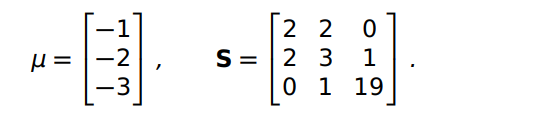import numpy as np
from numpy import sin, cos, pi
from matplotlib.pyplot import *
rng = np.random.default_rng(42)
N = 200
center = 10, 15
sigmas = 10, 2
theta = 20 / 180 * pi
# covariance matrix
rotmat = np.array([[cos(theta), -sin(theta)],[sin(theta), cos(theta)]])
diagmat = np.diagflat(sigmas)
mean =np.array([−1,−2,−3])
# covar = rotmat @ diagmat @ rotmat.T
covar= np.array([[2, 2 ,0],[2 ,3, 1],[0, 1 ,19]])
print('covariance matrix:')
print(covar)`enter code here`
eigval, eigvec = np.linalg.eigh(covar)
print(f'eigenvalues: {eigval}\neigenvectors:\n{eigvec}')
print('angle of eigvector corresponding to larger eigenvalue:',
180 /pi * np.arctan2(eigvec[1,1], eigvec[0,1]))
 after that I need to Perform PCA on the above data to one principal component and two principal components. What is the fractional explained variance in this two
cases
after that I need to Perform PCA on the above data to one principal component and two principal components. What is the fractional explained variance in this two
cases
CodePudding user response:
For generating the data, you need two tricks:
- Compute a "square root" of covariance matrix S using eigenvalue-eigenvector factorization
- Use the standard formula for generating a random normal with given mean and covariance. With Numpy it works on vectors (quoting from help(np.random.randn)):
For random samples from :math:`N(\mu, \sigma^2)`, use:
``sigma * np.random.randn(...) mu``
Example:
import numpy as np
# Part 1: generating random normal data with the given mean and covariance
N = 200
# covariance matrix
S = np.array([[2, 2, 0], [2, 3, 1], [0, 1, 19]])
# mean
mu = np.array([[-1, -2, -3]]).T
# get "square root" of covariance matrix via eigenfactorization
w, v = np.linalg.eig(S)
sigma = np.sqrt(w) * v
# ready, set, go!
A = sigma @ np.random.randn(3, N) mu
print(f'sample covariance:\n{np.cov(A)}')
print(f'sample mean:\n{A.mean(axis=1)}')
print(f'covariance condition number: {np.linalg.cond(S)}')
print('^^ note: this matrix is poorly conditioned; sample covariance will be noisy')
# Part 2: principal component analysis on random data A
# estimate the sample covariance
R = np.cov(A)
# do the PCA
lam, u = np.linalg.eig(R)
# fractional explained variance is the relative magnitude of
# the accumulated eigenvalues
# sort descending
col_order = np.argsort(lam)[::-1]
var_explained = lam[col_order].cumsum() / lam.sum()
print(f'fractional explained variance: {var_explained}')