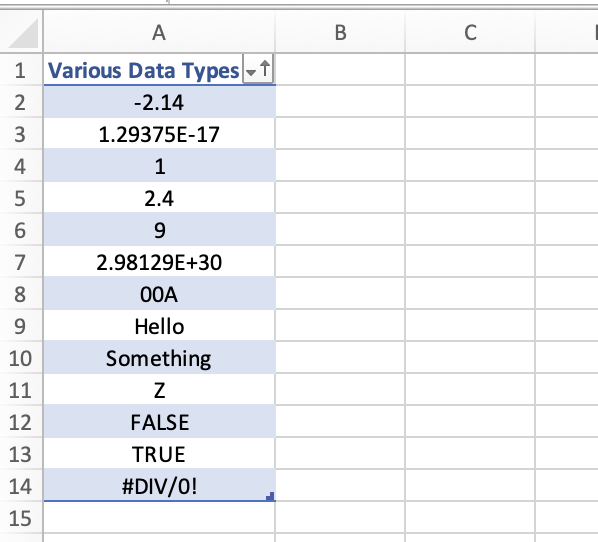
Conceptually, I would like to sort data of a single column of variant type, similar to how this is done in Excel:
Here we can see that Numbers are sorted before Strings before Booleans before Errors. So, I would like to have a function that works like this in SQL:
SELECT * FROM table ORDER BY
CASE WHEN type='number' THEN 0 WHEN type='string' THEN 1 /* ... */ END,
SortFunction(variantData)
Here is what I'd like to accomplish:
- The
SortFunctionneeds to return a value of a single data type, for example, a string, or a number, or a binary type. - I am fine limiting the length of a text field in the function, if that is necessary (for example, if we have a string that is 10,000 characters, just limiting it to the first 100 characters).
Any programming language is fine, I'm more concerned just about a technique to accomplish this Excel-like sorting.
For a numeric field, we can keep it as-is, for a date/time-related field we can do a unix timestamp, but how would we do it for a string or binary data type?
CodePudding user response:
Consider each element as byte array and apply the Comparator:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class SortAnyObjects {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object[] arr = {1, 'c', '&', "z", "testing", "hello world", '文',
'å'};
byte[][] a = new byte[arr.length][]; // <---- The column is not initialized
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i ) {
if (arr[i] instanceof Integer) {
a[i] = String.valueOf((int) arr[i]).getBytes();
}
else if (arr[i] instanceof Character) {
a[i] = String.valueOf((char) arr[i]).getBytes();
}
else { // <---- Here expand your else condition as you expect the datatypes
a[i] = ((String) arr[i]).getBytes();
}
}
Arrays.sort(a, new Comparator<byte[]>() {
@Override
public int compare(
final byte[] o1,
final byte[] o2
) {
if (o1 == null) {
return 1;
}
if (o2 == null) {
return -1;
}
if (o1 == o2) {
return 0;
}
if (o2.length > o1.length) {
return compare(o2, o1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < o1.length; i ) {
if (o1[i] == o2[i]) {
continue;
}
return Byte.compare(o1[i], o2[i]);
}
return 0;
}
});
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ) {
System.out.println(new String(a[i]));
}
}
}