I am fairly new to matplotlib and I am creating a dashboard for an IoT application where I want to plot data from multiple sensors. I wrote a simple script that reads data from a CSV file and plots it in a line graph just for a test. But as the data goes on plotting, the graph starts to squeeze together. Eventually, it becomes so clustered it's hard to distinguish.
Here is my code (In this code instead of reading from CSV file, I am generating random data)
from matplotlib import animation, pyplot as plt
from itertools import count
import random, pandas as pd
# Setting Styles
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
x_vals = []
y_vals = []
index = count()
def animate(i):
x_vals.append(next(index))
y_vals.append(random.randint(0, 5))
plt.cla()
plt.scatter(x_vals, y_vals)
plt.plot(x_vals, y_vals)
anime = animation.FuncAnimation(plt.gcf(), animate, interval=400)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
This is what output looks like after a while
Is there a way to automatically expand the x-axis or scroll to the last plot in the x-direction (meaning scroll horizontally)?
CodePudding user response:
This solution is based (lifted (stolen?)) from two examples in Matplotlib's gallery:
- https://matplotlib.org/stable/gallery/animation/animate_decay.html
- https://matplotlib.org/stable/gallery/animation/simple_scatter.html
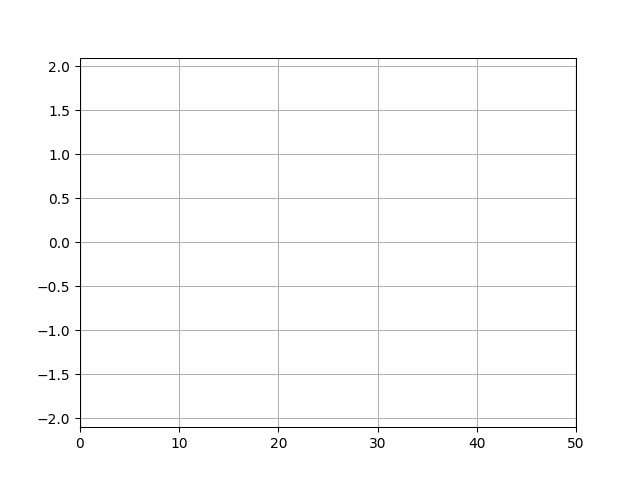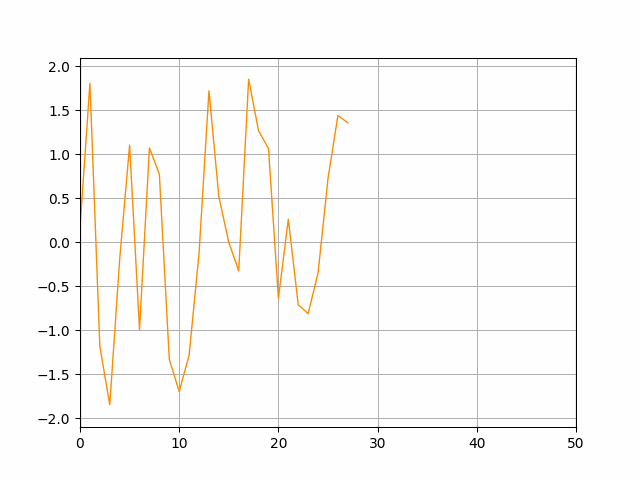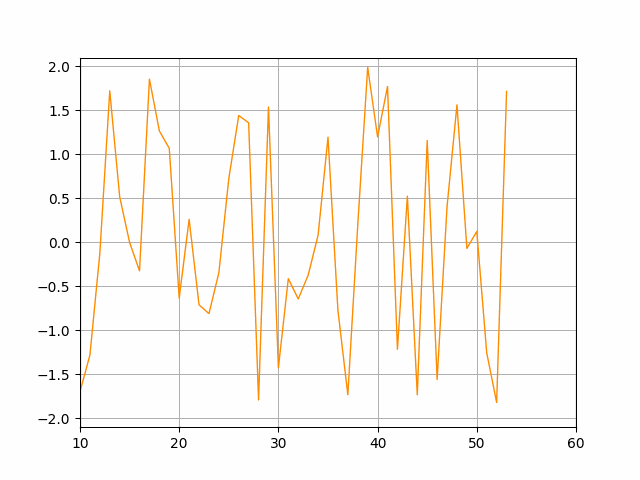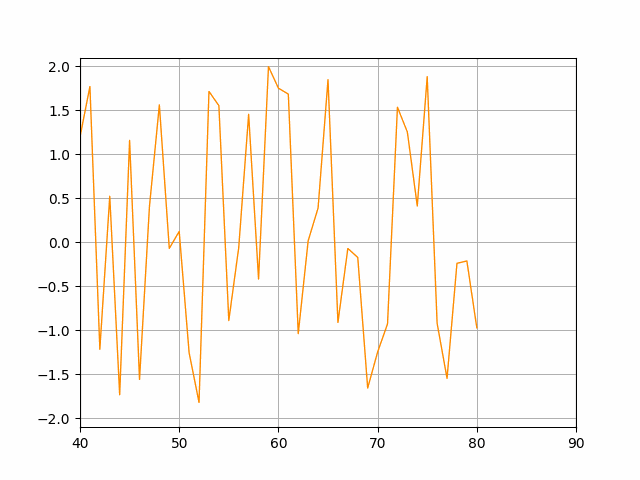
The idea is to keep the number of data points shown at each time limited (here it's limited to 51 points) moving the x-axis limits when we reach the maximum.
Maybe it's not what you want, if not just tell me and I'll remove my answer :-(
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.animation# as animation
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.grid()
# note that line, xdata, and ydata are global
line, = ax.plot([], [], lw=1, color='darkorange')
xdata, ydata = [], []
def new_data():
for t in range(81):
yield t, np.random.rand()*4-2
def initial_frame():
ax.set_ylim(-2.1, 2.1)
ax.set_xlim(0, 50)
del xdata[:]
del ydata[:] # erase the eventual contents
line.set_data(xdata, ydata)
return line,
def update_plot(data):
t, y = data
xdata.append(t)
ydata.append(y)
tmin, tmax = ax.get_xlim()
if t >= tmax:
tmin = tmin 10
tmax = tmax 10
ax.set_xlim(tmin, tmax)
ax.figure.canvas.draw()
line.set_data(xdata, ydata)
return line,
# you may want to remove saving stuff and add plt.show() at the end
writer = animation.PillowWriter()
animation.FuncAnimation(
fig, update_plot, new_data, initial_frame,
repeat=False).save('x_advance.gif', writer=writer)