I'm studying on my own and came across the following problem, and I don't know much C# (I'm coming from JavaScript). See below for my guess and any extra explanation/clarification/correction is welcome.
What does the following code do and how would you improve the code (Given n=1 and m=10)?
class Program
{ public static int DoSomething(int n, int m)
{
int x = n;
if (n < m)
{
n ;
return x = DoSomething(n, m);
}
return x;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter n: ");
int n = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("Enter m: ");
int m = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());
int x = DoSomething(n, m) ;
Console.WriteLine(x);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
So it's obviously a recursion problem right? It looks like it will increment n until it is greater than m and then write that number to the console. So eventually it will log 11 to the console (I'm assuming in total, it will log 1-11 to the console). The recursion is redundant and unnecessary and so the easy solution to me would be to just convert it to a simple while loop, where as long as n < m, Console.WriteLine(n) and n . Am I missing something, or is that the best simple solution in this scenario?
CodePudding user response:
Based on the following formula (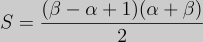
Note: α represents n and β represents m.
Which can be expressed in code as:
public static int DoSomething(int n, int m)
{
int numerator = (m - n 1) * (n m);
int result = numerator / 2;
return result;
}
