 I have 4 types of data.
each one has been pre-processed using:
I have 4 types of data.
each one has been pre-processed using:
x1,y1=Standardisation
x2,y2=Normalisation
x3,y3=Rescale
and one is completely unprocessed (x,y).
I have applied logistic regression to each like this:
#Building Logistic Regression model on the UNPROCESSED DATA
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
lr_model = LogisticRegression()
lr_model.fit(x_train,y_train)
lr_predict = lr_model.predict(x_test)
print('Logistic Regression - ',accuracy_score(lr_predict,y_test))
#Building Logistic Regression model on the NORMALISED DATA
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
lr_norm = LogisticRegression()
lr_norm.fit(x1_train, y1_train)
y_pred = lr_norm.predict(x1_test)
print("Accuracy of logistic regression on test set with Rescaled features: {:.2f}".format(lr_norm.score(x1_test, y1_test)))
and so on...
I want to make one graph, not sure which, that best represents the performance through its accuracy score, or whatever else there may be... but of the other models I wish to test down below:
svm_model = SVC(kernel='linear')
svm_model.fit(x_train,y_train)
svc_predict = svm_model.predict(x_test)
print('SVM - ',accuracy_score(svc_predict,y_test))
print('\t\t\t\tTRAIN DATA\n')
print(classification_report(y_train, svm_model.predict(x_train), target_names=encoder.inverse_transform([0,1,2])))
print('\n')
print('\t\t\t\tTEST DATA\n')
print(classification_report(y_test, svm_model.predict(x_test), target_names=encoder.inverse_transform([0,1,2])))
nb_model = GaussianNB()
nb_model.fit(x_train,y_train)
nb_predict = nb_model.predict(x_test)
print('Naive bayes - ',accuracy_score(nb_predict,y_test))
dt_model = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_leaf_nodes=3)
dt_model.fit(x_train,y_train)
dt_predict = dt_model.predict(x_test)
print('Decision Tree - ',accuracy_score(dt_predict,y_test))
rfc_model = RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=3)
rfc_model.fit(x_train,y_train)
rfc_predict = rfc_model.predict(x_test)
print('Random Forest - ',accuracy_score(rfc_predict,y_test))
knn_model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
knn_model.fit(x_train,y_train)
knn_predict = knn_model.predict(x_test)
print('knn - ',accuracy_score(knn_predict,y_test))
Hope this makes sense..
#preprare data
pre_processing=[('NOT PROCESSED', None)]
pre_processing.append(('RESCALED', MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0, 1))))
pre_processing.append(('STANDARDIZED', StandardScaler()))
pre_processing.append(('NORMALIZED', Normalizer()))
# prepare models
models = []
models.append(( 'LR' , LogisticRegression(max_iter=10000)))
models.append(( 'LDA' , LinearDiscriminantAnalysis()))
models.append(( 'KNN' , KNeighborsClassifier()))
models.append(( 'CART' , DecisionTreeClassifier()))
models.append(( 'NB' , GaussianNB()))
models.append(( 'SVM' , SVC(probability=True)))
results = []
names = []
higher_acc=0
standard=0
best_model=''
for process in pre_processing:
globals()['df_' process[0]] = pd.DataFrame(index=None, columns=None)
for algo in models:
estimators = [process,algo]
model = Pipeline(estimators)
ss = ShuffleSplit(n_splits=10, test_size=test_size, random_state=seed)
names.append(algo[0])
for scoring in performance_metrix:
cv_results = cross_val_score(model, X_train, Y_train, cv=ss, scoring=scoring)
globals()['df_' process[0]].loc[algo[0],scoring]= '%s\u00B1%s'%(round(cv_results.mean()*100.0,2),round(cv_results.std()*100.0,2))
if performance_metrix.index(scoring)==0:
results.append(cv_results)
if cv_results.mean()*100.0 > higher_acc:
higher_acc=cv_results.mean()*100.0
standard=cv_results.std()*100.0
best_model=process[0], algo[0]
elif cv_results.mean()*100.0 == higher_acc:
if cv_results.std()*100.0 < standard:
higher_acc=cv_results.mean()*100.0
best_model=process[0], algo[0]
print('For %s data we produced:\n\n'%(process[0]),globals()['df_' process[0]],'\n\n')
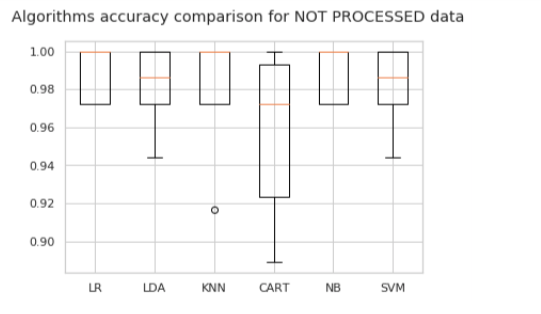
# boxplot algorithm comparison
fig = pyplot.figure()
fig.suptitle('Algorithms accuracy comparison for %s data'%(process[0]))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
pyplot.boxplot(results[:len(models)])
ax.set_xticklabels(names)
pyplot.show()
