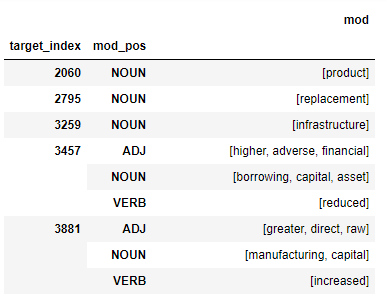
I am trying to transform a pandas dataframe resulting from a groupby([columns]). The resulting index will have for each "target_index" different lists of words (example in image below). Transforming it with to_dict() seems to not be working directly (I have tried several orient arguments).
The Input dataframe:
The desired output (only two keys for the example):
{
"2060": {
"NOUN": ["product"]
},
"3881": {
"ADJ": ["greater", "direct", "raw"],
"NOUN": ["manufacturing", "capital"],
"VERB": ["increased"]
}
}
In order to recreate the below dataset:
df= pd.DataFrame([
["2060", "NOUN", ["product"]],
["2060", "ADJ", ["greater"]],
["3881", "NOUN", ["manufacturing", "capital"]],
["3881", "ADJ", ["greater", "direct", "raw"]],
["3881", "VERB", ["increased"]]
], columns= ["a", "b", "c"])
df= df.groupby(["a", "b"]).agg({"c": lambda x: x})
CodePudding user response:
The input given in the constructor is different from the one in the image. I used the input in the constructor. You could use a lambda in groupby.apply to convert each group to dicts, then convert the aggregate to dict:
out = df.groupby(level=0).apply(lambda x: x.droplevel(0).to_dict()['c']).to_dict()
Another option is to use itertuples and dict.setdefault:
out = {}
for (ok, ik), v in df.itertuples():
out.setdefault(ok, {}).setdefault(ik, []).extend(v)
Output:
{'2060': {'ADJ': ['greater'], 'NOUN': ['product']},
'3881': {'ADJ': ['greater', 'direct', 'raw'],
'NOUN': ['manufacturing', 'capital'],
'VERB': ['increased']}}