There is a cetificate and original.xml
when I try to sign full part of this xml(set url in Reference as ""), I can get the same result in C# and java.
but when I try to sign part of this xml. The SignatureValue is different in java and C#.
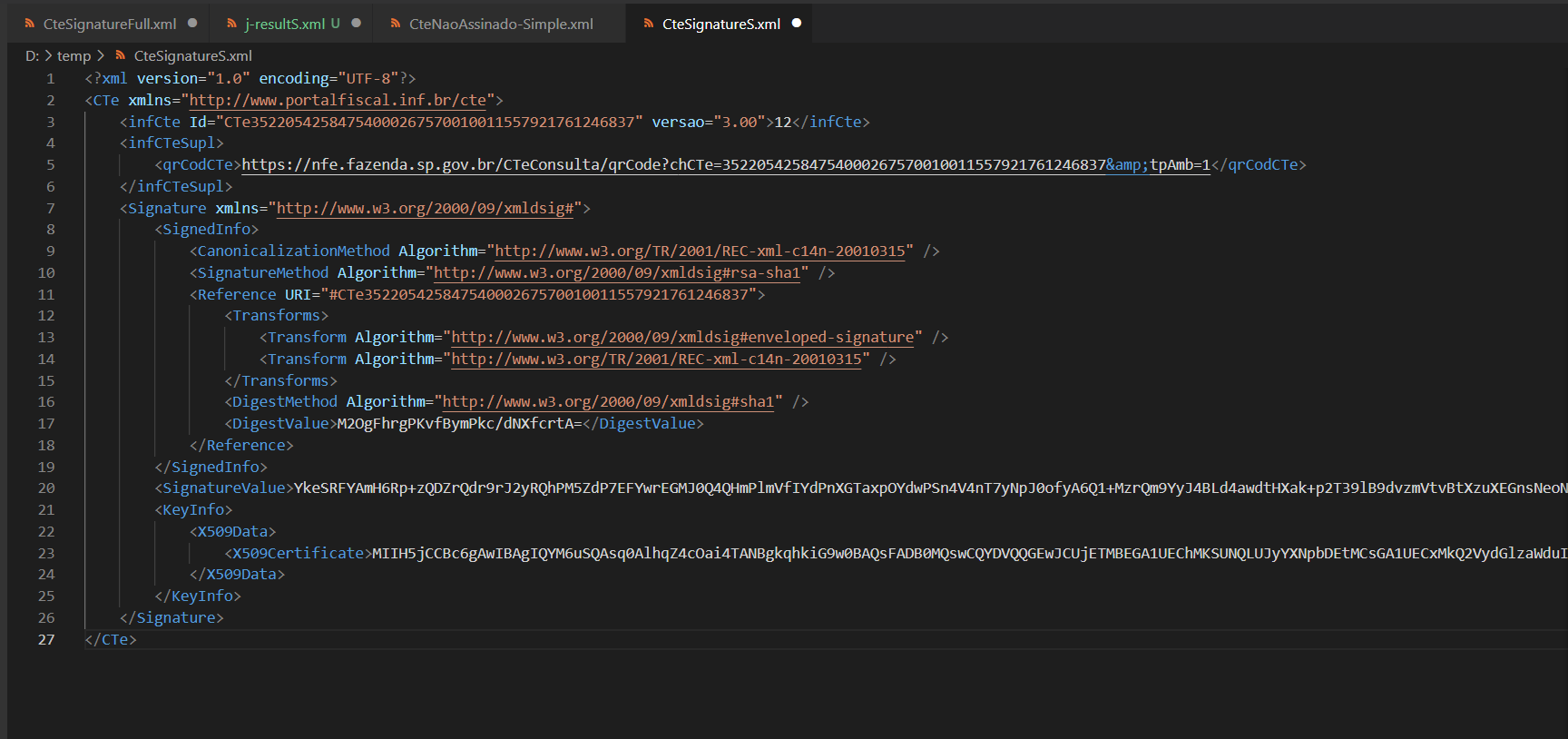
 the
the previous one is signed by C#, the next one is signed by java
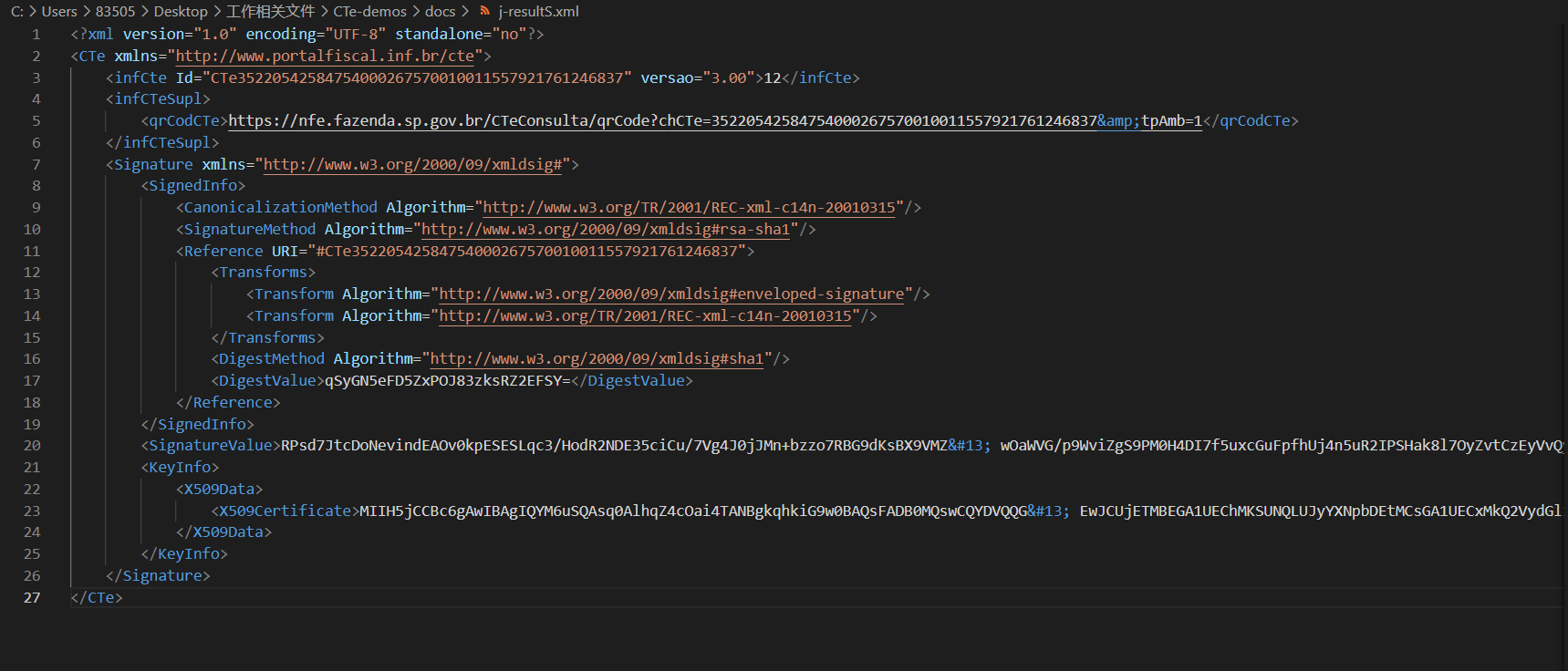
the
the previous one is signed by C#, the next one is signed by java
here is my core code in C#
public static void SignXml(XmlDocument Doc, X509Certificate2 certificado)
{
if (Doc == null)
throw new ArgumentException("Empty XML Document Object ?");
// Estou verificando se o certificado xml é nulo
if (certificado == null)
throw new ArgumentException("Empty certificate ?");
// Variavel do tipo string que recebe a URI padrão para criação do elemeto de assinatura digital XML.
string digestMethod = "http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#sha1";
// Variavel do tipo string que recebe a URI padrão para criação do elemeto de assinatura digital XML.
string signatureMethod = "http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#rsa-sha1";
// Variavel do tipo string que recebe a chave do Ct-e que será usada como URI de referencia para assinatura.
string chaveCTE = "#CTe35220542584754000267570010011557921761246837";
// Classe responsavel para realizar a assinatura do XML.
SignedXml signedXml = new SignedXml(Doc);
// Passamos a chave privada do certificado.
signedXml.SigningKey = certificado.PrivateKey;
// A classe recebe informaçoes padroes da assinatura.
signedXml.SignedInfo.SignatureMethod = signatureMethod;
// Criamos uma referencia para a assinatura, carregamos ela com a chave do CT-e e o padrão de elemento de assinatura digital
Reference reference = new Reference()
{
Uri = chaveCTE,
DigestMethod = digestMethod
};
// Adicionamos uma transformação enveloped à referencia.
