I'm new in VBA and I’m getting wrong results by doing a dictionary in VBA.
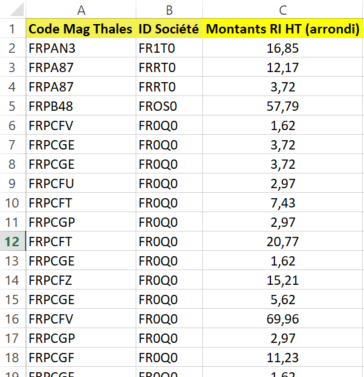
Input :
- column B : societies's ID
- column A : their stores'IDs
- column C : amounts
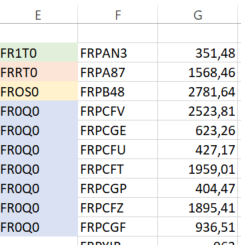
Output expected:
- Column E: societies ID
- Column F : stores ID (unique values)
- Column G : total amount of each stores ID
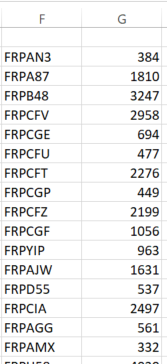
What I get :
Example: For the store ID FRPAN3 I’m supposed to have 351,48.
Code :
Option Explicit
Dim dico As Object, f As Worksheet, i&
Sub ValeursUniques()
Set dico = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
Set f = Sheets("Feuil1")
For i = 2 To f.Range("B" & Rows.Count).End(xlUp).Row
dico(f.Range("B" & i).Value) = dico(f.Range("B" & i).Value) Val(f.Range("C" & i))
Next i
Range("F2").Resize(dico.Count, 1) = Application.Transpose(dico.keys)
Range("G2").Resize(dico.Count, 1) = Application.Transpose(dico.items)
End Sub
Any idea why I get those results ?
CodePudding user response:
The Val function may not return the correct value. If your values in column F Val(f.Range("F" & i)) are actually non-integers their decimals can get cut off!
The documentation says
The Val function stops reading the string at the first character that it can't recognize as part of a number.
The Val function recognizes only the period ( . ) as a valid decimal separator. When different decimal separators are used, as in international applications, use CDbl instead to convert a string to a number.
So if there is any character in your number it will cut off. In your case the , counts as a character and therefore your values are turned into integers as the , is not treated as a decimal seperator.
Make sure to use Type conversion functions instead:
cDbl(f.Range("F" & i))
will convert the value into a floating point with double precision.
CodePudding user response:
Uniquify Data by Using a Dictionary
- If a value in the first Unique column (in this case column
2) is an error value or a blank,
the record will not be included. - If a value in the other Unique columns (in this case only column
1) is an error value,
it will be converted toEmpty(implicitly). - If a value in the Value column (in this case column
3) is not a number,
0(zero) will be used instead. - Adjust (play with) the values in the constants section.
Option Explicit
Sub UniquifyData()
' Source
Const sName As String = "Feuil1"
Const sFirstCellAddress As String = "A1"
Dim uCols As Variant: uCols = VBA.Array(2, 1)
Const svCol As Long = 3
' Destination
Const dName As String = "Feuil1"
Const dFirstCellAddress As String = "E1"
' Both
Const Delimiter As String = "@"
Dim wb As Workbook: Set wb = ThisWorkbook ' workbook containing this code
' Reference the source range and write its values to the source array.
Dim sws As Worksheet: Set sws = wb.Worksheets(sName)
Dim srg As Range: Set srg = sws.Range(sFirstCellAddress).CurrentRegion
Dim Data As Variant: Data = srg.Value
Dim srCount As Long: srCount = UBound(Data, 1)
Dim cCount As Long: cCount = UBound(Data, 2)
' Write the headers from the source array to the headers array.
Dim cUpper As Long: cUpper = UBound(uCols)
Dim Headers As Variant: ReDim Headers(1 To cUpper 2)
Dim c As Long
For c = 0 To cUpper
Headers(c 1) = Data(1, uCols(c))
Next c
Headers(cCount) = Data(1, svCol)
' Write the unique values from the source array to a dictionary.
Dim dict As Object: Set dict = CreateObject("Scripting.Dictionary")
dict.CompareMode = vbTextCompare
Dim Key As Variant
Dim sString As String
Dim r As Long
For r = 2 To srCount
For c = 0 To cUpper
Key = Data(r, uCols(c))
If c = 0 Then
If Not IsError(Key) Then
If Len(Key) > 0 Then
sString = CStr(Key)
End If
End If
If Len(sString) = 0 Then Exit For
Else
If IsError(Key) Then Key = ""
sString = sString & Delimiter & CStr(Key) ' join uniques
End If
Next c
If Len(sString) > 0 Then
If IsNumeric(Data(r, svCol)) Then
dict(sString) = dict(sString) Data(r, svCol)
Else
If Not dict.Exists(sString) Then dict(sString) = 0
End If
sString = ""
End If
Next r
' Define the destination array.
Dim drCount As Long: drCount = dict.Count 1
ReDim Data(1 To drCount, 1 To cCount)
' Write the headers from the headers array to the destination array.
For c = 1 To cCount
Data(1, c) = Headers(c)
Next c
' Write the values from the dictionary to the destination array.
r = 1
For Each Key In dict.Keys
r = r 1
' Write uniques.
uCols = Split(Key, Delimiter) ' split uniques
For c = 0 To cUpper
Data(r, c 1) = uCols(c)
Next
' Write value.
Data(r, cCount) = dict(Key)
Next Key
' Write the values from the destination array to the destination range.
Dim dws As Worksheet: Set dws = wb.Worksheets(dName)
With dws.Range(dFirstCellAddress).Resize(, cCount) ' reference first row
' Write data.
.Resize(drCount).Value = Data
' Clear below.
.Resize(dws.Rows.Count - .Row - drCount 1).Offset(drCount).Clear
' Apply some formatting.
'.Font.Bold = True ' headers
'.EntireColumn.AutoFit ' columns
End With
' Inform.
MsgBox "Data uniquified.", vbInformation
End Sub