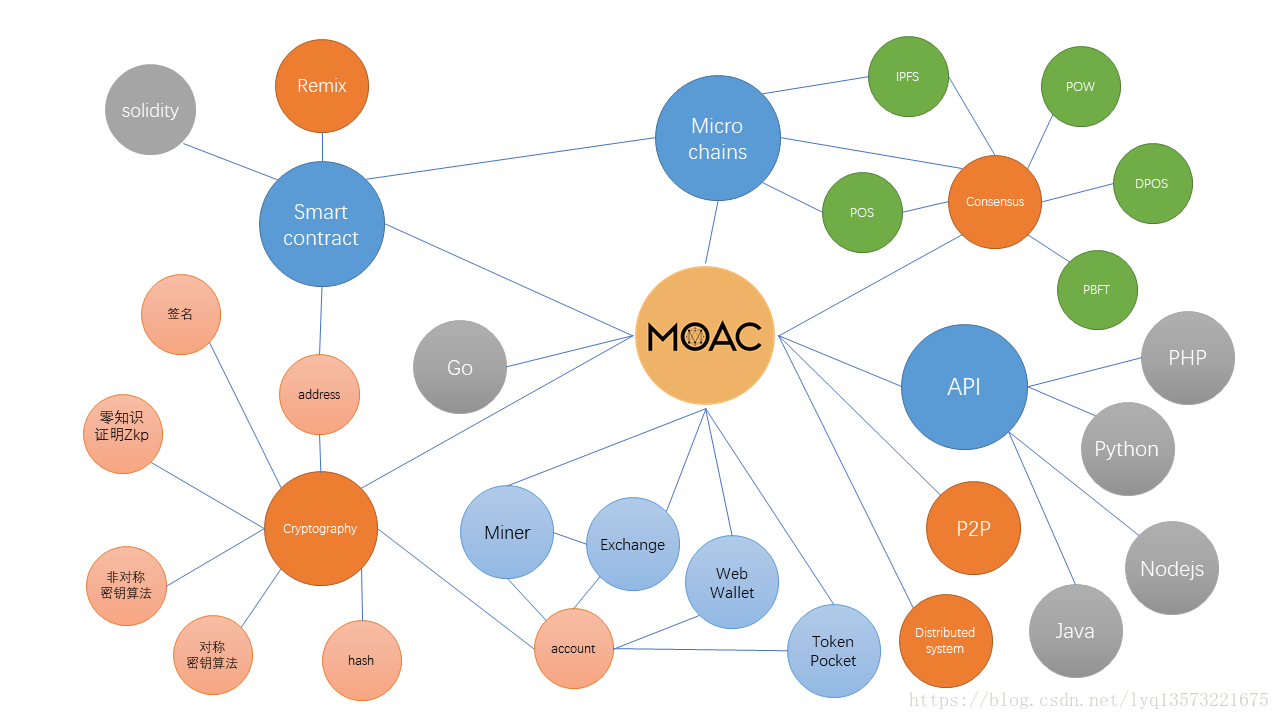
One explanation:
1. Block chain locations (MOAC BlockChain)
A substring function is achieved, the bottom of the chain, friendly to dapp
2. The substring (Micro Chains)
Derived in the main chain of the latter, which has the function of independent block chain,
3. The mechanism of Consensus (Consensus)
How solve the block chain in a distributed scenario to achieve consistency and validity of mechanism,
3.1 POW (Proof of the Work)
Based on the effort to prove the consensus of the mechanism,
3.2 POS (Proof of gaining)
Based on the consensus of interest mechanism,
3.3 DPOS (Delegated Proof of gaining)
Based on the authorization of the consensus of interest mechanism,
3.4 IPFS (Intel Planetary File System)
A distributed file system protocol,
3.5 PBFT (Practical Byzantine Fault how)
Practical Byzantine fault-tolerant algorithm,
4. The API (Application Programming Interface)
Application programming interfaces (apis),
5. Java
An architectural complex, a powerful object-oriented programming language,
6. PHP
A kind of applicable to general open source web development scripting language,
7. Python
An object-oriented interpreted programming language,
8. NodeJS
A JavaScript running environment,
9. Go
A combination of efficiency and safety of compiled programming language,
10. Intelligent (Smart Contract Contract)
Here especially can run on a block chain, similar to the computer to a contract agreement,
11. Solidity
A suitable writing smart contract language,
12. Want to
A browser version of the solidity development IDE,
13. A P2P network
A difference in the structure of the S/C peer network,
14. A distributed system
Building on computer network, software systems that support the distributed processing,
15. Cryptography (cryptography)
To transfer information security and secrecy of science or method,
16. Address
Stone block chain mainly account address and contract,
17. A digital signature
A numeric string, send are used to verify the authenticity of information,
18. Zero Knowledge Proof (Zero Knowledge Proof)
In the case of does not provide useful information to make people believe that a statement is correct verification,
19. The symmetric key algorithm
Use the same key to encrypt and decrypt algorithm,
20. Asymmetric keys algorithm
Algorithm of encryption and decryption use different keys,
21. The hash function (hash)
Convert the algorithm of arbitrary length input into the output of the fixed length,
22. The account
In block chain, a pair of public and private keys to form a unique identifier account,
23. Dig
According to block chain consensus competition mechanism, the process of charge to an account
24. The exchange
Ability of digital assets trading places,
25. The purse
Wallet manage digital assets, including web page version of the wallet and mobile wallet,
-- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
Author: Li_Yu_Qing
Source: CSDN
CodePudding user response:

