I'm trying to write a Python script that takes the text in a cell of an Excel spreadsheet, and makes certain characters subscript or superscript. I was using OpenPyxl, but I've read that it doesn't allow modifications smaller than a whole cell, so I'm open to using a different package if necessary.
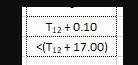
For reference, I need the 2 characters after the "T" in each cell to be a subscript. So take the string "T12 0.10", or "<(T12 17.00"and format it in place so that the "12" is a subscript, as in the image below.
Here's what I have so far:
style = XFStyle()
style.font = fnt
style.borders = borders
substyle = fnt.ESCAPEMENT_SUBSCRIPT
superstyle = fnt.ESCAPEMENT_SUPERSCRIPT
def compare(contents):
s = ""
for i in contents:
nextchar=contents[i 1].value
if i.value.contains ("T"):
j = i 1, substyle
s = str(s j)
else:
s = str(i)
wb = op.load_workbook("file_name.xlsx")
ws = wb["Sheet3"]
for row in ws.iter_rows("C{}:C{}".format(ws.min_row, ws.max_row)):
for cell in row:
contents = cell.value
compare(contents)
CodePudding user response:
With Xlwings you can do it this way, working on the assumption that where there is a 'T' in the cell contents the next two chars are subscripted.
import xlwings as xw
wb = xw.Book('Book1.xlsx)
ws = wb.sheets('Sheet1')
for x in range(1, 6):
contents = ws.range(1, x).value
if 'T' in contents: # Checks for T in the cell contents
i = contents.index('T') 1
ws.range(1, x).characters[i:i 2].api.Font.Subscript = True
wb.save()
wb.close()
As an example this changes the following cells A1:E1 from
T12 0.10 <(T12 17.00 A12 1.11 A 0.10T12 B14 111
to