I am looking for an elegant way to check if a given index is inside a numpy array (for example for BFS algorithms on a grid).
The following code does what I want:
import numpy as np
def isValid(np_shape: tuple, index: tuple):
if min(index) < 0:
return False
for ind,sh in zip(index,np_shape):
if ind >= sh:
return False
return True
arr = np.zeros((3,5))
print(isValid(arr.shape,(0,0))) # True
print(isValid(arr.shape,(2,4))) # True
print(isValid(arr.shape,(4,4))) # False
But I'd prefer something build-in or more elegant than writing my own function including python for-loops (yikes)
CodePudding user response:
You can try:
def isValid(np_shape: tuple, index: tuple):
index = np.array(index)
return (index >= 0).all() and (index < arr.shape).all()
arr = np.zeros((3,5))
print(isValid(arr.shape,(0,0))) # True
print(isValid(arr.shape,(2,4))) # True
print(isValid(arr.shape,(4,4))) # False
CodePudding user response:
It seems to me that simple
(np_shape > index) and all(ind >= 0 for ind in index)
is equivalent to your isValid function.
CodePudding user response:
Thank you for your answers, I have benchmarked them and it turns out the fastest way is indeed @Dmitri Chubarov 's answed:
def isValid(np_shape: tuple, index: tuple):
return (np_shape > index) and all(ind >= 0 for ind in index)
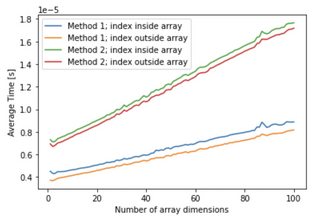
Method 1 by @Dmitri Chubarov, Method 2 by @mozway. Times measured for index inside array and outside array (example: For a 4x4 array, (2,3) is inside, (6,3) is not inside), times averaged over 10'000 inputs. Number of array dimensions is the shape size; for a normal mxn matrix it would be 2.
import numpy as np
import time
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def isValid_1(np_shape: tuple,index: tuple):
return np.all(np_shape > index) and all(ind >= 0 for ind in index)
def isValid_2(np_shape: tuple, index: tuple):
index = np.array(index)
return (index >= 0).all() and (index < np_shape).all()
nExp = 10000
max_dimensions = 100
max_shape_content = 100
dims = []
times_1_valid = []
times_1_invalid = []
times_2_valid = []
times_2_invalid = []
for counter,dimensions in enumerate(range(1,max_dimensions 1)):
print(f"Progress {(1000*counter//max_dimensions)/10}%",end="\r")
dims.append(dimensions)
times_1_valid.append(0)
times_1_invalid.append(0)
times_2_valid.append(0)
times_2_invalid.append(0)
for i in range(nExp):
np_shape = tuple(random.randint(1,max_shape_content) for i in range(dimensions))
valid_index = tuple(random.randint(0,n_i-1) for n_i in np_shape)
invalid_index = list(valid_index);
invalid_index[random.randint(0,dimensions-1)] = max_shape_content 1
invalid_index = tuple(invalid_index)
t0 = time.process_time()
isValid_1(np_shape,valid_index)
t1 = time.process_time()
isValid_1(np_shape,invalid_index)
t2 = time.process_time()
isValid_2(np_shape,valid_index)
t3 = time.process_time()
isValid_2(np_shape,invalid_index)
t4 = time.process_time()
times_1_valid[-1] = (t1-t0)
times_1_invalid[-1] = (t2-t1)
times_2_valid[-1] = (t3-t2)
times_2_invalid[-1] = (t4-t3)
times_1_valid = np.array(times_1_valid) / nExp
times_1_invalid = np.array(times_1_invalid) / nExp
times_2_valid = np.array(times_2_valid) / nExp
times_2_invalid = np.array(times_2_invalid) / nExp
plt.plot(dims,times_1_valid,label="Method 1; index inside array")
plt.plot(dims,times_1_invalid,label="Method 1; index outside array")
plt.plot(dims,times_2_valid,label="Method 2; index inside array")
plt.plot(dims,times_2_invalid,label="Method 2; index outside array")
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel("Number of array dimensions")
plt.ylabel("Average Time [s]")
plt.show()