Intrinsic semiconductor characteristic: the electronic concentration=hole concentration, carrier (electronic + holes), poor electrical conductivity,
P type semiconductor: in pure silicon crystal with trivalent elements such as boron, boron outer three outer electrons of the atoms and the four price of silicon atoms form a covalent bond, will produce a "hole", the hole may attract bound electron to "fill", make the boron atom becomes negatively charged ions, formation of p-type semiconductor, P type semiconductor, holes for many children, free electrons to Jane, mainly by hole conduction,
N-type semiconductor: price in pure silicon crystal with five elements, such as phosphorus, phosphorus atoms in the outer layer of the five electronic four and four price of silicon atoms form covalent bond, an electron to become more free electrons, the formation of n-type semiconductor, n-type semiconductor, free electrons for many children, holes for Jane, mainly by free electron conduction,
: PN junction near the interface due to the electrons and holes (children) concentration, the holes from the p-type semiconductor spreading n-type semiconductor, electronics from the n-type semiconductor spreading p-type semiconductors, compound cavity electronic meet, carrier disappeared, resulting in the junction area near the interface without carrier, for a short distance of fixed charged ions only distributed in space, known as the space charge area, form the space electric field, electric field in the space, the number of Jane to drift, in the absence of electric field under the action of excitation, such as diffusion movement participation is equal to the number of children participate in the number of Jane drift motion, so as to achieve dynamic balance, form a p-n junction,
If P type the positive side, N the cathode side, current from the side of P type, flow to the N type, both holes and electrons from moving interface, make the space charge region of the narrowing, even disappear, the electric current can pass, if N applied voltage of the positive side, P type the cathode side, are both holes and electrons to away from the direction of the interface, make the space charge area wide, electric current cannot flow through,
The characteristics of PN junction: with unidirectional conductivity,
2. Diode
Diode is transmitted only in the direction of a current of electronic components, is one kind has one parts box joint of the two terminals of the device, according to the direction of the applied voltage, the nature of the current flow or no flow within the two lead terminal lead a p-n junction, according to the direction of the applied voltage, the electronic device with unidirectional conductivity,

3. Triode
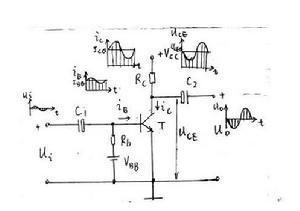
On a semiconductor substrate within easy reach of making two p-n junction, the whole piece of semiconductor two PN junction is divided into three parts, the middle section is the base area, on both sides of the part is the emitter and collector area, three lead terminal lead, triode PNP and NPN according to the arrangement, for NPN transistors, it is made of two pieces of n-type semiconductor with a middle of p-type semiconductor, p-n junction formed between the launch area and area known as the emitter junction, base and collector area and the formation of PN junction as collector knot, three lead respectively referred to as the emitter, the base and the collector,
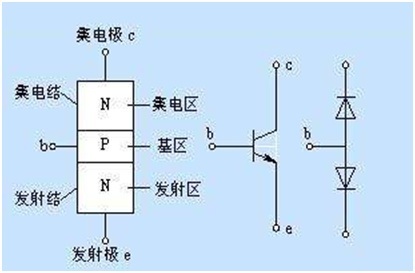
When b point potential higher than e point potential zero a few volts, launch junction is in forward bias condition, point potential higher than b and c point potential zero a few volts, collector junction in the partial state, the collector power Ec is higher than the base power Eb,
That is to say, in the base supplement a small current Ib, you can get a larger on collector current Ic, the so-called current amplification effect,
Triode current amplification effect in fact is to use small changes in the base current to control the great changes of the collector current,
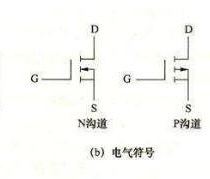
4. Field effect tube
Field effect tube by majority carrier to participate in conduction, also known as unipolar transistor,
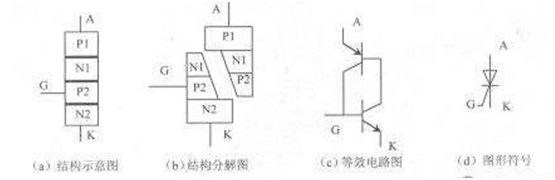
5. Thyristor
Thyristor is PNPN four layers of semiconductor structure, it has three pole: the anode (A) and cathode (K) and gate (G)
Thyristor anode and the forward voltage, only under the condition of the gate and forward voltage thyristor conduction, thyristor in are to the state at this moment, this is the gate flow characteristics of thyristor, namely controllable feature,
Thyristor anode add reverse voltage, no matter which kind of voltage, gate under thyristor is in reverse blocking state,
Thyristor in conduction case, as long as there is a certain positive anode voltage, however, the gate voltage thyristor conduction, namely the thyristor turn-on, after gate loss function, gate triggering role only,
Thyristor in conduction case, when the main circuit of voltage (or current) to close to zero, thyristor turn-off,
Analog circuit 6.
Dealing with electronic circuit of the analog signal,
"Analog" refers to the voltage (or current) for real signal proportional representation,
Basic analog circuit to solve two big aspects: 1, 2 signal source, when the image information and voice information changes, the signal waveform also change, namely the analog signal to the spread of the information contained in its waveform, analog signal is continuous,
The basic principle of amplifying circuit and analysis methods: 1. The principle: single pipe common emitter amplifier circuit; Bipolar transistors of the three sharing configuration - shoot base set; Field effect tube amplifier circuit, common source amplifier, partial pressure since the common source bias type amplifier, drain amplification and multistage amplifier,