I am learning the Java Builder Pattern from Section 6.1 (Builder Pattern Example) at: 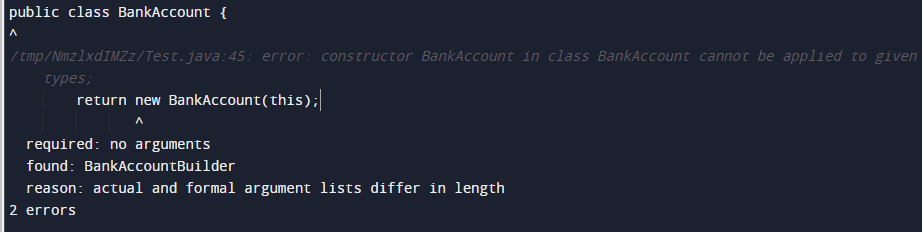
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankAccount newAccount = new BankAccount.BankAccountBuilder("Jon", "22738022275").withEmail("[email protected]").wantNewsletter(true).build();
System.out.print(newAccount);
}
}
public class BankAccount {
private String name;
private String accountNumber;
private String email;
private boolean newsletter;
// constructors/getters
public static class BankAccountBuilder {
private String name;
private String accountNumber;
private String email;
private boolean newsletter;
public BankAccountBuilder(String name, String accountNumber) {
this.name = name;
this.accountNumber = accountNumber;
}
public BankAccountBuilder withEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
return this;
}
public BankAccountBuilder wantNewsletter(boolean newsletter) {
this.newsletter = newsletter;
return this;
}
public BankAccount build() {
return new BankAccount(this);
}
}
}
CodePudding user response:
You are missing the private constructor, something like:
//The constructor that takes a builder from which it will create the object
//the access to this is only provided to builder
private BankAccount(BankAccountBuilder builder) {
this.name = builder.name;
this.accountNumber = builder.accountNumber;
this.email = builder.email;
this.newsletter = builder.newsletter;
}
I assume the article leaves it to the reader in the section that says // constructors/getters on the code.
In addition, not completely related but the System.out.print you have will not print the object but its reference, you don't have a toString() method.
CodePudding user response:
This is probably a duplicate but you just didn't declare a constructor. This code needs a constructor:
public class BankAccount {
private String name;
private String accountNumber;
private String email;
private boolean newsletter;
// constructors/getters
// ** you didn't put anything here **
So just add a constructor
// constructors/getters
private BankAccount( BankAccountBuilder b ) {
// initialize your class here
}
