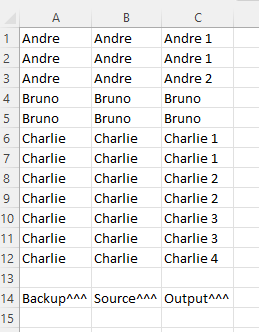
The results I need is shown in this image.
Example using variable rowlimit:
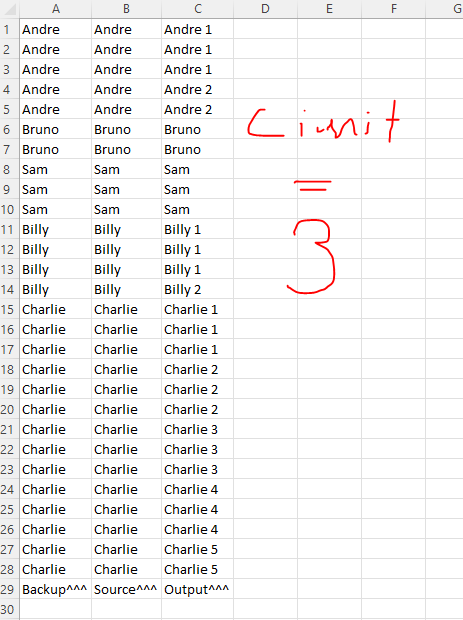
CodePudding user response:
Append Indexes in a Particular Way
Option Explicit
Sub AppendIndexes()
' Define constants.
' Source
Const sName As String = "Sheet1"
Const sFirstCellAddress As String = "B2"
Const sRowLimitCellAddress As String = "D7"
' Destination
Const dName As String = "Sheet1"
Const dFirstCellAddress As String = "B16"
Const dDelimiter As String = " "
' Reference the workbook ('wb').
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook ' workbook containing this code
' Reference the source worksheet ('sws').
Dim sws As Worksheet: Set sws = wb.Worksheets(sName)
' Attempt to store the row limit in a variable ('sRowLimit').
Dim sRowLimit As Long
On Error Resume Next
sRowLimit = sws.Range(sRowLimitCellAddress).Value
On Error GoTo 0
' Validate the row limit.
If sRowLimit < 1 Then
MsgBox "The row limit needs to be an integer greater than 0.", vbCritical
Exit Sub
End If
' Reference the first source cell ('sfCell').
Dim sfCell As Range: Set sfCell = sws.Range(sFirstCellAddress)
Dim srg As Range
' Reference the source (one-column) range ('srg').
With sfCell.CurrentRegion.Columns(sfCell.Column)
Set srg = sfCell.Resize(.Row .Rows.Count - sfCell.Row)
End With
' Note that there are many different ways to do it.
' To see if it is the correct range you can use e.g.:
'Debug.Print srg.Address(0, 0)
' or:
'MsgBox srg.Address(0, 0)
' Store the number of rows of the source range in a variable ('rCount').
Dim rCount As Long: rCount = srg.Rows.Count
Dim Data() As Variant
' Store the values from the source range
' in a 2D one-based one-column array, the data array ('Data').
If rCount = 1 Then
ReDim Data(1 To 1, 1 To 1): Data(1, 1) = srg.Value
Else
Data = srg.Value
End If
' Define a new dictionary (dict).
' Its 'keys' will hold the unique strings from the source range.
' Its 'items' will hold the rows in the unique counts array.
Dim dict As Object: Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
dict.CompareMode = vbTextCompare ' case-insensitive i.e. 'A = a'
' Define the unique counts array ('uCounts'), a 1D one-based array
' with the same number of rows as the number of rows in the data array,
' to hold the count of each unique string.
Dim uCounts() As Long: ReDim uCounts(1 To rCount)
' The size of the array is probably too big but the 'mrCount' variable
' will determine the number of rows of interest, the mapping rows count.
Dim r As Long ' Current Data Array Row
Dim mr As Long ' Current Mapping Row
Dim mrCount As Long ' Current and Final Mapping Rows Count
Dim cString As String ' Current Data Array Value Converted to a String
' Loop through the rows of the data array...
For r = 1 To rCount
' Retrieve the current value from the data array converted to a string.
cString = CStr(Data(r, 1))
' Replace the value with the string.
Data(r, 1) = cString
' Check if the string exists in the 'keys' of the dictionary.
If Not dict.Exists(cString) Then
mrCount = mrCount 1 ' increment the mapping rows count...
dict(cString) = mrCount ' ... and write it to the associated 'item'
mr = mrCount ' retrieve the current mapping row
Else
mr = dict(cString) ' retrieve the current mapping row
End If
' In the current mapping row of the unique counts array,
' increment the number by 1.
uCounts(mr) = uCounts(mr) 1
Next r
' Define the unique indexes array ('uIndexes'), a 1D one-based array
' with the same number of rows as the mapping rows count ('mrCount'),
' to hold the current index.
Dim uIndexes() As Long: ReDim uIndexes(1 To mrCount)
' Loop through the elements of the unique array and for each value
' greater than the row limit, write 1 to it.
For mr = 1 To mrCount
If uCounts(mr) > sRowLimit Then
uIndexes(mr) = 1
End If
Next mr
Erase uCounts
' Define the indexes counts array ('uIndexes'), a 1D one-based array
' with the same number of rows as the mapping rows count ('mrCount'),
' to hold the current indexes count, a number from 1 to the row limit.
Dim iCounts() As Long: ReDim iCounts(1 To mrCount)
Dim iCount As Long ' Current Index Count
Dim uIndex As Long ' Current Unique Index
' Write the resulting strings to the data array.
' Loop through the rows of the data array.
For r = 1 To rCount
' Retrieve the string from the current row of the data aray.
cString = Data(r, 1)
' Retrieve the mapping row for the current string.
mr = dict(cString)
' Retrieve the unique index for the current mapping row.
uIndex = uIndexes(mr)
If uIndex > 0 Then
' Increment the current index count by 1.
iCount = iCounts(mr) 1
' Check if the current index count is greater than the row limit.
If iCount > sRowLimit Then ' it is greater
iCount = 1 ' reset the current index count
uIndex = uIndex 1 ' increment the 'uIndex' by 1, and...
uIndexes(mr) = uIndex ' ... write it to the unique indexes array
'Else ' the current count is not greater than the row limit
End If
iCounts(mr) = iCount ' write the count to the indexes counts array
' Build and write the resulting string to the current row
' of the data array (overwriting the (previous) string).
Data(r, 1) = cString & dDelimiter & CStr(uIndex)
End If
Next r
Erase iCounts
Erase uIndexes
Set dict = Nothing
' Reference the destination worksheet ('dws').
Dim dws As Worksheet: Set dws = wb.Worksheets(dName)
' Reference the first destination cell ('dfCell').
Dim dfCell As Range: Set dfCell = dws.Range(dFirstCellAddress)
' Reference the destination (one-column) range ('drg').
Dim drg As Range: Set drg = dfCell.Resize(rCount)
' Write the strings from the data array to the destination range.
drg.Value = Data
' Clear below.
drg.Resize(dws.Rows.Count - drg.Row - rCount 1).Offset(rCount).Clear
' Inform.
MsgBox "Indexes appeded.", vbInformation
End Sub