I want to hide my API key when I am making a post request from my browser. I need to input a number plate and send the request to the API and the API responds me with details about it. I have managed to get this working with a GET request to another API by using nodeJS but I can't manage to make it work with a post request. Keep in mind the request needs information from my input field in the browser which is the registration number of the vehicle to send me information back about it.
Here is my function in my browser JS file.
const searchBtn = document.getElementById("search-btn")
function startFetch() {
let plate = document.getElementById("plate").value
let reg = {registrationNumber: `${plate}`}
fetch(`https://driver-vehicle-licensing.api.gov.uk/vehicle-enquiry/v1/vehicles`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'x-api-key': `my key is here`,
},
body: JSON.stringify(reg),
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(response => {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(err);
});
};
searchBtn.addEventListener("click", startFetch);
Any help and method would be appreciated. Thanks in advance.
CodePudding user response:
You are already sending the body.
A very minor modification to you code:
function startFetch() {
let plate = "abc123";
let reg = { registrationNumber: `${plate}` };
fetch(`https://driver-vehicle-licensing.api.gov.uk/vehicle-enquiry/v1/vehicles`,
{
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"x-api-key": `my key is here`,
},
body: JSON.stringify(reg),
}
);
}
startFetch();
You can see your api-key in the header (though you should never send secret via http):
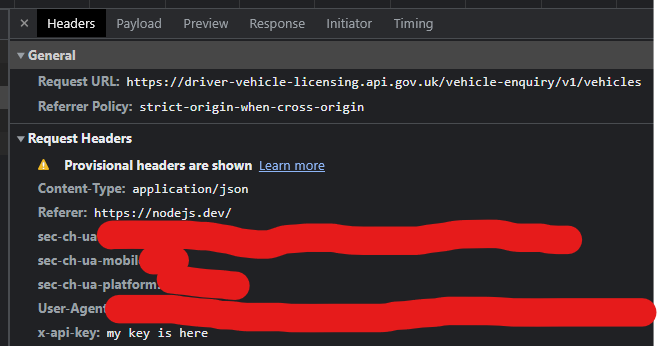
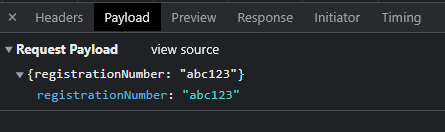
Then in the body (in chrome they call it payload):
CodePudding user response:
For anyone in the same boat. I have managed to achieve what I want.
Client side JS file:
function startFetch() {
let plate = document.getElementById("plate").value
let reg = {registrationNumber: `${plate}`}
fetch(`http://localhost:3000/v`, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
body: JSON.stringify(reg),
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(response => {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(err);
});
};And the backend using Express, NodeJS, body-parser and axios
require("dotenv").config()
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = express();
const axios = require('axios');
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(express.static("src"))
//Env vars
const API_URL = process.env.API_URL
const API_KEY = process.env.API_KEY
app.post('/v', (req, res) => {
const body = req.body;
// Make a request to the backend API
axios.post(`${API_URL}`, body,
{
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
'x-api-key': `${API_KEY}`
}
}
)
.then((response) => {
// Return the response from the backend API to the client
res.send(response.data);
})
.catch((error) => {
// Handle any errors
res.status(500).send(error);
});
});
app.listen(3000, () => {
console.log('API proxy server is listening on port 3000');
});