So I encountered this weird issue that is self explanatory in this photo: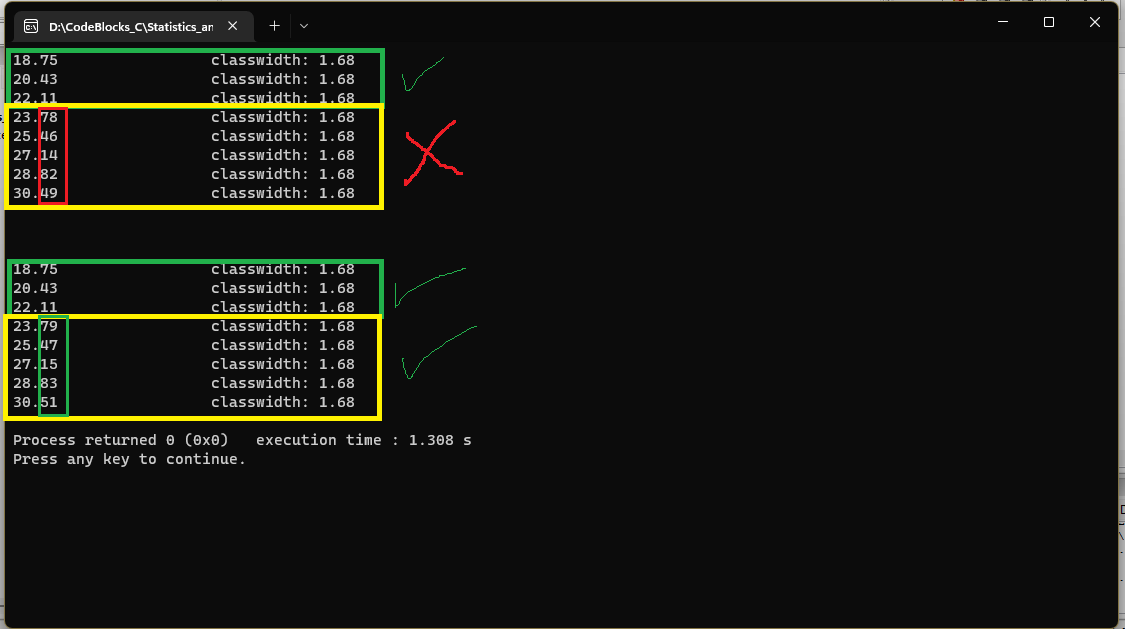
In the first 8 lines, I used a variable called classwidth to add increments to l which is set to have an initial value of 18.75. Each iteration of the loop prints l value.
However in the second 8 lines, I do the same thing but, I replaced classwidth variable with a constant 1.68, the results are identical in the first 2 lines in each iteration, but in the second 8 lines the program calculates numbers correctly and as expected, while in the first 8 lines, the code starts to lose precession in the fourth line as shown in the photo.
I don't want to use a constant value of 1.68, because this value is calculated by range and k parameters, so it will not always be 1.68.
What should I do to have the precession in the second eight lines while using constant classwidth?
This is my code:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// cout << fixed;
// cout << setprecision(2);
// cout << 20.42 1.68*3 << endl;
double range;
double l;
int k = 8;
range = 32.17 -18.75;
double classwidth = range/k;
cout << fixed;
cout << setprecision(2);
l = 18.75;
for(int n = 1; n<=k ; n ){
cout<< l << " classwidth: "<< classwidth<<endl;
l = classwidth;
}
cout << "\n\n\n";
l = 18.75;
for(int n = 1; n<=k ; n ){
cout<< l << " classwidth: "<< 1.68 <<endl;
l = 1.68;
}
//groupedData();
}
I commented the
cout << fixed;
cout << setprecision(2);
line of code so it is nonfunctional and I still didn't achieve what I want:
This is the full program:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
//CURRENTLY UNFINISHED YET!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
void groupedData()
{
int b = 0;
int j;
double numberOfClasses = 0;
int i = 0;
double arr[300];
cout << "Will you specify number of classes (k) 1(yes), 0(no)?"<<endl;
bool k_manual;
cin >> k_manual;
if(cin.fail())
{
cout <<"Invalid input."<<endl;
exit(0);
}
else if(k_manual == 1)
{
cout << "What is it?\n";
cin >> numberOfClasses;
if(cin.fail())
{
cout <<"Invalid input."<<endl;
exit(0);
}
}
cout << "Enter grouped discrete quantitative data to calculate measures of central tendency and measures of variation.\nUse 0 to terminate.\n";
cout << "======================================"<<endl;
while (i < 300)
{
cin >> arr[i];
if (!cin.fail() && arr[i] == 0)
{
int classesK[150];
if (numberOfClasses == 0)
{
numberOfClasses = ceil(1 3.3*log10(i));
}
for(j=0; j<= numberOfClasses; j )
{
b = 1;
classesK[j] = b;
}
double classWidthPrecession;
cout << "Class width precession (1/0.1/0.01)?"<<endl;
cin >> classWidthPrecession;
