I have a 5 dimensional ndarray called self.q_table. I've got a regular array, the length of which is 4. When I try to find out the maximum value in that row like this...
max = np.max(self.q_table[regular_array])
...I get an IndexError, even though the elements of regular_array are smaller than the dimensions of q_table.
I tried to alter the dimensions of both arrays, but it didn't get better.
Edit:
The error is IndexError: index 11 is out of bounds for axis 0 with size 10
Numpy is imported as np, and the last line in this sample throws the error.
class AgentBase:
def __init__(self, observation_space):
OBSERVATION_SPACE_RESOLUTION = [10, 15, 15, 15]
self.q_table = np.zeros([*OBSERVATION_SPACE_RESOLUTION, 4])
max_val = np.max(self.q_table[self.quantize_state(observation_space, [-150, 100, 3, 3])])
print(max_val)
@staticmethod
def quantize_state(observation_space, state):
state_quantized = np.zeros(len(state))
lin_spaces = []
for i in range(len(observation_space)):
lin_spaces.append(np.linspace(observation_space[i][0], observation_space[i][1],
OBSERVATION_SPACE_RESOLUTION[i] - 1, dtype=int))
for i in range(len(lin_spaces)):
state_quantized[i] = np.digitize(state[i], lin_spaces[i])
return state_quantized.astype(int)
self.observation_space is a parameter with the following values:
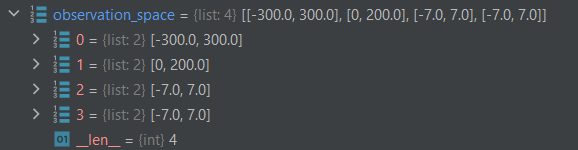
CodePudding user response:
When you index an ndarray with a list (or, to quote the numpy docs, "a non-tuple sequence object"), you invoke advanced indexing, so when you index with [3,7,11,11] it tries to apply all those values to the first dimension.
I agree with @hpaulj’s comment that you may want to index with a tuple instead.
