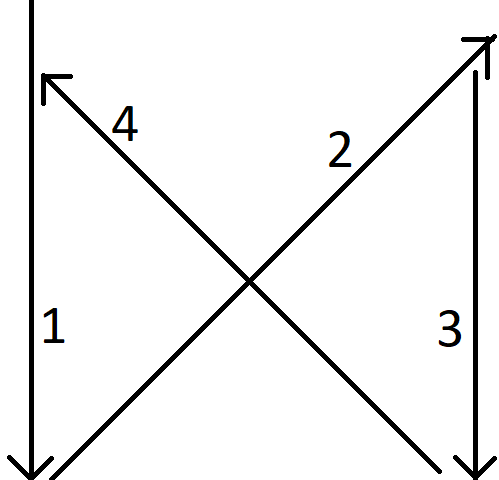
I am working with JavaScript to move an HTML div across the page. Below is the movement that I want the element to follow:
It should be starting and following routes 1, 2, 3 and 4. It should only change the route once the element reaches the max width/height of the page. I am using the below code and I am stuck on how to continue further.
var box = document.getElementById("box");
var height = document.getElementById("container").offsetHeight;
var widht = document.getElementById("container").offsetWidth;
window.setInterval(() => {
let addPosition = (parseInt(box.style.top) 10);
let subPosition = (parseInt(box.style.top) - 10);
if (addPosition > height)
box.style.top = subPosition 'px';
else
box.style.top = addPosition 'px';
}, 100);#container {
position: absolute;
background: purple;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
#box {
position: absolute;
background: red;
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
}<div id="container">
<div id="box" style="top: 0px; left: 0px;"></div>
</div>CodePudding user response:
No JS is needed to make this animation. You can use CSS-Animations for this.
For that, you use keyframes and change the position where the element should move to. You can define the speed with the animation-duration property and repeat it with animation-iteration-count
body {
margin: 0;
height: 100vh;
}
div {
height: 50px;
width: 50px;
background-color: red;
position: fixed;
animation-name: moveBox;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
}
@keyframes moveBox {
0% { top: 0; left: 0; }
20% { top: calc(100% - 50px); left: 0; }
50% { top: 0; left: calc(100% - 50px); }
70% { top: calc(100% - 50px); left: calc(100% - 50px); }
100% { top: 0; left: 0; }
}<div></div>CodePudding user response:
As someone else mentioned, this is normally done with CSS animations, but if you have to use javascript you basically want a state system that keeps track of what your current target is.
Here's roughly how you could do it:
let box = document.getElementById("box");
let height = document.getElementById("container").offsetHeight;
let width = document.getElementById("container").offsetWidth;
let getAngle=function(x1,y1,x2,y2)
{
return Math.atan2(y2-y1,x2-x1);
}
let state=0;
let speed=10;//how many pixels to move per interval
let x=0,y=0;
let xTarget=0,yTarget=0;
window.setInterval(() => {
//we do not account for the box's size here, but if we needed to we could add or subtract it to the target as needed
switch(state) {
case 0:
xTarget=0;
yTarget=height;
break;
case 1:
xTarget=width;
yTarget=0;
break;
case 2:
xTarget=width;
yTarget=height;
break;
case 3:
xTarget=0;
yTarget=0;
break;
}
//do we still have more steps left? calculate the angle to the target, then step in that direction
if (state<4)
{
var angle=-getAngle(x,y,xTarget,yTarget) Math.PI/2;
x =Math.sin(angle)*speed;
y =Math.cos(angle)*speed;
}
//are we close enough to the target? snap to the target, then switch to the next state
//note: you may want to calculate the actual distance here instead
if (Math.abs(xTarget-x)<speed && Math.abs(yTarget-y)<speed)
{
x=xTarget;
y=yTarget;
state ;
}
if (state>=4) state=0;//if you want the movement to loop
box.style.left=x 'px';
box.style.top=y 'px';
}, 100);#container {
position: absolute;
background: purple;
width: 300px;
height: 200px;
}
#box {
position: absolute;
background: red;
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
}<div id="container">
<div id="box" style="top: 0px; left: 0px;"></div>
</div>