Say there are these tables:
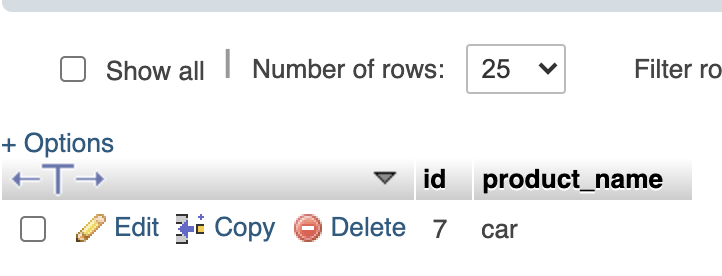
product
-----
id
product_name
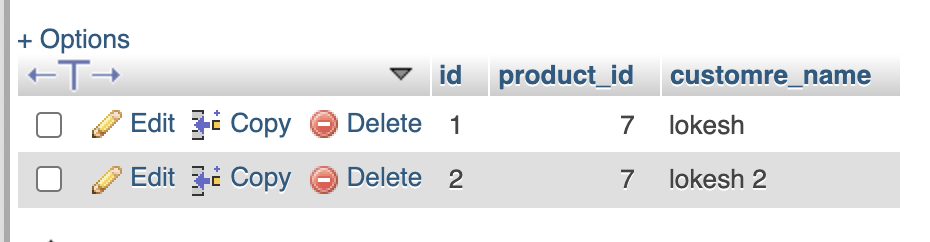
leads
-----
id
product_id
customer_name
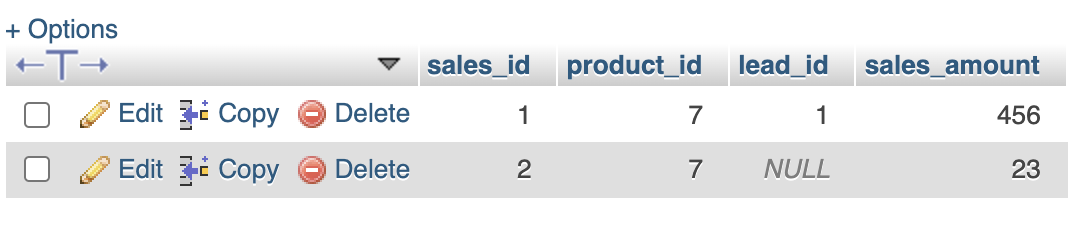
sales
-----
id
product_id
lead_id <- can be null
sales_amount
Not all sales will come from a lead. Not all leads will have any sales.
I want a list of all combined sales and leads together.
Something like: given a product_id = 7
Give me all sales and leads for product_id 7
product_id lead_id sale_id
---------- ------- -------
7 101 501
7 102 NULL
7 NULL 502
I tried a select on leads with a FULL OUTER JOIN and a WHERE below
FULL OUTER JOIN on sales ON leads.id = sales.lead_id
WHERE clause product_id=7 and leads.product_id=sales.product_id,
but I got fewer results than were in the leads or sales tables.
Hope that's clear enough.
