I am doing some optical flow analysis. The goal is to iterate through every frame in a long movie, calculate the dense optical flow, and append the resulting angles and magnitudes to a growing numpy array. I found that it takes longer and longer to complete every consecutive loop, and I'm not sure why. Here is a simple example loop that recapitulates the problem:
import numpy as np
arraySize = (1, 256, 256) # correct array size
emptyArray = np.zeros(arraySize) # empty array to fill with angles from every image pair
timeElapsed = [] # empty list to fill with time values
for i in range(100): # iterates through the frames in the image stack
start = time.time() # start the time
newArray = np.zeros(arraySize) # makes an example new array
emptyArray = np.concatenate((emptyArray, newArray)) # concats new and growing arrays
end = time.time() # stop the time
timeElapsed.append(end-start) # append the total time for the loop to the growing list
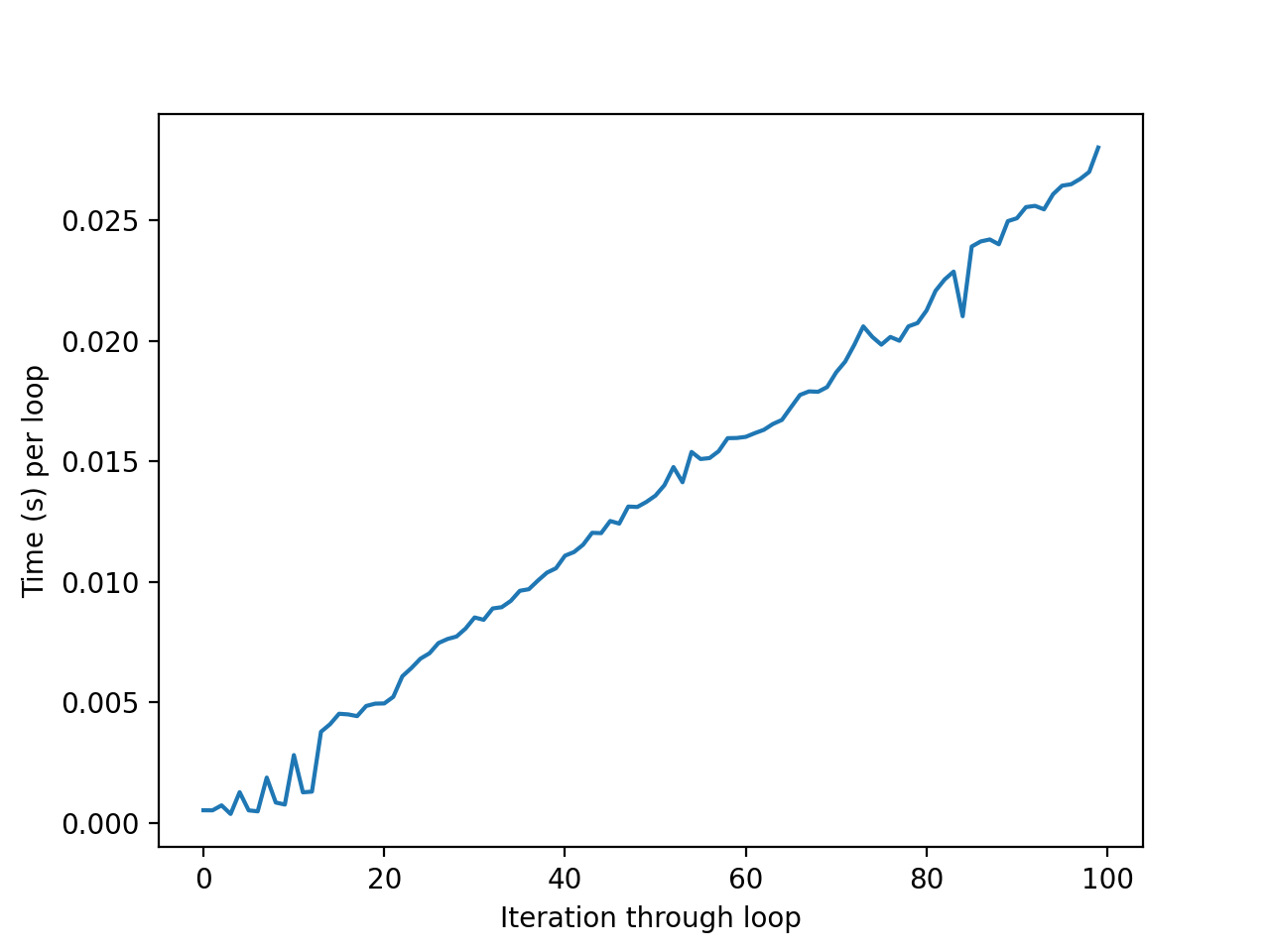
If I then plot the time elapsed for each loop I get a linear increase for every trip through the loop. In this example it's still tolerable, but with my actual dataset it isn't.
I am guessing that the larger arrays take more time to work with, but I'm not sure what to do to avoid that. Is there a better, faster, or more Pythonic way to do this?