XmlDsigEnvelopedSignatureTransform env = new XmlDsigEnvelopedSignatureTransform();
reference.AddTransform(env);
//XmlDsigC14NTransform c14Transform = new XmlDsigC14NTransform();
//reference.AddTransform(c14Transform);
// Adicionamos a referência ao objecto SignedXml.
signedXml.AddReference(reference);
KeyInfo keyInfo = new KeyInfo();
keyInfo.AddClause(new KeyInfoX509Data(certificado));
signedXml.KeyInfo = keyInfo;
// Assinamos.
signedXml.ComputeSignature();
// Extraimos a representação da assinatura em XML
XmlElement xmlDigitalSignature = signedXml.GetXml();
// Juntamos a assinatura XML ao documento.
Doc.DocumentElement.AppendChild(Doc.ImportNode(xmlDigitalSignature, true));
}
here is my code in java
(refer from here)
public static Document signAssertion(Document doc, SAMLKeyStore samlKeyStore) throws Exception {
// Instance main XML Signature Toolkit.
XMLSignatureFactory fac = XMLSignatureFactory.getInstance("DOM");
XPathFactory xPathfactory = XPathFactory.newInstance();
// Retreive PrivateKey and Public Certificate from Specified KeyStore.
PrivateKey privateKey = samlKeyStore.getPrivateKey();
X509Certificate publicCertificate = samlKeyStore.getPublicCertificate();
// Retreive Assertion Node to be signed.
XPath xpath = xPathfactory.newXPath();
XPathExpression exprAssertion = xpath.compile("//*[local-name()='Response']//*[local-name()='Assertion']");
Element assertionNode = (Element) exprAssertion.evaluate(doc, XPathConstants.NODE);
// Must mark ID Atrribute as XML ID to avoid BUG in Java 1.7.25.
assertionNode.setIdAttribute("ID", true);
// Retreive Assertion ID because it is used in the URI attribute of the signature.
XPathExpression exprAssertionID = xpath.compile("//*[local-name()='Response']//*[local-name()='Assertion']//@ID");
String assertionID = (String) exprAssertionID.evaluate(doc, XPathConstants.STRING);
// Retreive Subject Node because the signature will be inserted before.
XPathExpression exprAssertionSubject = xpath.compile("//*[local-name()='Response']//*[local-name()='Assertion']//*[local-name()='Subject']");
Node insertionNode = (Node) exprAssertionSubject.evaluate(doc, XPathConstants.NODE);
// Create the DOMSignContext by specifying the signing informations: Private Key, Node to be signed, Where to insert the Signature.
DOMSignContext dsc = new DOMSignContext(privateKey, assertionNode, insertionNode);
dsc.setDefaultNamespacePrefix("ds");
// Create a CanonicalizationMethod which specify how the XML will be canonicalized before signed.
CanonicalizationMethod canonicalizationMethod = fac.newCanonicalizationMethod(CanonicalizationMethod.EXCLUSIVE, (C14NMethodParameterSpec) null);
// Create a SignatureMethod which specify how the XML will be signed.
SignatureMethod signatureMethod = fac.newSignatureMethod(SignatureMethod.RSA_SHA1, null);
// Create an Array of Transform, add it one Transform which specify the Signature ENVELOPED method.
List<Transform> transformList = new ArrayList<Transform>(1);
transformList.add(fac.newTransform(Transform.ENVELOPED, (TransformParameterSpec) null));
// Create a Reference which contain: An URI to the Assertion ID, the Digest Method and the Transform List which specify the Signature ENVELOPED method.
Reference reference = fac.newReference("#" assertionID, fac.newDigestMethod(DigestMethod.SHA1, null), transformList, null, null);
List<Reference> referenceList = Collections.singletonList(reference);
// Create a SignedInfo with the pre-specified: Canonicalization Method, Signature Method and List of References.
SignedInfo si = fac.newSignedInfo(canonicalizationMethod, signatureMethod, referenceList);
// Create a new KeyInfo and add it the Public Certificate.
KeyInfoFactory kif = fac.getKeyInfoFactory();
List x509Content = new ArrayList();
x509Content.add(publicCertificate);
X509Data xd = kif.newX509Data(x509Content);
KeyInfo ki = kif.newKeyInfo(Collections.singletonList(xd));
// Create a new XML Signature with the pre-created : Signed Info & Key Info
XMLSignature signature = fac.newXMLSignature(si, ki);
signature.sign(dsc);
// Return the Signed Assertion.
return doc;
}
Thanks!
CodePudding user response:
https://stackoverflow.com/a/9219056/14291554
Thanks for this answer!This question trouble me fews of days.It is working.
This solution is just read the xml file and convert it to string, then convert it to xml again.It's very werid.
