I would like to flatten the DF so that what is currently ~8 (depending) rows, into 1 row as the time associated is the same. I only want to overwrite NaN cells.
I'm reading the data in from a premade CSV.
try:
csv = pd.read_csv(csv_path,usecols=lambda c: c in {"Time","Num","MyCols..."})
except ValueError:
print("No Tracking Data")
return
csv = csv.dropna(thresh=2)
This returns a csv of ~20K rows at least.
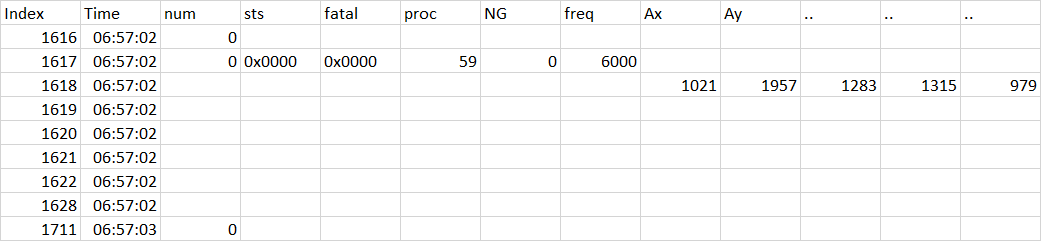
Current format
| index | Time | Num | sts | fatal | proc | NG | Freq | Ax | Ay | .. | .. | .. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 06:50 | 0 | 0x0000 | 0x0000 | 59 | 0 | 6000 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 2 | 06:50 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 1201 | 1957 | 1283 | 1315 | 979 |
| 3 | 06:50 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 4 | 06:50 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
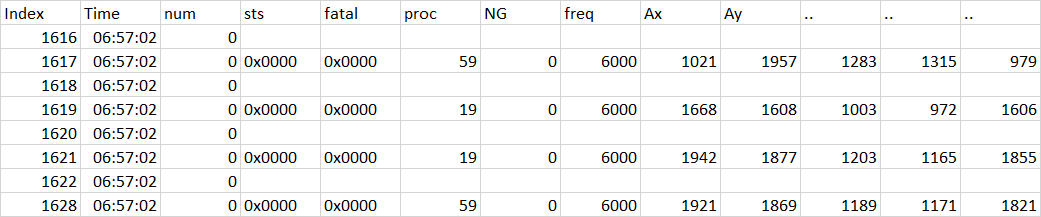
Desired format
| index | Time | Num | sts | fatal | proc | NG | Freq | Ax | Ay | .. | .. | .. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 06:50 | 0 | 0x0000 | 0x0000 | 59 | 0 | 6000 | 1201 | 1957 | 1283 | 1315 | 979 |
| 8 | 06:51 | 0 | 0x0000 | 0x0000 | 59 | 0 | 6000 | 1400 | 1483 | 1260 | 1304 | 965 |
| 16 | 06:52 | 0 | 0x0000 | 0x0000 | 59 | 0 | 6000 | 1501 | 1827 | 1345 | 1340 | 982 |
| 24 | 06:53 | 0 | 0x0000 | 0x0000 | 59 | 0 | 6000 | 1401 | 1462 | 1239 | 1535 | 990 |
v:
Expected Output:
CodePudding user response:
Let's fake some data:
import pandas as pd
data = [
{"time": "06:50", "A": 1}, {"time": "06:50", "B": 2}, {"time": "06:50", "C": 3},
{"time": "06:51", "A": 4}, {"time": "06:51", "B": 5}, {"time": "06:51", "C": 6},
{"time": "06:52", "A": 7}, {"time": "06:52", "B": 8}, {"time": "06:52", "C": 9},
]
frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
It looks like your sample:
time A B C
0 06:50 1.0 NaN NaN
1 06:50 NaN 2.0 NaN
2 06:50 NaN NaN 3.0
3 06:51 4.0 NaN NaN
4 06:51 NaN 5.0 NaN
5 06:51 NaN NaN 6.0
6 06:52 7.0 NaN NaN
7 06:52 NaN 8.0 NaN
8 06:52 NaN NaN 9.0
Then it should be as simple as:
frame = frame.melt(id_vars=["time"]).dropna()
frame = frame.pivot_table(index="time", columns="variable", values="value", aggfunc="first")
Which returns:
variable A B C
time
06:50 1.0 2.0 3.0
06:51 4.0 5.0 6.0
06:52 7.0 8.0 9.0
CodePudding user response:
You could also make use of the built in Python CSV library to parse the data. This would work on the fly and so would also not require much memory.
It works by reading groups of rows with the same Time value and then flattening them into a single output row.
from itertools import groupby
import csv
with open('input.csv') as f_input, open('output.csv', 'w', newline='') as f_output:
csv_input = csv.reader(f_input)
csv_output = csv.writer(f_output)
header = next(csv_input)
csv_output.writerow(header)
for entry_time, input_rows in groupby(csv_input, lambda x: x[1]):
output_row = []
for input_row in input_rows:
if output_row:
for col, value in enumerate(input_row[2:], start=2):
if value not in ['', '--']:
output_row[col] = value
else:
output_row = input_row
csv_output.writerow(output_row)
