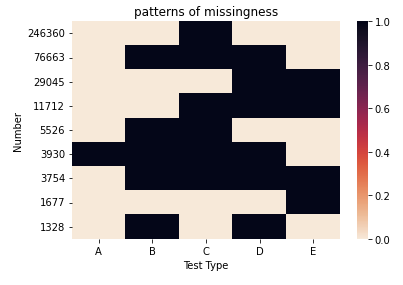
I have the following data:
my_array = array([[0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 1, 1, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0]])
and
df.values = array([246360, 76663, 29045, 11712, 5526, 3930, 3754, 1677,
1328])
I am producing a heat-map as such:
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
cmap = sns.cm.rocket_r
ax = sns.heatmap(my_array, xticklabels=["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"], yticklabels=df.values, cmap = cmap)
ax.set(xlabel='Test Type', ylabel='Number', title='patterns of missingness')
fig=plt.figure(figsize=(40,30), dpi= 20, facecolor='w', edgecolor='k')
fig
My question is, how do I get rid of the continuous color scale and select only two different colors: white for 0 and green for 1?
CodePudding user response:
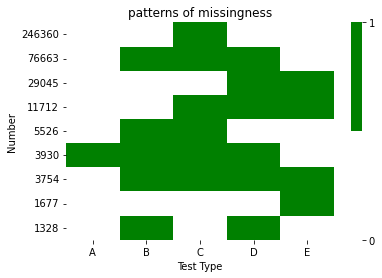
You can do this using a LinearSegmentedColormap rather than the current cmap you're using.
import matplotlib as mpl
cmap = mpl.colors.LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('my_cmap', ['white', 'green'], 2)
Then pass the ticks argument to the cbar_kws argument when you call sns.heatmap:
ax = sns.heatmap(my_array, xticklabels=["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"],
yticklabels=df.values, cmap=cmap, cbar_kws={"ticks":[0,1]})
Which gives:
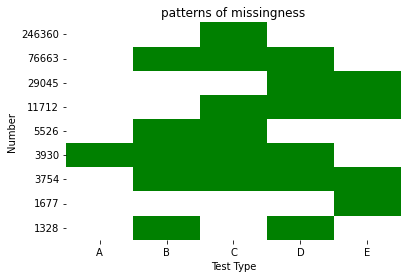
If it's clear what green and white represent, you could also just turn the cbar off altogether with cbar=False.
ax = sns.heatmap(my_array, xticklabels=["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"],
yticklabels=df.values, cmap=cmap, cbar=False)