Suppose I have the following DataFame:
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
'id':[112, 130, 200],
'name':['Lara', 'Kasia', 'Rocco'],
'level/income':[{1:400, 2:800}, {1:100}, {1:1000, 2:2000, 3:5000}]
}
)
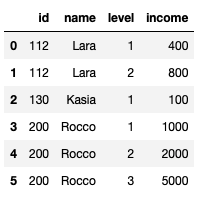
I would like this to be the end result:
I tried to do this on my own but I failed spectacularly. I was trying to recreate the original DataFrame by finding which id and name would appear multiple times but this proved too much.
len_need = []
id2 = []
name2 = []
level2 = []
income2 = []
for index,row in df.iterrows():
len_need.append(len(row['level/income']))
I'm sure there's a better way to do this.
CodePudding user response:
try this:
(df.set_index(['id', 'name'])
.squeeze()
.apply(pd.Series)
.rename_axis('level', axis=1)
.stack()
.reset_index(name='income'))
>>>
id name level income
0 112 Lara 1 400.0
1 112 Lara 2 800.0
2 130 Kasia 1 100.0
3 200 Rocco 1 1000.0
4 200 Rocco 2 2000.0
5 200 Rocco 3 5000.0
CodePudding user response:
Variation using json_normalize:
from pandas import DataFrame, json_normalize
df = DataFrame(
{
"id": [112, 130, 200],
"name": ["Lara", "Kasia", "Rocco"],
"level/income": [{1: 400, 2: 800}, {1: 100}, {1: 1000, 2: 2000, 3: 5000}],
}
)
income_cols = list(range(1, 3 1))
id_cols = ["id", "name"]
final = (
df["level/income"]
.pipe(json_normalize)
.assign(id=df["id"], name=df["name"])
.melt(
id_vars=id_cols, value_vars=income_cols, var_name="level", value_name="income"
)
.dropna()
)
print(final)
# id name level income
# 0 112 Lara 0 400.0
# 1 130 Kasia 0 100.0
# 2 200 Rocco 0 1000.0
# 3 112 Lara 1 800.0
# 5 200 Rocco 1 2000.0
# 8 200 Rocco 2 5000.0