# Create a pipeline that standardizes the data then creates a model
print("The overall best performance was the one obtained with %s data, using %s algorithm. \nIt's Accuracy resulted to be %s with a standard deviation of %s" %(best_model[0],best_model[1],round(higher_acc,2),round(standard,2)))
CodePudding user response:
datasets = {
"Unprocessed": (x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test),
"Standardisation": (x1_train, x1_test, y1_train, y1_test),
"Normalisation": (x2_train, x2_test, y2_train, y2_test),
"Rescale": (x3_train, x3_test, y3_train, y3_test),
}
models = {
"Logistic Regression": LogisticRegression(),
"Decision Tree": DecisionTreeClassifier(max_leaf_nodes=3),
"Random Forest": RandomForestClassifier(max_depth=3)
}
def evaluate_model(model, dataset):
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = data
model.fit(x_train, y_train)
pred = model.predict(x_test)
return accuracy_score(pred, y_test)
model_scores_for_datasets = {}
for dataset_name, dataset in datasets.items():
dataset_scores = {}
for model_name, model in models.items():
model_score = evaluate_model(model, dataset)
dataset_scores[model_name] = model_score
model_scores_for_datasets[dataset_name] = dataset_scores
Here, model_scores_for_datasets will contain the accuracy results for every dataset for each model and will look something like:
{
"Unprocessed" :
{
"Logistic Regression" : 10,
"Decision Tree": 5,
"Random Forest": 20
},
"Standardisation" :
{
"Logistic Regression" : 10,
"Decision Tree": 5,
"Random Forest": 20
},
"Normalisation" :
{
"Logistic Regression" : 10,
"Decision Tree": 5,
"Random Forest": 20
},
"Rescale" :
{
"Logistic Regression" : 10,
"Decision Tree": 5,
"Random Forest": 20
},
}
You now have the results for each dataset and can create your required plots. Something along these line:
for dataset_name, scores in model_scores_for_datasets.items():
# For example:
# dataset_name will be "Unprocessed"
# scores will be a dict like so:
# {
# "Logistic Regression" : 10,
# "Decision Tree": 5,
# "Random Forest": 20
# }
generate_plot(dataset_name scores)
Of course, you need to figure out the generate_plot function. Hope this helps and gives you some idea.
CodePudding user response:
ValueError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-276-55fc2cf2a210> in <module>
26
27 for model_name, model in models.items():
---> 28 model_score = evaluate_model(model, dataset)
29 dataset_scores[model_name] = model_score
30
<ipython-input-276-55fc2cf2a210> in evaluate_model(model, dataset)
16 def evaluate_model(model, dataset):
17 x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = data
---> 18 model.fit(x_train, y_train)
19 pred = model.predict(x_test)
20 return accuracy_score(pred, y_test)
/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/linear_model/_logistic.py in fit(self, X, y, sample_weight)
1506 _dtype = [np.float64, np.float32]
1507
-> 1508 X, y = self._validate_data(
1509 X,
1510 y,
/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/base.py in _validate_data(self, X, y, reset, validate_separately, **check_params)
579 y = check_array(y, **check_y_params)
580 else:
--> 581 X, y = check_X_y(X, y, **check_params)
582 out = X, y
583
/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/utils/validation.py in check_X_y(X, y, accept_sparse, accept_large_sparse, dtype, order, copy, force_all_finite, ensure_2d, allow_nd, multi_output, ensure_min_samples, ensure_min_features, y_numeric, estimator)
962 raise ValueError("y cannot be None")
963
--> 964 X = check_array(
965 X,
966 accept_sparse=accept_sparse,
/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/sklearn/utils/validation.py in check_array(array, accept_sparse, accept_large_sparse, dtype, order, copy, force_all_finite, ensure_2d, allow_nd, ensure_min_samples, ensure_min_features, estimator)
744 array = array.astype(dtype, casting="unsafe", copy=False)
745 else:
--> 746 array = np.asarray(array, order=order, dtype=dtype)
747 except ComplexWarning as complex_warning:
748 raise ValueError(
/opt/anaconda3/lib/python3.8/site-packages/numpy/core/_asarray.py in asarray(a, dtype, order)
81
82 """
---> 83 return array(a, dtype, copy=False, order=order)
84
85
ValueError: could not convert string to float: 'SepalLengthCm'