------------- edit -------------
Per mathfux's suggestion: I modified the loop as follows:
arraySize = (1, 256, 256) # correct array size
emptyArray = np.concatenate([np.zeros(arraySize) for i in range(100)]) # empty array to fill with angles from every image pair
timeElapsed = [] # empty list to fill with time values
for i in range(100): # iterates through the frames in the image stack
start = time.time() # start the time
newArray = np.zeros(arraySize) # makes an example new array
emptyArray[i] = newArray[0] # overwrites empty array with newarray values at the relevant position
end = time.time() # stop the time
timeElapsed.append(end-start) # append the total time for the loop to the growing list
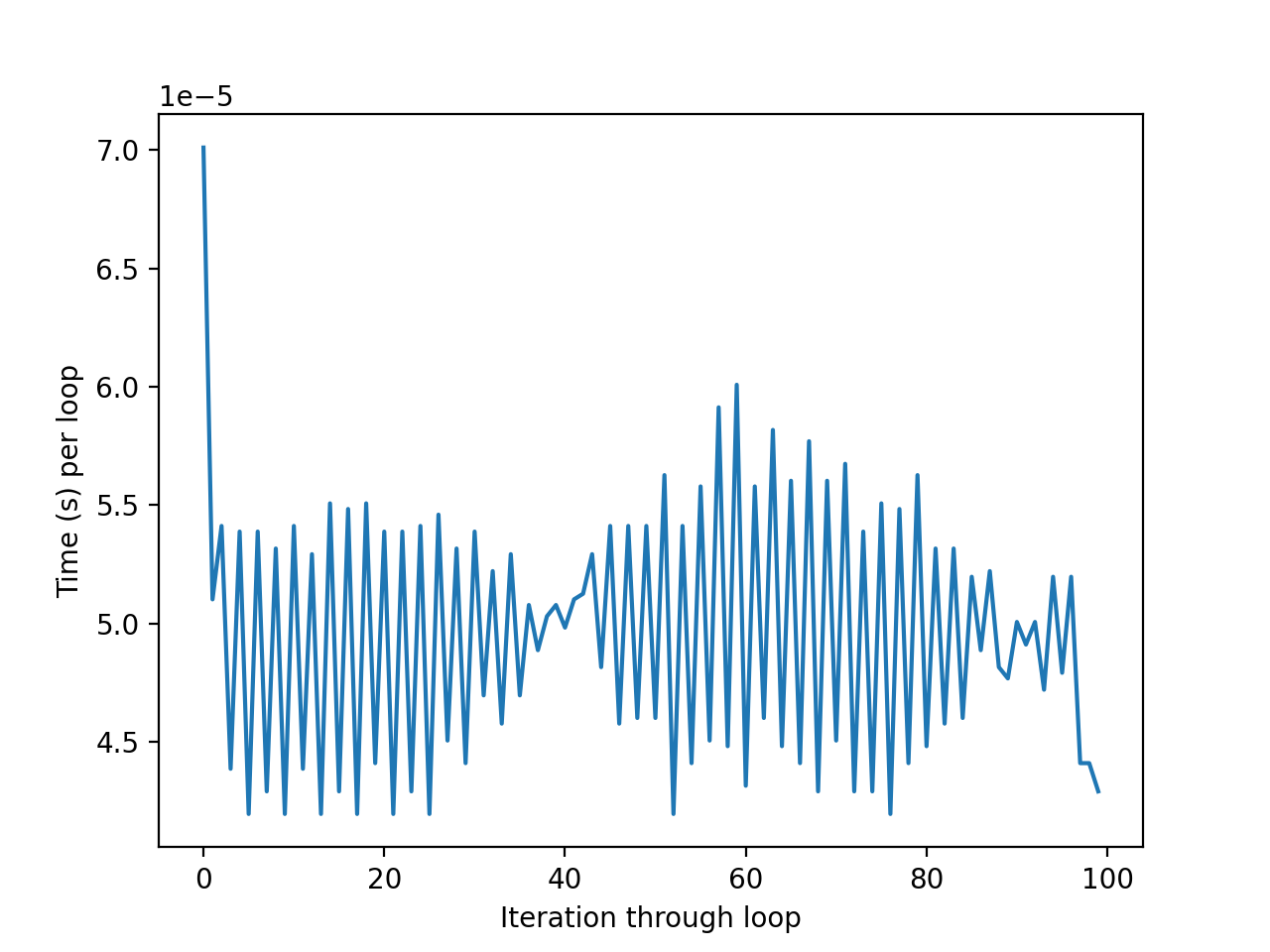
Now the time/loop is pretty consistent between iterations:
Thank you!
CodePudding user response:
Every time you append a new array, new memory is being allocated to create a bigger one and record data into it. This is very expensive. A better solution is to allocate a specific size of memory once and then record your date using np.concatenate only once:
np.concatenate([np.zeros(arraySize) for i in range(100)])
CodePudding user response:
This way seems to be 28 times faster in my Pc
start = time.time() # start the time
arrays = []
for i in range(100): # iterates through the frames in the image stack
arrays.append(np.zeros(arraySize))
#Concatenate all in one time
newArray=np.concatenate(arrays)
end = time.time() # stop the time
timeElapsed2 = end-start
print("Elapesed:",timeElapsed2)
print("sum elapsed times of first method:", np.sum(timeElapsed))
Elapsed : 0.021436214447021484
Sum elapsed times of first method: 0.6163454055786133