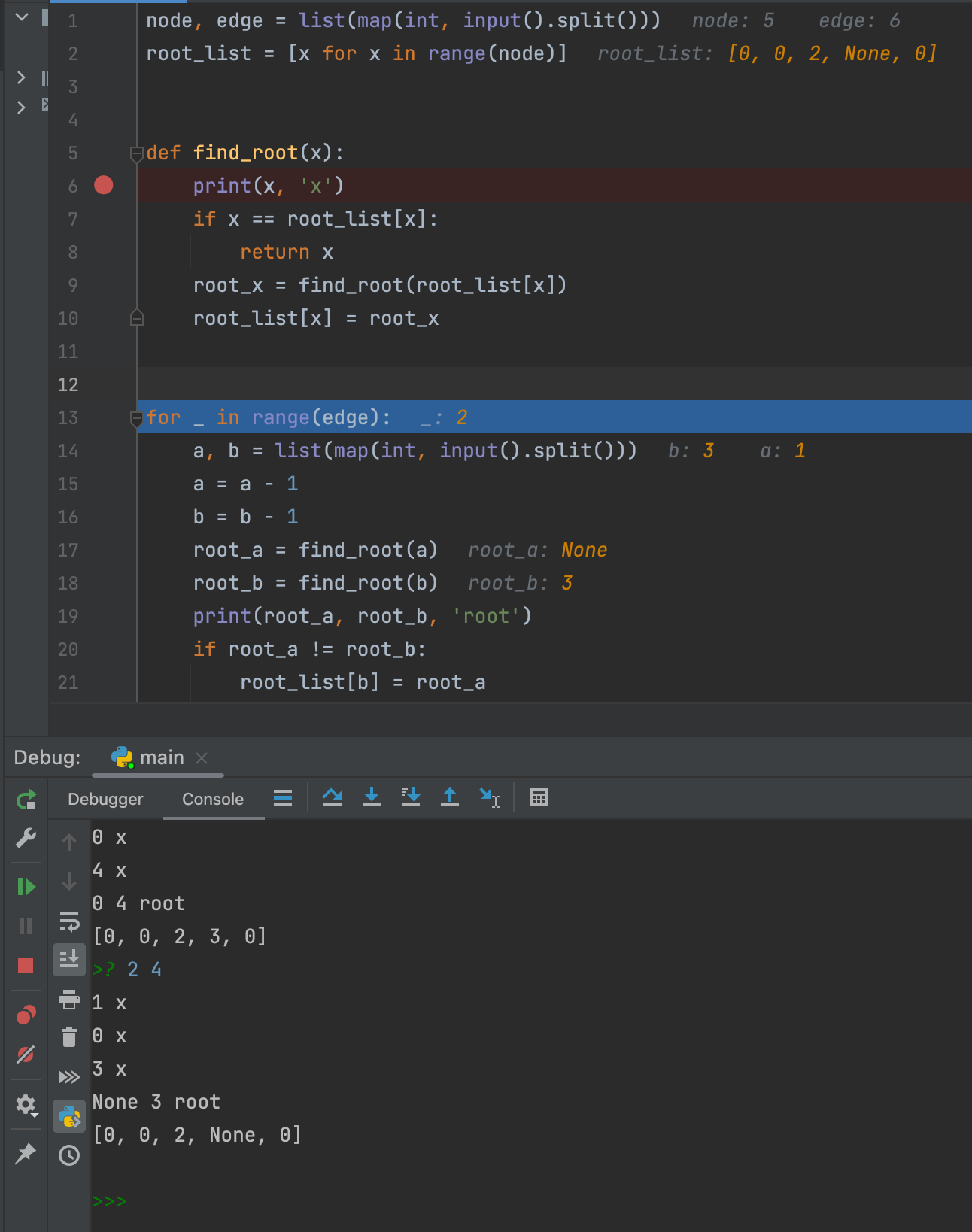
My code is like this and the input is here.
5 6
1 2
1 5
2 4
3 4
3 5
4 5
when i put 2 4 , the value root_a is None. but i don't understand why root_a return None . i tried to debug on pycharm but i don't know why... Does anyone can help?
node, edge = list(map(int, input().split()))
root_list = [x for x in range(node)]
def find_root(x):
print(x, 'x')
if x == root_list[x]:
return x
root_x = find_root(root_list[x])
root_list[x] = root_x
for _ in range(edge):
a, b = list(map(int, input().split()))
a = a - 1
b = b - 1
root_a = find_root(a)
root_b = find_root(b)
print(root_a, root_b, 'root')
if root_a != root_b:
root_list[b] = root_a
print(root_list)
CodePudding user response:
I apologize if I understand your code wrongly. I'm not quite sure what you are trying to achieve ;(
But I can tell you why it's None when you input 2 4
that is because in the function find_root you are returning nothing if x != root_list[x]
see below for find_root function with comments
def find_root(x):
print(x, 'x')
if x == root_list[x]:
return x
# here if x != root_list[x], the code will continue
# but there is no return, hence it's treated as if it returns None
root_x = find_root(root_list[x])
root_list[x] = root_x
# you might need a return here?
return root_x
CodePudding user response:
You don't return the found value in find_root.
If you return no value 'None' is returned.
In the third iteration of your loop _ == 2 you call find_root(1) which then calls find_root(0) but that value isn't returned after being assigned to root_x. Instead None is returned implicitly and root_a becomes None. As None != 3 you assign None into your root_list in line 21.
I'm unsure what you program wants to do but try this:
def find_root(x):
print(x, 'x')
if x == root_list[x]:
return x
root_x = find_root(root_list[x])
root_list[x] = root_x
return root_x # add this line