Consider the following markup which is also available via this Fiddle:
<!DOCTYPR html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<title>Flex Box Test</title>
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
position: relative;
}
html,
body {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
overflow: clip;
}
header,
div {
border-width: 6px;
border-style: solid;
text-align: center;
overflow: clip;
}
header,
#content,
#footer {
padding: 1em;
}
header {
border-color: #090;
background-color: #0c0;
color: #030;
flex: none;
}
#application_container {
border-color: #c90;
background-color: #fc0;
color: #330;
flex: auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
#sidebar {
border-color: #ccc;
background-color: #fff;
color: #999;
flex: none;
width: 150px;
}
#workbench_container {
border-color: #f3f;
background-color: #f6f;
color: #939;
flex: auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
overflow: clip auto;
}
#content_container {
border-color: #36c;
background-color: #69f;
color: #039;
flex: 1 0 auto;
}
#content {
border-color: #900;
background-color: #c00;
color: #300;
}
#content.small {
min-height: 150px;
}
#content.large {
min-height: 1500px;
}
#footer {
border-color: #999;
background-color: #ccc;
color: #333;
flex: none;
}
</style>
<head>
<body>
<header>The header shall always be visible at the top</header>
<div id="application_container">
<div id="sidebar">This is the sidebar</div>
<div id="workbench_container">
<div id="content_container">
<!-- Toggle the class between "small" and "large" to see the (failing) effect -->
<div id="content" >
This is the real content whose size is unknown in advance.
Hence, it is wrapped into a content container which is at least as large as the actual content,
but can grow such that the footer is at the bottom.
</div>
</div>
<div id="footer">
For small content the footer shall be located at the bottom.
But for large content the footer shall be placed at the end of the content and be scrolled as part of the (pink) workbench container.
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
which should give you the following box layout

The green header at the top and the left sidebar shall always remain at their fixed position of the viewport. The scrollable area shall be the pink box (called workbench_container in the code). As long as the content is small, they footer (grey box) shall be placed at the bottom of the viewable area as shown in the screenshot. But if the content becomes larger, the footer shall be scrolled as part of the pink box.
The markup works as intended for Chrome. But it does not work for Firefox. To test it, toggle the class of div#content between small and large. Firefox does not restrict the height of the pink box, but the height of the pink box grows together with its children (i.e. the content and the footer). Hence, no scrollbar appears.
Firefox shows a scrollbar as soon as div#workbench-container has an explicit (and too small) absolute height, e.g. adding
#workbench_container {
height: 200px;
}
makes a scrollbar appear. But obviously, this is not a solution as I don't know the height in advance. If I set height: 100% nothing changes. According the the CSS specs this should assign the height of the nearest, positioned ancestor which is #application-container.
Is this a Firefox bug or do I miss something? How do make this work in a cross-browser compatible way? If it is a Firefox bug, how do I work around this bug?
As long as the view port is large enough the Firefox Developer tools show something like this:
- Content size: 275px
- Flexibility (element is growable): 18px
- Final size: 293px
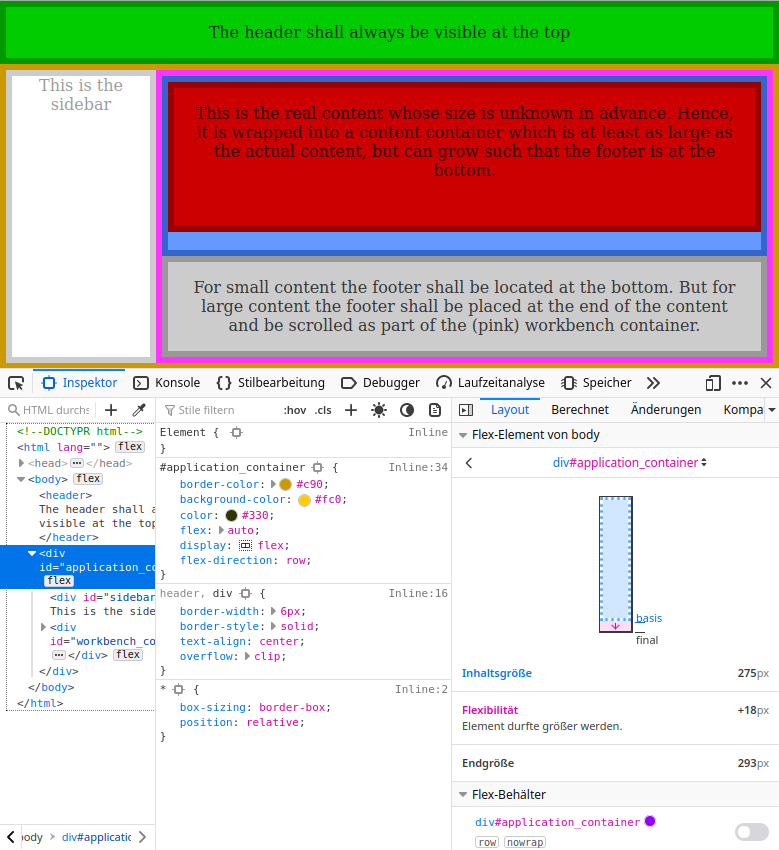
However, in the bad case without sufficient space, we get
- Content size: 275px
- Flexibility (element is shrinkable): -18px
- Minimum size: 275px
- Final size: 275px In other words, the box is not shrinking (why?!) and instead a tiny padlock appears in the Firefox Developer Tools.