//int arr[] = {1,2,3,3,2,5,4,4,3,1,2,1,4,6,5,5,4,2,3,2};
cout << "\n\nCalculating..."<<endl;
cout << "------------------"<<endl;
//mean calculation
double mean;
double sum = 0;
for (j=0; j < i; j )
{
sum = arr[j];
}
mean = sum / i;
cout << "\nMeasures of central tendency:\n----------------------------\n";
cout <<"Mean(x_-): "<< mean <<endl;
//median calculation
sort(arr, arr i, less<double>());
if (!((i % 2) == 0))
{
int median_index = (i 1) / 2;
double median = arr[median_index - 1];
cout << "Median (x_~): " << median;
}
else
{
double median = (arr[i/2 - 1] arr[i/2] ) / 2.0;
cout << "Median (x_~): " << median;
}
//range calculation
double range = arr[i-1] - arr[0];
cout << "\n\nMeasures of variability:\n-------------------------\n";
cout << "Range: " << range;
sum = 0;
for (j=0; j<i; j )
{
sum = pow((arr[j] - mean), 2);
}
double variance = sum / (i-1);
double stdDeviation = sqrt(variance);
double COV = (stdDeviation/mean) * 100;
cout << "\nVariance_s2: " << variance;
cout << "\nStandard Deviation: " << stdDeviation;
cout << "\nCoefficient of Variation: " << COV << "%";
//mean deviation calc
sum = 0;
for (j=0; j<i; j )
{
sum = abs(arr[j] - mean);
}
double meanDeviation = sum / i;
cout << "\nMean Deviation: " << meanDeviation <<endl;
cout << "-----------------------------------------------------------"<<endl;
int frqArr[150];
double XiArr[150];
for(j=0; j<150; j )
{
frqArr[j]=0;
}
int k = 0;
// for(j=0; j<i; j )
// {
// if(arr[j] == arr[j 1])
// {
// frqArr[k] = 1;
// continue;
// }
// else
// {
// k ;
// XiArr[k] = arr[j];
// }
// }
// int cumArr[150];
// int sumInt = 0;
// for(j=0; j<=k; j )
// {
// sumInt = frqArr[j];
// cumArr[j] = sumInt;
//
// }
sort(arr, arr i, less<double>());
double classWidth = range/numberOfClasses;
if(classWidthPrecession == 1)
{
classWidth = ceil(classWidth);
}
cout << fixed;
cout << setprecision(3);
double temp = 1.0;
double ll = arr[0];
double ul;
double ulArr[150];
double llArr[150];
ul = (ll classWidth) - classWidthPrecession;
double num = classWidth;
for(j=0; j<=numberOfClasses; j )
{
ulArr[j] = ul;
llArr[j] = ll;
temp = 2.0;
ll = ll (temp-1.0)*(classWidth);
ul = ul (temp-1.0)*(classWidth);
}
b=0;
k=0;
for(j=0; j<=i; j )
{
if((arr[j] >= llArr[b]) && (arr[j] <= ulArr[b]))
{
frqArr[k] ;
continue;
}
else
{
b ;
k ;
continue;
}
}
frqArr[0] -= 1;
int cumArr[150];
int sumInt = 0;
for(j=0; j<=k; j )
{
sumInt = frqArr[j];
cumArr[j] = sumInt;
}
cout << fixed;
cout << setprecision(2);
cout << "k\t\b|classes\t\t\t\b|Fi\t\t\b|FiXi\t\b|(Xi - X_)^2\t\b|Fi(Xi - X_)^2\t\b|Xi - X_|\t\b|Fi|Xi - X_|"<<endl;
for(j=1; j<=numberOfClasses; j )
{
//table output..........................
