I am trying to call Fortran code from C#. I am using Visual Studio 2019 and the Intel Fortran Compiler (iFort).
I created a fortran DLL project with the following code that compiles without issue (project set to 'release', 'x64'):
module Fortran_DLL_Lib
implicit none
contains
subroutine adder(a,b,x,y)
!DEC$ ATTRIBUTES DLLEXPORT, ALIAS:'adder' :: adder
!DEC$ ATTRIBUTES REFERENCE :: x,y
implicit none
integer, intent(in) :: a,b
integer, intent(out) :: x,y
y = a b
x = 2*a 3*b
end subroutine
end module
I then created a C# console application with the following code (project also set to 'Release', 'x64'):
using System;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace Call_Fortran_Dll_FromCS_Test
{
class Program
{
[DllImport("Fortran_DLL_Lib.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern void adder(int a, int b, [Out] int x, [Out] int y);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 4;
int b = 3;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.WriteLine(b);
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(y);
adder(a, b, x, y); //error occurs here
Console.WriteLine(a);
Console.WriteLine(b);
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.WriteLine(y);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
The program runs up until the line that calls the fortran function, then returns the error
Exception thrown: 'System.DllNotFoundException' in Call_Fortran_Dll_FromCS_Test.dll
An unhandled exception of type 'System.DllNotFoundException' occurred in Call_Fortran_Dll_FromCS_Test.dll
Unable to load DLL 'Fortran_DLL_Lib.dll' or one of its dependencies: Access is denied. (0x80070005 (E_ACCESSDENIED))
I have copied both the 'Fortran_DLL_Lib.dll' and 'Fortran_DLL_Lib.lib' files into both the folder that contains the c# project files, as well as the location where the executable project is located, neither seems to help/matter.
This is just based on example code I found trying to find ways to do this and isn't specific to what I'm doing. I'm just trying to get a 'proof of concept' together before jumping into more complex applications. The solution doesn't even necessarily be a DLL, that's just what I saw people recommending as the solution to this (in 7 year old questions on this site). Open to any solutions that successfully call Fortran code from a C# project (eventually, a C# project with a WPF GUI, if that matters).
I am in a situation where I can't install Dependency Walker, change environment variables, or pretty much anything that requires elevated privileges.
Any help would be greatly appreciated!
Update: The very thorough and detailed answer by @JAlex below works perfectly, for both .NET Framework and .NET Core. My ongoing issues are due to user account policies at my workplace that prevent running *.dll files (apparently). Trying the solution on a normal, un-restricted system worked perfectly without issue.
CodePudding user response:
First make sure the dll is next to the C# driver binary, add the dll into the CSharp solution. Use add-existing and then add as link
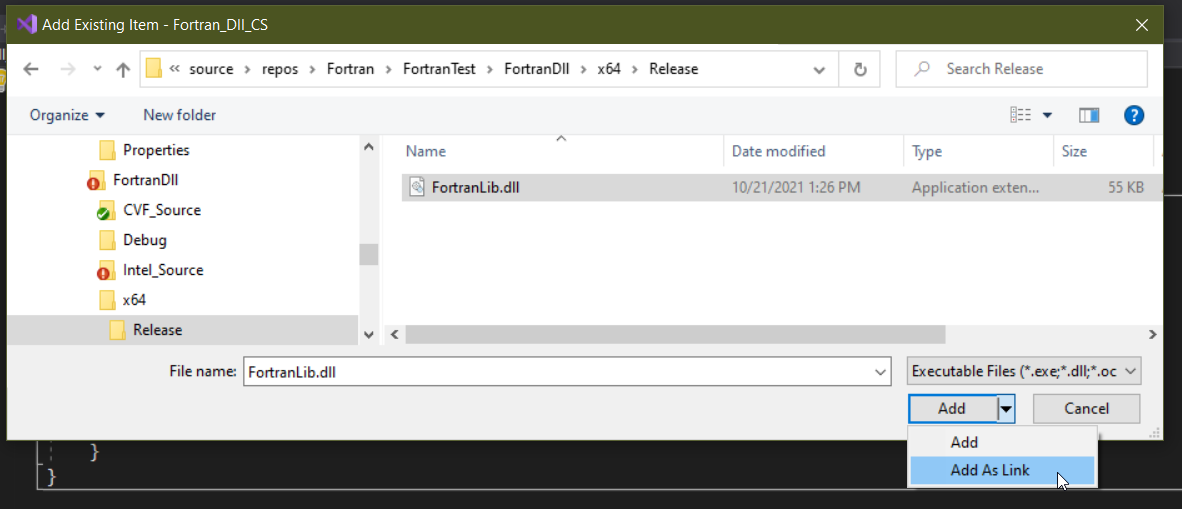
then select the link in the solution and set to copy if newer
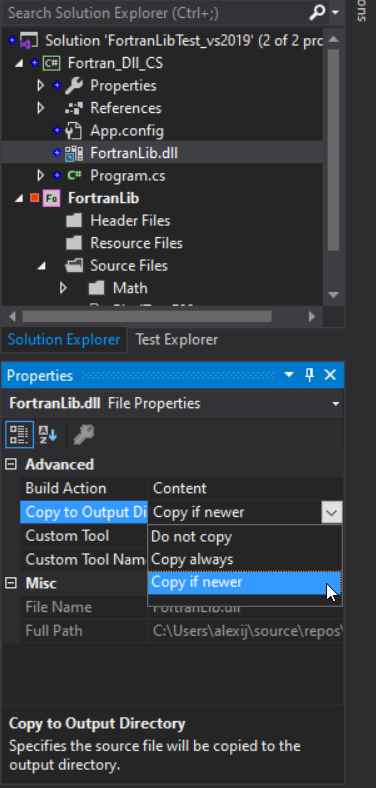
this will place the dll in the output folder
additionally, I set the calling convention in Fortran as CVF, although I think this is optional as I specify explicitly which argument is REFERENCE and which is VALUE.
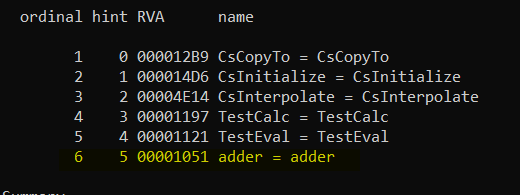
I checked the DLL export using dumpbin /exports
The following code works as indented:
Fortran Project
Note the addition of the VALUE attributes as well as the REFERENCE ones.
module mod_Fortran_dll
use iso_c_binding
implicit none
contains
subroutine adder(a,b,x,y)
!DEC$ ATTRIBUTES DLLEXPORT, alias:'adder' :: adder
!DEC$ ATTRIBUTES VALUE :: a,b
!DEC$ ATTRIBUTES REFERENCE :: x,y
implicit none
integer, intent(in) :: a,b
integer, intent(out) :: x,y
y = a b
x = 2*a 3*b
end subroutine
end module
CSharp Project
Note the removal of the CDecl calling convention, and the specific EntryPoint specification.
static class Program
{
#region Fortran
[DllImport("FortranLib.dll", EntryPoint = "adder")]
public static extern void adder(int a, int b, [Out] out int x, [Out] out int y);
#endregion
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int a = 4;
int b = 3;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
Console.WriteLine($"a={a}, b={b}, x={x}, y={y}");
// a = 4, b = 3, x = 0, y = 0
adder(a, b, out x, out y);
Console.WriteLine($"a={a}, b={b}, x={x}, y={y}");
// a = 4, b = 3, x = 17, y = 7
}
}
Note that the [Out] attribute is required for structure types, but not for primitive types.