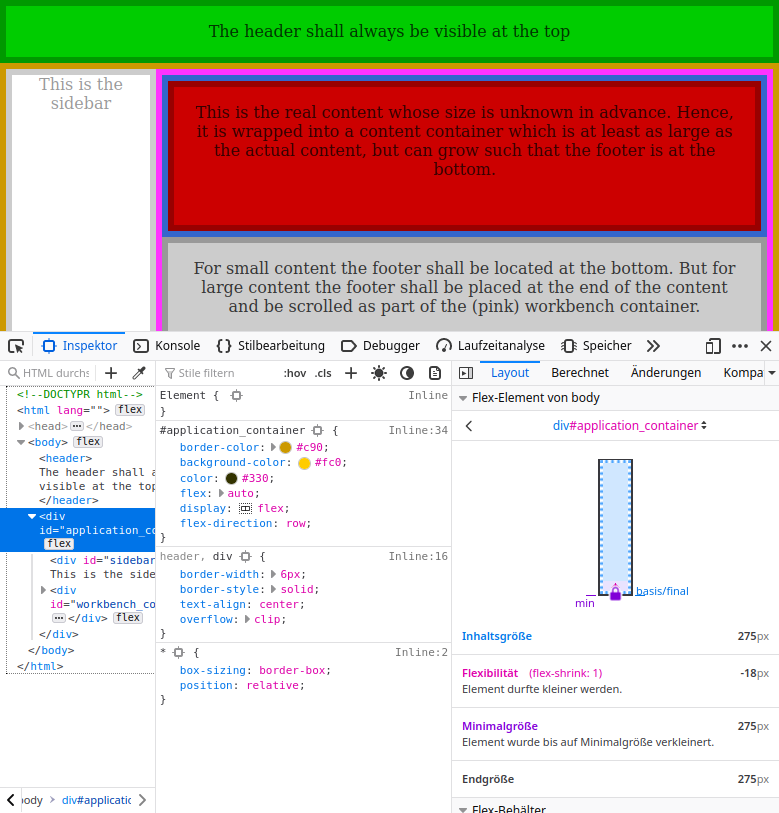
Additional constraints:
- The size of the footer is not known in advance as it shows user-provided content and hence may have several lines of text. Otherwise (if the size would be known), I could imagine a workaround using CSS
calc, which is not an option here.
CodePudding user response:
If I've understood your requirements correctly, all you need to do is to add height: 0 to #application_container.
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
position: relative;
}
html,
body {
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
overflow: clip;
}
header,
div {
border-width: 6px;
border-style: solid;
text-align: center;
overflow: clip;
}
header,
#content,
#footer {
padding: 1em;
}
header {
border-color: #090;
background-color: #0c0;
color: #030;
flex: none;
}
#application_container {
border-color: #c90;
background-color: #fc0;
color: #330;
flex: auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
height: 0;
}
#sidebar {
border-color: #ccc;
background-color: #fff;
color: #999;
flex: none;
width: 150px;
}
#workbench_container {
border-color: #f3f;
background-color: #f6f;
color: #939;
flex: auto;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
overflow: clip auto;
}
#content_container {
border-color: #36c;
background-color: #69f;
color: #039;
flex: 1 0 auto;
}
#content {
border-color: #900;
background-color: #c00;
color: #300;
}
#content.small {
min-height: 150px;
}
#content.large {
min-height: 1500px;
}
#footer {
border-color: #999;
background-color: #ccc;
color: #333;
flex: none;
}<!DOCTYPR html>
<html lang="">
<head>
<title>Flex Box Test</title>
<head>
<body>
<header>The header shall always be visible at the top</header>
<div id="application_container">
<div id="sidebar">This is the sidebar</div>
<div id="workbench_container">
<div id="content_container">
<!-- Toggle the class between "small" and "large" to see the (failing) effect -->
<div id="content" >
This is the real content whose size is unknown in advance.
Hence, it is wrapped into a content container which is at least as large as the actual content,
but can grow such that the footer is at the bottom.
</div>
</div>
<div id="footer">
For small content the footer shall be located at the bottom.
But for large content the footer shall be placed at the end of the content and be scrolled as part of the (pink) workbench container.
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Whether or not this is a Firefox bug is harder. What Firefox is doing is taking the height of the containing block only if it has a definite size, and is using the height value to decide that, even though it's growing under the flex rules.