cout<<classesK[j-1]<< "\t\b|" << llArr[j-1] << " - " << ulArr[j-1] << "\t\t\b|" << frqArr[j-1]<<endl;
}
// int frqArrSorted [150];
// copy(frqArr, frqArr k, frqArrSorted);
// sort(frqArrSorted, frqArrSorted k);
// // cout << "\n\n" << frqArrSorted[k-1];
// int largestFrq = frqArrSorted[k-1];
// bool isMultimodal = 0;
//
//
// for(b=2; b<=k; b )
// {
// if(largestFrq == frqArrSorted[k-b])
// {
// isMultimodal = 1;
// continue;
//
// }
// else if(!isMultimodal)
// {
// break;
// }
// }
// b = 0;
// int ModeValIndex[150];
// for(j=0; j<=k; j )
// {
// if (frqArr[j] == largestFrq && !isMultimodal)
// {
// ModeValIndex[0] = j;
// break;
// }
// else if(frqArr[j] == largestFrq && isMultimodal)
// {
// ModeValIndex[b] = j ;
// b ;
// }
// continue;
// }
//
// if(isMultimodal)
// {
// cout << "\n\nModes are: " <<endl;
// for(j=0; j<b; j )
// {
// cout << XiArr[ModeValIndex[j] 1] <<endl;
// }
// if(b==2)
// {
// cout << "\nMode is BiModal." << endl;
// }
// else
// {
// cout << "\nMode is MultiModal." << endl;
// }
//
//
//
// }
//
// else
// {
// cout << "\n\nMode is: " << XiArr[ModeValIndex[0] 1] << " (UniModal) " <<endl;
//
// }
//
// int max_frqArrVal = 0;
// for(j=0; j<=k; j ){
// if(frqArr[j] > frqArr[j 1]){
// if(frqArr[j] > max_frqArrVal){
// max_frqArrVal = frqArr[j];
// continue;
// }else if()
// else{
// continue;
// }
//
// }else{
// continue;
// }
//
// }
exit(0);
}
else if (!cin.fail())
{
i ;
continue;
}
else
{
cout<<"Wrong!"<<endl;
system("pause");
exit(0);
}
}
}
int main()
{
// cout << fixed;
// cout << setprecision(2);
// cout << 20.42 1.68*3 << endl;
double range;
double l;
int k = 8;
range = 32.17 -18.75;
double classwidth = range/k;
// cout << fixed;
// cout << setprecision(2);
l = 18.75;
for(int n = 1; n<=k ; n )
{
cout<< l << " classwidth: "<< classwidth<<endl;
l = classwidth;
}
cout << "\n\n\n";
l = 18.75;
for(int n = 1; n<=k ; n )
{
cout<< l << " classwidth: "<< 1.68 <<endl;
l = 1.68;
}
//groupedData();
}
These are the test data that I use:
21.52
19.83
23.11
18.75
20.5
22.48
21.61
19.24
20.48
22.25
19.72
24.36
20.84
22.74
19.37
21.75
20.21
32.17
20.38
20.76
21.87
19.81
21.95
20.93
19.05
23.39
21.05
22.87
22.17
21.24
24.1
20.15
19.84
23.6
20.26
21.47
22.98
21.13
20.04
22.05
21.33
21.36
24.87
19.42
21.23
25.12
20.58
21.75
19.95
21.94
CodePudding user response:
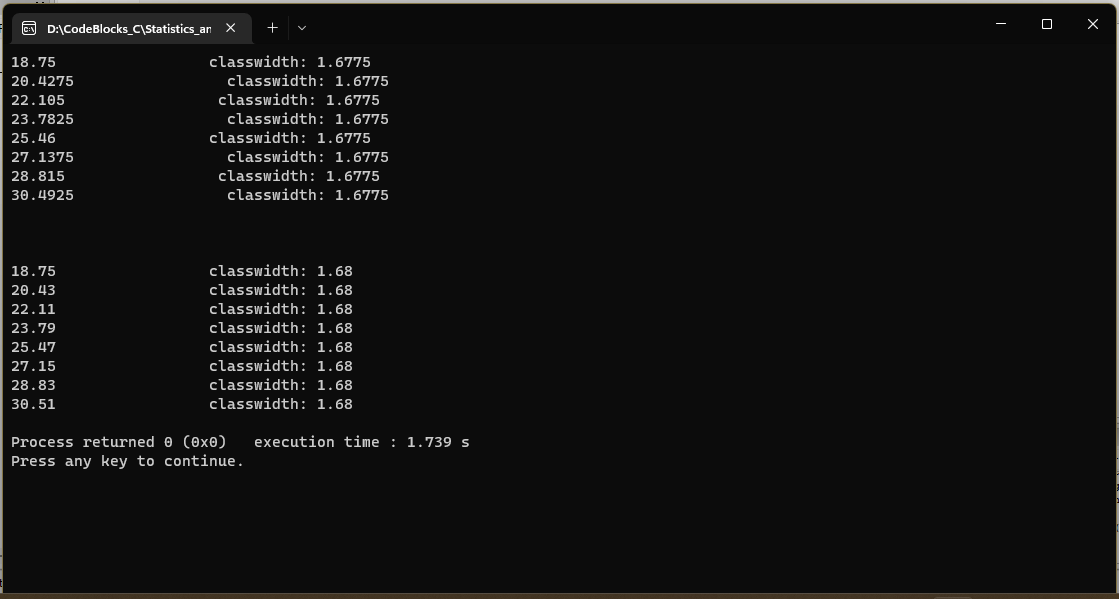
(32.17−18.75)/8 is 1.6775, not 1.68, so it is unclear why you would expect 1.68 to maintain accuracy.
To avoid accumulating rounding errors in a loop, recalculate the value from scratch in each iteration instead of adding to a previous value:
double start = 18.75, end = 32.17;
for (int n = 0; n < k; n)
{
l = start (end-start)*n/k;
cout << l << endl;
}
CodePudding user response:
So I finally found an answer, which relies on using this function to round every number that requires so:
double rounderFunction(double request, int decimalPlaces)
{
double newNum;
double shiftAmount = pow(10, decimalPlaces);
newNum = round(request * shiftAmount) / shiftAmount;
return newNum;
}