Thanks in advance
CodePudding user response:
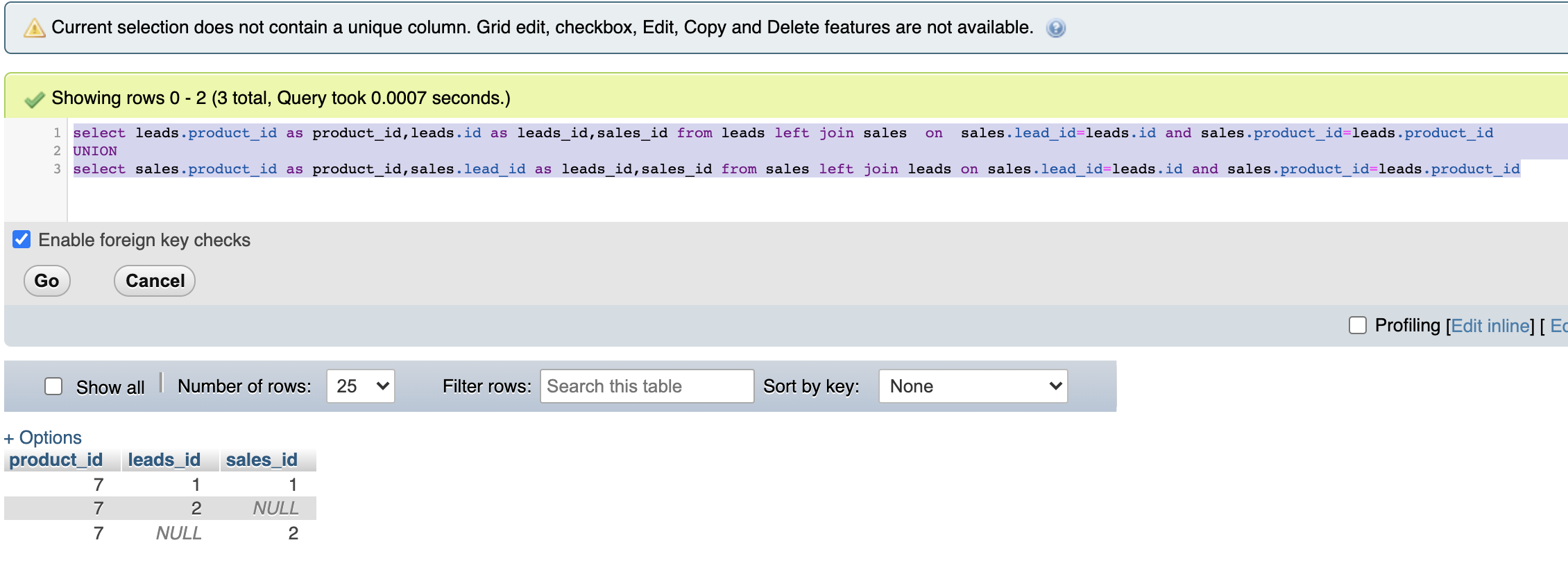
Looks like you want the union of two different queries.
I tried to simulate the all the tables below are the screenshots:
You can use union operator to join outcomes of two different queries. In this case query will be :
select leads.product_id as product_id,leads.id as leads_id,sales_id from leads left join sales on sales.lead_id=leads.id and sales.product_id=leads.product_id UNION select sales.product_id as product_id,sales.lead_id as leads_id,sales_id from sales left join leads on sales.lead_id=leads.id and sales.product_id=leads.product_id
This will give the expected result :
CodePudding user response:
If you UNION ALL the sales with the leads that have no sales, then you get both.
Sample data
create table product ( id serial primary key, product_name varchar(30) not null ); insert into product (product_name) values ('apple'), ('egg'), ('bacon') , ('milk'), ('carrot'), ('tomato') , ('cheese'), ('bean'), ('grape') ; create table leads ( id int primary key, product_id int not null, customer_name varchar(30) not null, foreign key (product_id) references product(id) ); insert into leads (id, product_id, customer_name) values (101, 7, 'john doe') , (102, 7, 'jane doe') , (103, 1, 'bob modest') ; create table sales ( id int primary key, product_id int not null, lead_id int, sales_amount decimal(10,2), foreign key (product_id) references product(id), foreign key (lead_id) references leads(id) ); insert into sales (id, product_id, lead_id, sales_amount) values (501, 7, 101, 12) , (502, 7, null, 4) ;
Query
with cte_products as ( select id as product_id from product where product_name = 'cheese' ) select product_id, lead_id, sale_id from ( -- sales with or without leads select sale.product_id , sale.lead_id , sale.id as sale_id from sales as sale join cte_products using (product_id) union all -- leads without sales select lead.product_id , lead.id as lead_id , null as sale_id from leads as lead join cte_products using (product_id) where not exists ( select 1 from sales sale where sale.product_id = lead.product_id and sale.lead_id = lead.id ) ) q
But FULL JOIN also works
with cte_products as ( select id as product_id from product where product_name = 'cheese' ) select product_id, lead_id, sale_id from ( select coalesce(sale.product_id, lead.product_id) as product_id , lead.id as lead_id , sale.id as sale_id from sales as sale full join leads as lead on lead.id = sale.lead_id join cte_products cte on cte.product_id in (sale.product_id, lead.product_id) ) q;
| product_id | lead_id | sale_id |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | 101 | 501 |
| 7 | null | 502 |
| 7 | 102 | null |
Demo on db<>fiddle here