I have:
Column A: (IDs)
A
A
A
C
C
Z
Column B: (Values)
3
2
-6
-12
6
2
I'm trying to create a macro that fills all unique ID's into column C, and counts whether they pass/fail in column D. A pass would be having an associated value in column B between -5 and 5.
Column C/D would look like:
| C | D |
|---|---|
| A | 2 |
| C | 0 |
| Z | 1 |
If anyone can start me off or link a similar example id appreciate.
CodePudding user response:
You can do it using formulas. But if you like/want VBA, please try the next piece of code. It uses arrays and a dictionary. Working only in memory, it should be very fast, even for large ranges:
Sub CountPassed()
Dim dict As Object, sh As Worksheet, lastR As Long
Dim arr, arrFin, i As Long
Set sh = ActiveSheet
lastR = sh.Range("A" & sh.rows.count).End(xlUp).row
arr = sh.Range("A2:B" & lastR).value 'place the range in an array for faster iteration
Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
For i = 1 To UBound(arr) 'extract unique keys and their item value according to the rule:
dict(arr(i, 1)) = dict(arr(i, 1)) IIf(arr(i, 2) >= -5 And arr(i, 2) <= 5, 1, 0)
Next i
'create the necessary final array:
ReDim arrFin(1 To dict.count, 1 To 2)
For i = 0 To dict.count - 1
arrFin(i 1, 1) = dict.Keys()(i)
arrFin(i 1, 2) = dict.items()(i)
Next i
'drop the final array at once
sh.Range("C2").Resize(UBound(arrFin), 2).value = arrFin
End Sub
CodePudding user response:
Count Unique With Limits
- Adjust the values in the constants section.
Option Explicit
Sub CountUniqueWithLimits()
Const sName As String = "Sheet1"
Const sFirstCellAddress As String = "A1"
Const dName As String = "Sheet1"
Const dFirstCellAddress As String = "C1"
Const lLimit As String = ">=-5"
Const uLimit As String = "<=5"
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook ' workbook containing this code
Dim sws As Worksheet: Set sws = wb.Worksheets(sName)
Dim srg As Range
Dim rCount As Long
With sws.Range(sFirstCellAddress)
Dim lCell As Range: Set lCell = .Resize(sws.Rows.Count - .Row 1) _
.Find("*", , xlFormulas, , , xlPrevious)
If lCell Is Nothing Then Exit Sub
rCount = lCell.Row - .Row 1
Set srg = .Resize(rCount, 2)
End With
Dim Data As Variant: Data = srg.Value
Dim dict As Object: Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
dict.CompareMode = vbTextCompare
Dim Key As Variant
Dim nkey As Variant
Dim r As Long
For r = 1 To rCount
Key = Data(r, 1)
If Not IsError(Key) Then
If Len(Key) > 0 Then
If Not dict.Exists(Key) Then
dict(Key) = 0
End If
nkey = Data(r, 2)
If IsNumeric(nkey) Then
If Len(nkey) > 0 Then
If Evaluate(nkey & lLimit) Then
If Evaluate(nkey & uLimit) Then
dict(Key) = dict(Key) 1
End If
End If
End If
End If
End If
End If
Next r
rCount = dict.Count
If rCount = 0 Then Exit Sub
ReDim Data(1 To rCount, 1 To 2)
r = 0
For Each Key In dict.Keys
r = r 1
Data(r, 1) = Key
Data(r, 2) = dict(Key)
Next Key
Dim dws As Worksheet: Set dws = wb.Worksheets(dName)
With dws.Range(dFirstCellAddress).Resize(, 2)
.Resize(rCount).Value = Data
.Resize(dws.Rows.Count - .Row - rCount 1).Offset(rCount).ClearContents
End With
MsgBox "Unique values with limits counted.", vbInformation
End Sub
CodePudding user response:
Well, it may happen you are not familiar of writing VBA Codes, then you may try any of the options using Excel Formula (Formulas Shown Below Are Exclusively For Excel 2021 & O365 Users)
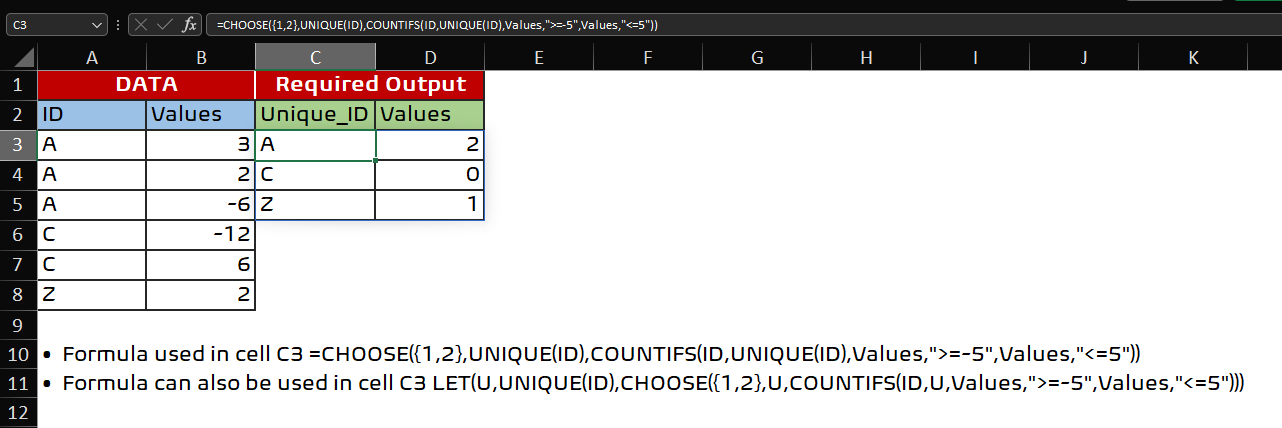
=CHOOSE({1,2},UNIQUE(ID),COUNTIFS(ID,UNIQUE(ID),Values,">=-5",Values,"<=5"))
In the above formula, we are combining two arrays within a CHOOSE Function.
• The first array contains the unique values in the database
UNIQUE(ID)
Where ID refers to the range =$A$3:$A$8, created using the Define Name Manager.
• The second array is essentially the COUNTIFS Function,
COUNTIFS(ID,UNIQUE(ID),Values,">=-5",Values,"<=5")
Where Values refers to the range =$B$3:$B$8, created using the Define Name Manager.
The CHOOSE function combines both the arrays into a single array, which produces as a two-column table as shown in the image below.
Note that we can also use the LET function to elegantly perform, by defining a variable, U to hold the unique values,
• Formula can also be used in cell C3
=LET(U,UNIQUE(ID),CHOOSE({1,2},U,COUNTIFS(ID,U,Values,">=-5",Values,"<=5")))
You may see that this version of the formula calls the UNIQUE function once only, storing the result in U, which is used twice!