I need to interpolate a in 3D and I want to do this only for the area where I actually have observed x and y values. This can be done in the following steps:
- Find outer points of the 2d x and y area (see my question
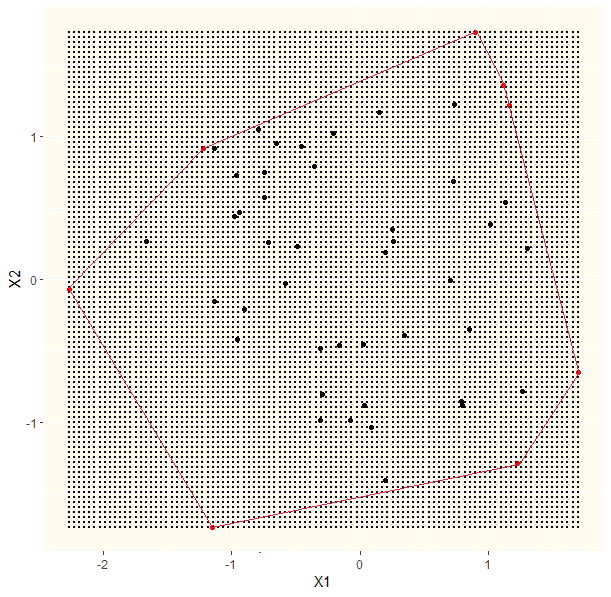
In the first step I found out the outer points of the observed data (here observed data as big black points and the outer points in red). In a second step I generated a grid (small black points). Now I need to know which grid points lay inside the outer points area (which I here marked by connecting the red points with a red line). How to find those grid points?
Code and data
set.seed(3) df <- data.frame(matrix(rnorm(100), ncol= 2)) library(ggplot2) grid_df <- expand.grid(seq(min(df$X1), max(df$X1), length.out= 100), seq(min(df$X2), max(df$X2), length.out= 100)) df$outer <- FALSE df$outer[chull(df$X1, df$X2)] <- TRUE ggplot() geom_point(data= df, mapping= aes(X1, X2)) geom_point(data= df[df$outer, ], mapping= aes(X1, X2), col= "red") geom_point(data= grid_df, mapping= aes(Var1, Var2), col= "black", size= .5)Expected output is a third column in
grid_dfwhich isTRUEif the point lays inside the area. I look for a R base solution.CodePudding user response:
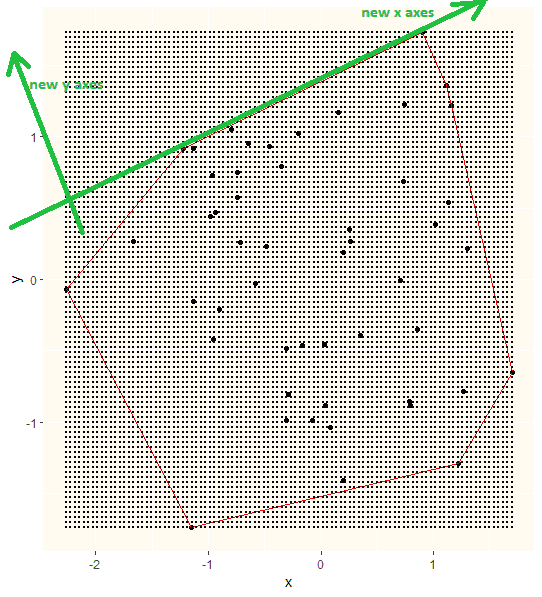
I solved it with base R using axis rotation.
Imagine that the area borders would be the x and y axis:
Now it is easy to exclude grid points outside the area: We just need to exclude points that lay above the new x axis. We need to repead this for all the area borders and then we know what grid points to exclude.
The code for this:
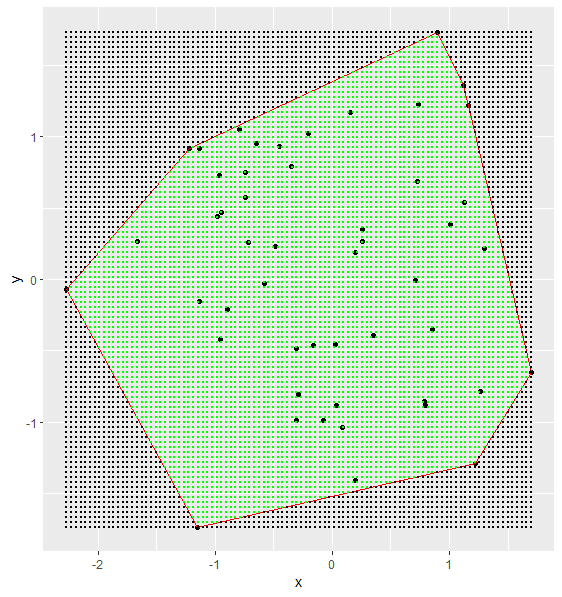
# Data as in question (just variable names changed). set.seed(3) df <- setNames(data.frame(matrix(rnorm(100), ncol= 2)), c("x", "y")) library(ggplot2) grid_df <- setNames(expand.grid(seq(min(df$x), max(df$x), length.out= 100), seq(min(df$y), max(df$y), length.out= 100)), c("x", "y")) # Create dataframe with border points (rbind to connect the last with the # first points). border <- rbind.data.frame(df[chull(x= df), ], df[chull(x= df), ][1, ]) # See for every border whether grid points are outside. grid_outside <- sapply(2:nrow(border), function(row_i){ # Extract one border line. border_i <- border[(row_i-1):row_i, ] # See what points must lay inside the area. point_inside <- data.frame(x= median(df$x), y= median(df$y)) # Find slope of the border line. slope <- diff(border_i$y)/diff(border_i$x) # Calculate angle from slope. angle <- atan(slope)*(180/pi) angle <- ifelse(angle < 0, angle 180, angle) # Rotating function. rotate <- function(data, angle){ data.frame(x= data$x * cos(angle* pi / 180) data$y * sin(angle* pi / 180), y= -data$x * sin(angle* pi / 180) data$y * cos(angle* pi / 180)) } # Rotate the data. border_new_i <- rotate(data= border_i, angle= angle) grid_df_new <- rotate(data= grid_df, angle= angle) point_inside_new <- rotate(point_inside, angle= angle) # Depending on rotation results inner area is under or over # the new border point y. Define outside grid points accordingly. if(border_new_i$y[1] < point_inside_new$y){ outside_border_i <- grid_df_new$y < border_new_i$y[1] } else{ outside_border_i <- grid_df_new$y > border_new_i$y[1] } outside_border_i }) # Is a row outside the area according to one of the border? grid_outside <- rowSums(grid_outside) >= 1 # Show points inside area. grid_df_inside <- grid_df[!grid_outside, ]For the data in the question the resulting plot is:
ggplot() geom_point(data= df, mapping= aes(x, y)) geom_path(data= border, mapping= aes(x, y), col= "red") geom_point(data= grid_df, mapping= aes(x, y), col= "black", size= .5) geom_point(data= grid_df_inside, mapping= aes(x, y), col= "green", size= .5)CodePudding user response:
I know you're looking for a base R solution, but this might be way harder than you think. Here's a
sfsolution:library(sf) hull<- df[chull(df$X1, df$X2), 1:2] mat <- list(as.matrix(rbind(hull, hull[1, ]))) poly <- st_polygon(mat) df <- st_as_sf(df, coords = c("X1", "X2")) df$within <- st_intersects(df, poly, sparse = F)