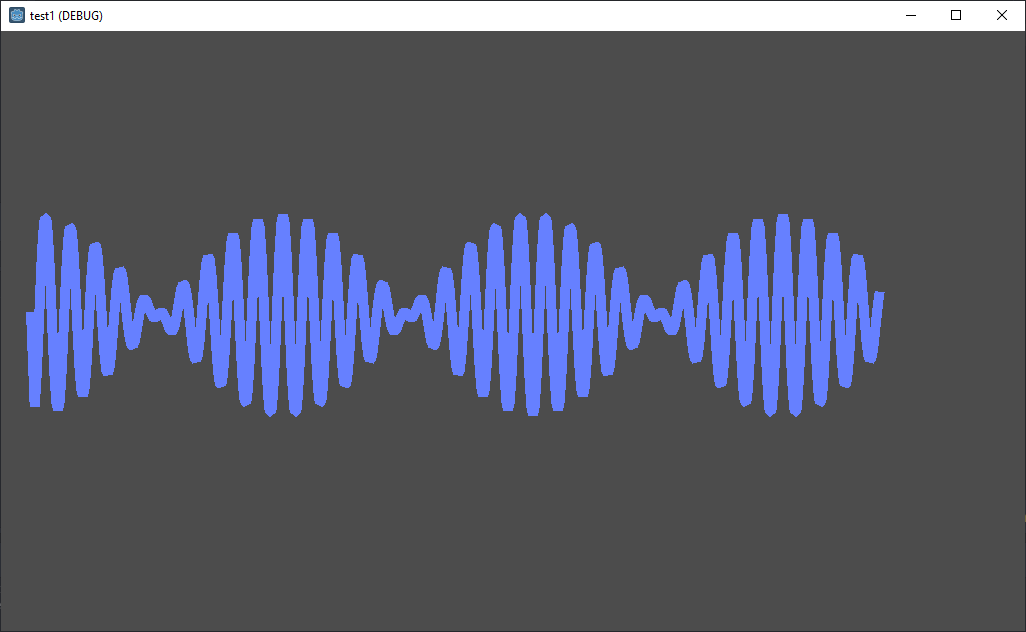
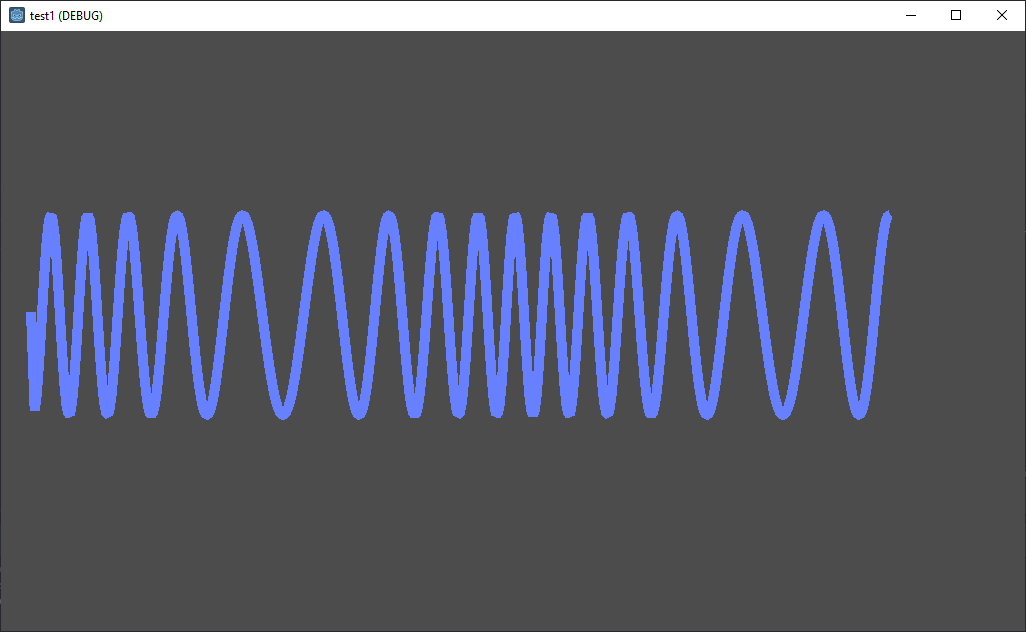
FM Modulation Example
extends Control
var time: float = 0.0
var frequency: float = 2
var modulation_index : float = 4
var modulation_frequency : float = 0.2
const pixels_per_x = 100; # zoom on x
const pixels_per_y = 100; # zoom on y
func _physics_process(delta):
var point : Vector2
time = delta
var fm_signal = cos( (2 * PI * frequency * time) modulation_index*sin(2 * PI * modulation_frequency * time) ) # this is another method that adds offset onto phase
point.y = pixels_per_y * (fm_signal)
point.x = pixels_per_x * (time)
$Line2D.add_point(point)
CodePudding user response:
your AM looks OK to me I see no frequency change and the formula is OK (if your amplitude(time) = 200.0*time). However I see one problem and that is that you "increment" the y = axis which is wrong and should be y= , for the x value its OK.
The FM is wrong, I would expect at least linear interpolation, You need some constrains/constants first:
f0 - min output frequency
f1 - max output frequency
a0 - min value of input signal
a1 - max value of input signal
A(t) - input signal you want to modulate with
B - output amplitude
t - time
then:
// constants
B = 200.0
a0 = 0.0
a1 = amplitude * time_duration
f0 = 1500.0
f1 = 2500.0
---------------------
t = delta
A = amplitude*time
f = f0 (f1-f0)*(A-a0)/(a1-a0)
point.y = B * cos(f * t) * delta
point.x = 100.0 * delta
You might also want to add clamping of f to <f0,f1> ...