I have an input image of a fully transparent object:
I need to detect the 42 rectangles in this image. This is an example of the output image I need (I marked 6 rectangles for better understanding):
The problem is that the rectangles look really different. I have to use this input image. How can I achieve this?
Edit 1: Here is a input image as png:
CodePudding user response:
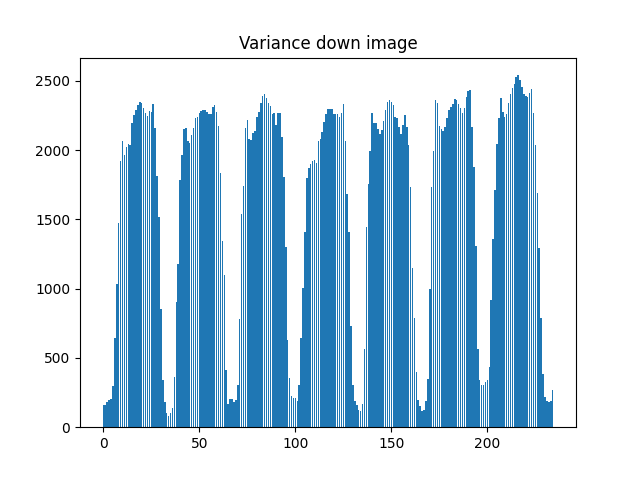
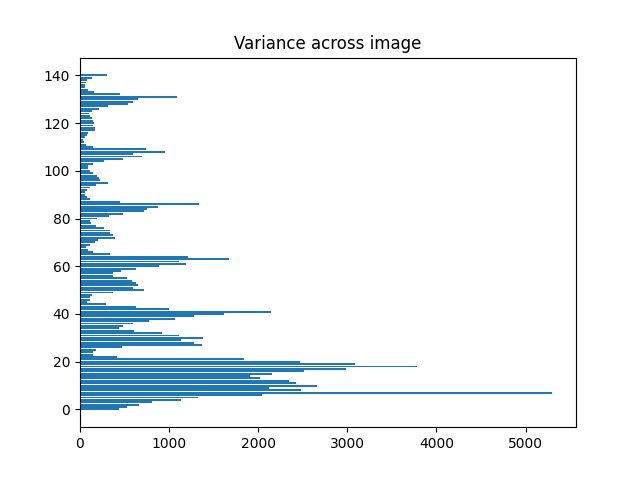
If you calculate the variance down the rows and across the columns, using:
import cv2
import numpy as np
im = cv2.imread('YOURIMAGE', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
# Calculate horizontal and vertical variance
h = np.var(im, axis=1)
v = np.var(im, axis=0)
You can plot them and hopefully locate the peaks of variance which should be your objects:
CodePudding user response:
Mark Setchell's idea is out-of-the-box. Here is a more traditional approach.
Approach:
The image contains boxes whose intensity fades away in the lower rows. Using global equalization would fail here since the intensity changes of the entire image is taken into account. I opted for a local equalization approach in OpenCV this is available as 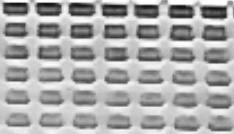
Notice the image above, the boxes in the lower regions appear slightly darker as expected. This will help us later on.
# apply Otsu threshold
r,th_cl = cv2.threshold(cl, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# dilation performed using vertical kernels to connect disjoined boxes
vertical_kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (1, 3))
dilate = cv2.dilate(th_cl, vertical_kernel, iterations=1)
# find contours and draw bounding boxes
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dilate, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
img2 = img.copy()
for c in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area > 100:
x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
img2 = cv2.rectangle(img2, (x, y), (x w, y h), (0,255,255), 1)
(The top-rightmost box isn't covered properly. You would need to tweak the various parameters to get an accurate result)
Other pre-processing approaches you can try:
- Global equalization
- Contrast stretching
- Normalization