I am trying to train a very basic linear regression model to predict a linear equation Y = m*X c
The Weight parameter is optimized to 5 but the Bias parameter is stuck at 0. Am I doing something wrong?
X = np.array(range(1,1000))
Y = 5 * X 7
def forward(W, X ,b):
return W * X b
def getcost(Y, y):
return np.sum((Y-y)**2) / 1000
def backward(W, b, X, Y, y, lr):
dW = -2 * np.dot((Y-y).T, X) / 1000
db = -2 * np.sum(Y-y) / 1000
W -= lr * dW
b -= lr * db
return W, b
W = 0.0
b = 0.0
for i in range(80):
y = forward(W, X ,b)
cost = getcost(Y, y)
W, b = backward(W, b, X, Y, y, lr=0.000001)
print(int(cost), W, b)
CodePudding user response:
The range of X is too extensive since X and Y have a linear relationship the model can be trained on a small range of values. The learning rate is very small it will take much more time to converge since your input set is very big. If you really want to use the same data then You can normalize X.
X = np.array(range(1,30))
Y = 5 * X 7
# Normalize the X values
#X = (X - np.mean(X)) / np.std(X)
N = len(Y)
learning_rate = 0.001
# Initialize the model with the correct values for m and b
m, b = 0.0, 0.0
errors = []
for p in range(8000):
hyp = m * X b
error = Y - hyp
m_gradient = -(2/N) * np.sum(X * error)
b_gradient = -(2/N) * np.sum(error)
m = m - learning_rate * m_gradient
b = b - learning_rate * b_gradient
errors.append(np.mean(error ** 2))
if p@0==0:
print(f'm={m} b={b} ' )
# prediction for x = 231 , y should be 5*200 7 = 1007
print( m*200 b)
plt.plot(errors)
#
plt.xlabel('Iteration')
plt.ylabel('Error')
plt.show()
CodePudding user response:
I agree with @Ahsan Nawaz The only changes I made are -
- Scaled your features (for otherwise, increasing the learning_rate gave NANs)
- Increased the learning rate
- Increased the number of epochs
Here is your code modified -
import numpy as np
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
X = np.array(range(1,1000))
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(X.reshape(-1,1))
X = scaler.transform(X.reshape(-1,1)).reshape(-1)
Y = 5 * X 7
def forward(W, X ,b):
return W * X b
def getcost(Y, y):
return np.sum((Y-y)**2) / 1000
def backward(W, b, X, Y, y, lr):
dW = -2 * np.dot((Y-y).T, X) / 1000
db = -2 * np.sum(Y-y) / 1000
W -= lr * dW
b -= lr * db
return W, b
W = 0.0
b = 0.0
for i in range(8000):
y = forward(W, X ,b)
cost = getcost(Y, y)
W, b = backward(W, b, X, Y, y, lr=0.001)
print(int(cost), W, b)
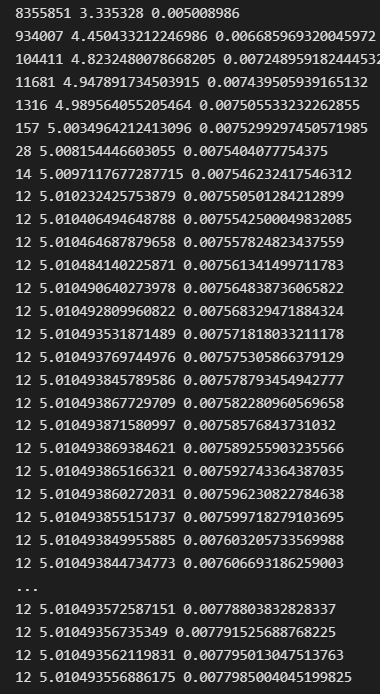
Here is the final output -
0 4.999999437318114 6.999999212245364