I just started a VBA course and I am stuck on something probably simple. Starting with this
I am trying find unique combos of letters in a column and copy them to a seperate column. I've used different code, but each time I run it, nothing happens. What end result should look like
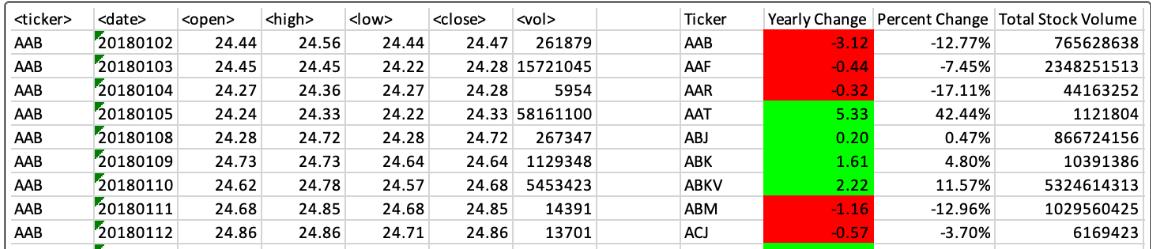
First attempt:
Sub ModChallenge()
'First step, label our terms
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim Ticker As String
'Then cycle through all sheets in book
For Each ws In Worksheets
'Loop for each row to the last row
For i = 2 To LastRow = ws.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
'If the row the loop on one doesn't match the one below it, copy it to a cell
If Cells(i 1, 1).Value <> Cells(i, 1).Value Then
Ticker = Cells(i, 1).Value
Cells(i, 9) = Ticker
Else
End If
Next i
Next ws
End Sub
Second Attempt:
Sub ModChallenge()
'First step, label our terms
Dim ws As Worksheet
Dim Ticker As String
'Then cycle through all sheest in book
For Each ws In Worksheets
'Loop for each row to the last row
For i = 2 To LastRow = ws.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
'If the row the loop on one doesn't match the one below it, copy it to a cell
If Cells(i 1, 1).Value <> Cells(i, 1).Value Then
Cells(i, 9).Value = Cells(i, 1).Value
Else
End If
Next i
Next ws
End Sub
CodePudding user response:
Single-Column Unique Values
Option Explicit
Sub RetrieveUniqueValues()
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook ' workbook containing this code
Dim dict As Object: Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
dict.CompareMode = vbTextCompare
Dim ws As Worksheet, rg As Range, cell As Range, Data(), rKey
Dim r As Long, rCount As Long, rString As String
For Each ws In wb.Worksheets
' Reference the last source cell.
Set cell = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp)
If cell.Row > 1 Then
' Reference the source range.
Set rg = ws.Range("A2", cell)
rCount = rg.Rows.Count
' Write the values from the source range to an array.
If rCount = 1 Then
ReDim Data(1 To 1, 1 To 1): Data(1, 1) = rg.Value
Else
Data = rg.Value
End If
' Write the unique values from the array to a dictionary.
For r = 1 To rCount
rString = CStr(Data(r, 1))
If Len(rString) > 0 Then
dict(rString) = Empty
End If
Next r
rCount = dict.Count
If rCount > 0 Then
' Write the values from the dictionary to the array.
r = 0
ReDim Data(1 To rCount, 1 To 1)
For Each rKey In dict.Keys
r = r 1
Data(r, 1) = rKey
Next rKey
End If
End If
dict.RemoveAll
' Reference the first destination cell.
Set cell = ws.Range("I2")
' Reference the destination range.
Set rg = cell.Resize(rCount)
' Write the values from the array to the destination range.
rg.Value = Data
' Clear below.
rg.Resize(ws.Rows.Count - rg.Row - r 1).Offset(r).ClearContents
Next ws
MsgBox "Unique values retrieved.", vbInformation
End Sub
Microsoft 365
- In Microsoft 365, it becomes much simpler by using the
Uniquefunction. - It will accept an empty string as a unique value though.
Sub RetrieveUniqueValues365()
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook ' workbook containing this code
Dim ws As Worksheet, rg As Range, cell As Range, Data(), r As Long
For Each ws In wb.Worksheets
' Reference the last source cell.
Set cell = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp)
If cell.Row > 1 Then
' Reference the source range.
Set rg = ws.Range("A2", cell)
r = rg.Rows.Count
' Write the unique values from the source range to an array.
If r = 1 Then
ReDim Data(1 To 1, 1 To 1): Data(1, 1) = rg.Value
Else
Data = Application.Unique(rg)
End If
r = UBound(Data, 1)
' Reference the first destination cell.
Set cell = ws.Range("I2")
' Reference the destination range.
Set rg = cell.Resize(r)
' Write the values from the array to the destination range.
rg.Value = Data
' Clear below.
rg.Resize(ws.Rows.Count - rg.Row - r 1).Offset(r).ClearContents
End If
Next ws
MsgBox "Unique values retrieved.", vbInformation
End Sub
Loop
- If the data is sorted, and you want to know how this is achieved by using a loop, you could use the following. This will be less efficient (slower) than the previous versions.
Sub RetrieveUniqueValuesLoop()
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook ' workbook containing this code
Dim ws As Worksheet, rg As Range, sCell As Range, dCell As Range
Dim oStr As String, nStr As String
For Each ws In wb.Worksheets
' Reference the last source cell.
Set sCell = ws.Cells(ws.Rows.Count, "A").End(xlUp)
If sCell.Row > 1 Then
' Reference the source range.
Set rg = ws.Range("A2", sCell)
' Reference the first destination cell.
Set dCell = ws.Range("I2")
' Loop through the source cells.
For Each sCell In rg.Cells
nStr = CStr(sCell.Value)
If Len(nStr) > 0 Then ' is not blank
If nStr <> oStr Then ' new group
dCell.Value = nStr ' write
Set dCell = dCell.Offset(1) ' next destination cell
oStr = nStr ' new becomes old
End If
'Else ' is blank; do nothing
End If
Next sCell
' Clear below.
dCell.Resize(ws.Rows.Count - dCell.Row 1).ClearContents
oStr = vbNullString ' reset for the next iteration (worksheet)
'Else ' no data; do nothing
End If
Next ws
MsgBox "Unique values retrieved.", vbInformation
End Sub
CodePudding user response:
you could use Excel built in RemoveDuplicates() functionality
Option Explicit
Sub ModChallenge()
Dim ws As Worksheet
For Each ws In Worksheets
With ws 'reference current worksheet
.Range("A2", .Cells(.Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp)).Copy Destination:=.Range("I2") ' copy referenced worksheet column "A" cells from row 2 down to last not empty one and paste it from range I2 downwards
.Range("I2", .Cells(.Rows.Count, "I").End(xlUp)).RemoveDuplicates Columns:=Array(1), Header:=xlNo ' remove duplicates from pasted cells
End With
Next
End Sub
