The mission complete time: April 28, 2020,
Author: Qiu Qingjing
Development tools and key technology: Supermap & amp; & The basic concept of Supermap
Display effects: the basic concept of Supermap
~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~
The content of the article is about the basic concept of supermap, divided into eight: the software is used by supermap iDesktop 9 d)
A, work space
A)
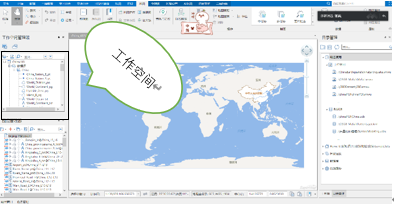
B) it is used to store the user workspace a work environment, it includes the data source (in the data source and data sets), maps, layout, 3 d scene, etc.; And there are two way, saved the file holds (*. Sxwu, *. Smwu, *. SXW, *. SMW method, holds in database (SQL Server, Oracle)
Second, the data source
A)
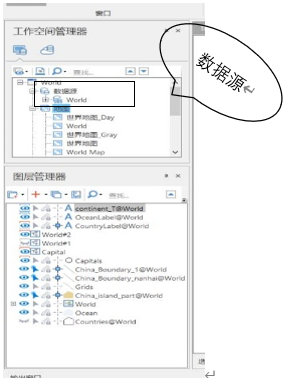
B) it has talked about the data source in work space, and the data source is consists of various types of data sets in a data source can have one or more types of data sets, it also includes vector data and raster data;
C) data source preservation mode and work space has two kinds: data are stored in files (*. Udb/udd) are stored in the database (SQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, DB2, BeyonDB)
Three, the data collection of
A)
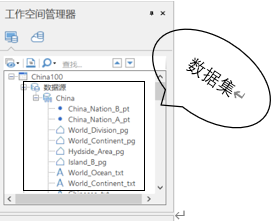
B) there is mentioned in the data source data sources are of various types of data sets, so there was no data set corresponding physical storage file, its physical storage in the corresponding data source, and the data set is the same type of data collection, according to the storage structure is divided into vector data and raster data
C) there are many types of data sets:
Point data sets, line data set, data sets, pure attribute data set, the network data sets, a composite data set (CAD), text data sets, routing data sets, image data sets, raster datasets, such as
Four, the layer
A)
B) layer is data collection display mode, the data set object for a certain style is added to the map window layer, the layer is the spatial data organization according to the project in the vertical direction of a means of thematic map is also to preservation and management layer way
Five, map
A)
B) in the above small squares to select a map, right-click the selected drag map will be displayed in large squares,
C) one or more 2 d data set is given a certain style, in the same map window display, became a map, map layer and will be with the change of the content of data sets and dynamic update, it is through the working space in the form of file or database physical storage, so save a map to save working space,
Six, the layout
A) place a picture or more maps in the layout window, and add other aided drawing elements, as shown in figure, illustrations, maps than scale and so on, became the layout, as dependent on its save working space of preservation,
Seven, 3 d
A)
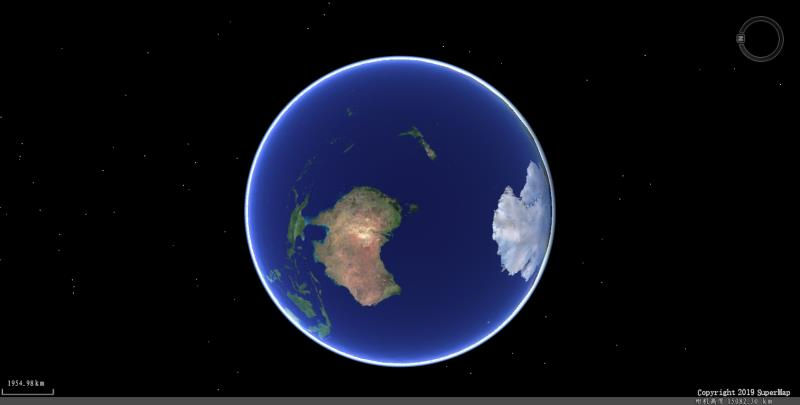
B) the three-dimensional scene to 2 d point \ 3 d points, 2 d line \ 3 d line, text, DEM, the GRID, model (*, *. The 3 ds, SGM), image data real time 3 d browsing; Two 3 d integration display and management, it's save is also depend on the working space of save,
Eight, resource
A) symbol
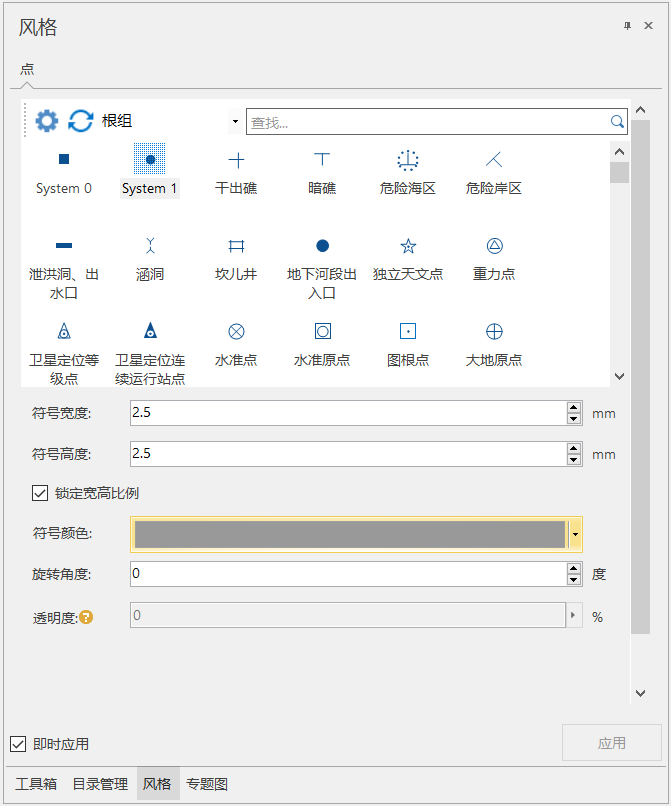
B) line filling
C) filling