Dynamic host configuration protocol (developed the bootp) DHCP, dynamic host configuration protocol, formerly the bootp protocol, network protocol is a local area network (LAN), use the UDP protocol, the commonly used two port: 67 (DHCP server), 68 (DHCP client),
DHCP is often used in LAN environment, main effect is centralized management, assign IP addresses, give client a dynamic IP address, Gateway address and DNS server address and other information, and can improve address usage, in simple terms, the DHCP is a don't need account password, to network machine automatically assign IP address information such as agreement,
Advantages: convenient management, IP can be recycled in the use of
Disadvantages: can only manage their assigned IP
The/etc/resolve. Conf specifies the DNS server
Nameserver ip_address
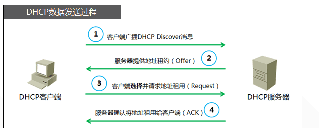
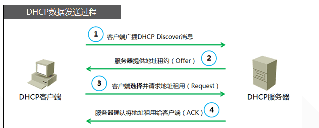
Working principle:
DHCP IP mode, in exchange with the environment to send radio (that is, under the same switches)
DHCP through "lease" to realize the function of dynamically assigned IP, IP time-division multiplexing, so as to solve the problem of IP resource shortages,
There are three kinds of its address allocation:
Manual configuration (by the administrator to specify a address each specific computer),
Automatic configuration (server for the first time a permanent address to connect to the Internet computer allocation)
Dynamic configuration (in a certain period of time will address to the computer at the end of the lease must continue renting or stop using the address) from the customers, for the router, often using the address allocation is dynamic configuration,
2, the two leases table
Static lease table: corresponds to a static lease store file, read from the file server runtime static lease table,
Dynamic lease table: store file corresponds to a period, the server periodically will lease table into the file, at the beginning of the program will read the last store lease list, (the lease table records the current all the assignment of the lease, including static linking),
3, the basic logic
In principle the DHCP SERVER is always in a state of passive to accept the request, when there is a client request, the SERVER will read for the client in the current state and the client's information, and in the static lease tables and dynamic lease item search to find the corresponding table in the table, then according to the state of the client perform different reply, when I received the client's request for the first time, first find static DHCP SERVER leases table; If any request list items, returns the static IP address of the client; Otherwise, the IP addresses from the pool of choices available IP assigned to the customer, and adding information to the dynamic database, in addition, the server will be periodic refreshes the lease write file, in this process will lease inspections of dynamic lease table, by the way,
Do reply:
DHCPOFFER:
Static rent:
First match the MAC address, look to whether can find the corresponding item in the table in the static lease, if you can find the IP assigned to him, static IP cannot be used by other customers in the table,
Dynamic rent:
1. Server attempts to assigned to the client last time distribution over IP, before that, check whether the IP is used,
2. Discover is contained in the request IP, check whether the IP in the address pool, and is being used, whether due, whether static IP, whether already exists on the network,
3. Discover excluding request IP, from a pool of addresses for a minimum of available IP allocation,
? DHCPACK: according to whether containing request IP and server IP to identify the client now init_reboot, selecting, renewing/rebinding which of the state, and according to the following rules perform DHCPACK reply:
1. If the client is in selecting position, verify whether the request IP and server IP with the server match,
2. If the client is in a state init_reboot, validation request IP is in line with the lease record,
3. If the client is in renewing/rebinding condition, verify the client IP address is in accordance with the lease record,
? DHNAK:
1. The requested IP is static IP, but cannot be corresponding MAC address,
2. Above the DHCPACK validation fails,
? Server may also receive other packages:
DHCPDECLINE: server will lease related client hardware address blank in the table, and save this address for a period of time,
DHCPRELEASE: recycling of empty lease IP,
DHCPINFORM: reply DHCPACK, packet contains information about the server,