I am trying to import an SQL file with the following command using GitHub actions workflow .sql file contains some test data which will be further used to run unit test cases in laravel.
I am unable to understand if the file path is wrong or import command is wrong. I have saved SQL file on the root directory of laravel.
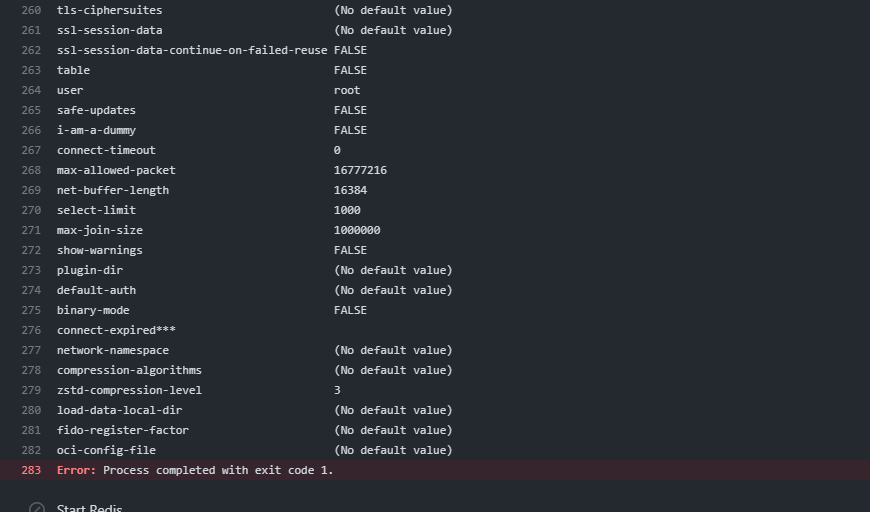
I am facing the following error:
Error: Process completed with exit code 1.
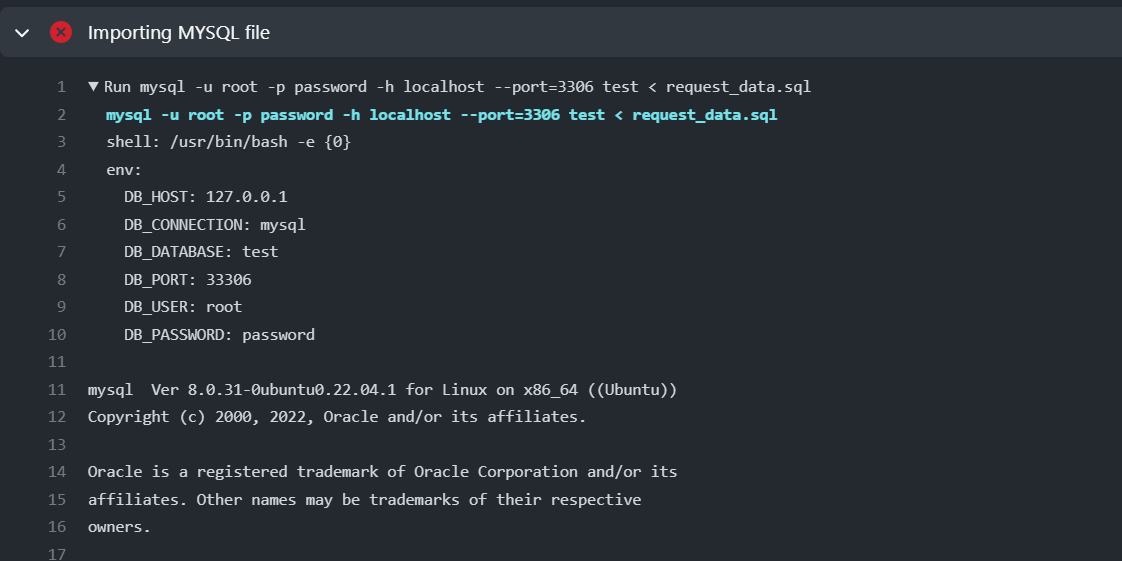
Below is the command used in the .yml file which is used in the workflow for laravel.
- name: Importing MYSQL file
env:
DB_HOST: 127.0.0.1
DB_CONNECTION: mysql
DB_DATABASE: test
DB_PORT: ${{ job.services.mysql.ports[3306] }}
DB_USER: root
DB_PASSWORD: password
run: mysql -u root -p password -h localhost --port=3306 test < request_data.sql
Implementing database seeds will be a bit time-consuming that's why I'm using this way to import .sql data. Also, I am a bit new to this workflow thing. let me know if there is some issue in running the command or if it is not possible to import an existing .sql file.
Please note the migrations I have run using the workflow file are running successfully.
The following code is used to create MySQL service:
jobs:
phpunit:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
services:
mysql:
image: mysql:5.7
env:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: password
MYSQL_DATABASE: test
ports:
- 33306:3306
options: --health-cmd="mysqladmin ping" --health-interval=10s --health-timeout=5s --health-retries=3
Here's the workflow error:
CodePudding user response:
I tried to reproduce your scenario with a small .sql file but it's working fine with the mysql:5.7 Docker image.
Here's the complete workflow:
name: MySQL Import Test
on:
workflow_dispatch:
jobs:
import:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
services:
mysql:
# https://hub.docker.com/_/mysql
image: mysql:5.7
env:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: password
MYSQL_DATABASE: test
ports:
- 33306:3306
options: --health-cmd="mysqladmin ping" --health-interval=10s --health-timeout=5s --health-retries=3
steps:
- name: Import MySQL file
env:
SQL: |
SET SQL_MODE = "NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO";
START TRANSACTION;
SET time_zone = " 00:00";
CREATE TABLE `person` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO `person` (`id`, `name`, `email`)
VALUES
(111, 'abc', '[email protected]'),
(222, 'def', '[email protected]'),
(333, 'ghi', '[email protected]'),
(444, 'jkl', '[email protected]');
ALTER TABLE `person` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`);
COMMIT;
run: |
mysql --host 127.0.0.1 --port 33306 -uroot -ppassword -e "SHOW DATABASES LIKE 'test';" 2>/dev/null
echo "$SQL" > person.sql
echo "--- SQL ---"
cat person.sql
echo "--- --- ---"
echo "Importing from person.sql file"
mysql --host 127.0.0.1 --port 33306 -uroot -ppassword test < person.sql 2>/dev/null
echo "Checking the imported data"
mysql --host 127.0.0.1 --port 33306 -uroot -ppassword test <<< 'SELECT id,name,email FROM person;' 2>/dev/null
Output
Database (test)
test
--- SQL ---
SET SQL_MODE = "NO_AUTO_VALUE_ON_ZERO";
START TRANSACTION;
SET time_zone = " 00:00";
CREATE TABLE `person` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(255) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO `person` (`id`, `name`, `email`)
VALUES
(111, 'abc', '[email protected]'),
(222, 'def', '[email protected]'),
(333, 'ghi', '[email protected]'),
(444, 'jkl', '[email protected]');
ALTER TABLE `person` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`);
COMMIT;
--- --- ---
Importing from person.sql file
Checking the imported data
id name email
111 abc [email protected]
222 def [email protected]
333 ghi [email protected]
444 jkl [email protected]
Apart from that, the command i.e. sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start (and its other variants e.g. service and systemctl) is for the preinstalled MySQL. Here's the relevant issue: https://github.com/actions/runner-images/issues/576
In your scenario, as the requirement is to test on a Docker container, issuing commands for the locally installed MySQL (which is disabled by default) is not required at all.