(len(axes)):
axes[i].set_title(f'n = {i 1}')
plot_shape(axes[i], n=i 1)
plt.tight_layout()